10-K: Annual report pursuant to Section 13 and 15(d)
Published on March 10, 2022
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | |||||
For the fiscal year ended December 31 , 2021
OR
| TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | |||||
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 001-40887
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | ||||
(952 ) 947-0000
(Address of principal executive offices, including zip code and Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class | Trading Symbol | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered | ||||||
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports); and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes x No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☐ | |||||||||||
| x | Smaller reporting company | |||||||||||||
| Emerging growth company | ||||||||||||||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No x
As of June 30, 2021, the last day of the registrant's most recently completed second quarter, the registrant's common stock was not publicly traded. The registrant's common stock, $0.01 par value per share, began trading on the New York Stock Exchange, or NYSE, on October 7, 2021. As of March 7, 2022, the aggregate market value of the registrant’s common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $392.9 million (based upon the closing sale price of the common stock on that date on the NYSE).
As of March 7, 2022, the registrant had 193,059,949 shares of common stock outstanding, par value $0.01 per share.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| Page | |||||
F-1 |
|||||
1
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K (this "Annual Report") includes forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the "Securities Act"), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"), which are subject to the "safe harbor" created by those sections. Forward-looking statements include all statements that are not historical facts, including statements reflecting our current views with respect to, among other things, our plans, strategies and prospects, both business and financial, including our financial outlook, possible or assumed future actions, business strategies, events or results of operations. These forward-looking statements are included throughout this Annual Report, including in the section entitled "Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and in the section entitled "Risk Factors." These statements may be preceded by, followed by or include the words "anticipate," "assume," "believe," "continue," "could," "estimate," "expect," "intend," "may," "plan," "potential," "predict," "project," "future," "will," "seek," "foreseeable," the negative version of these words or similar terms and phrases. In addition, any statements or information that refer to expectations, beliefs, plans, projections, objectives, performance or other characterizations of future events or circumstances, including any underlying assumptions, are forward-looking.
The forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report are based on management’s current expectations and are not guarantees of future performance. The forward-looking statements are subject to various risks, uncertainties, assumptions or changes in circumstances that are difficult to predict or quantify. Actual results may differ materially from these expectations due to numerous factors, many of which are beyond our control, including as summarized immediately below under “—Summary Risk Factors” and as detailed under the section entitled "Risk Factors" in this Annual Report, as such risk factors may be updated from time to time in our periodic filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, and are accessible on the SEC's website at www.sec.gov.
Any forward-looking statements made by us in this Annual Report speak only as of the date of this Annual Report and are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements included in this Annual Report. Factors or events that could cause our actual results to differ may emerge from time to time, and it is not possible for us to predict all of them. We may not actually achieve the plans, intentions or expectations disclosed in our forward-looking statements and you should not place undue reliance on our forward-looking statements. Our forward-looking statements do not reflect the potential impact of any future acquisitions, mergers, dispositions, joint ventures, investments or other strategic transactions we may make. Except as required by law, we do not have any obligation to update or revise, or to publicly announce any update or revision to, any of the forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Summary Risk Factors
We are subject to a number of risks, including risks that may prevent us from achieving our business objectives or that may adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and prospects. You should carefully consider the risks discussed in the section entitled “Risk Factors,” including the following risks, before investing in our common stock:
Risks Relating to Our Business Operations and Competitive Environment
•the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic;
•our ability to attract and retain members and to increase annual revenue per center membership, including our ability to anticipate and satisfy consumer preferences and shifting views of health, fitness and wellness;
•competition in the health, fitness and wellness industry;
•events such as severe weather conditions, natural disasters, global pandemics or other health crises, hostilities and social unrest, among others;
•our dependence on a limited number of suppliers for equipment and certain products and services;
•rising costs related to our business, including construction of new centers, employees and maintenance and operation of our existing centers, and our inability to pass these cost increases through to our members;
2
Risks Relating to Our Brand
•a deterioration in the quality or reputation of our brand or the health, fitness and wellness industry;
•risks relating to social media platforms and our use of email, text messaging and social media marketing;
•our inability to protect and enforce our intellectual property rights or defend against intellectual property infringement suits against us by third parties;
Risks Relating to the Growth of Our Business
•our inability to identify and acquire suitable sites for centers;
•potential negative impacts resulting from the opening of new centers, including in our existing markets;
•increased investments in future centers in wealthier demographic areas and the risk that the level of return will not meet our expectations;
•delays in new center openings;
•strains on our management, employees, information systems and internal controls;
•costs we may incur in the development and implementation of new businesses with no guarantee of success;
•risks relating to acquisitions, including our inability to acquire suitable businesses or, if we do acquire them, risks relating to asset impairment or the integration of the business into our own;
Risks Relating to Our Technological Operations
•our ability to deliver connected and digital experiences and to adapt to significant and rapid technological changes;
•our inability to properly maintain the integrity and security of our data or the data of our members, to comply with applicable privacy laws, or to strategically implement, upgrade or consolidate existing information systems;
•disruptions and failures involving our information systems;
•risks related to automated clearing house (“ACH”), credit card, debit card and digital payments we accept;
Risks Relating to Our Capital Structure
•our ability to generate cash flow to service our substantial debt obligations;
•our ability to operate our business under the restrictions in our senior secured credit facilities and indentures that limit our current and future operating flexibility;
•our ability to incur additional debt;
Risks Relating to Our Human Capital
•our inability to retain our key employees and hire additional highly qualified employees;
•labor shortages or increased labor costs;
•attempts by labor organizations to organize groups of our employees or changes in labor laws;
Risks Relating to Legal Compliance and Risk Management
•our ability to comply with extensive governmental laws and regulations, and changes in these laws and regulations;
•claims related to our health, fitness and wellness-related offerings;
•our inability to maintain the required level of insurance coverage on acceptable terms or at an acceptable cost;
3
•claims related to construction or operation of our centers and in the use of our premises, facilities, equipment, services, activities or products;
Risks Relating to Our Financial Performance
•risks associated with leases on certain of our centers;
•seasonal and quarterly variations in our revenues and net income;
•delayed payments or failure to pay by our members and difficulties negotiating and collecting amounts due from members;
Risks Relating to Ownership of Our Common Stock
•significant changes to our share price and a liquid trading market for our common stock may not develop;
•potential conflicts of interest between the private equity investment funds that control us and our public stockholders;
•other risks relating to ownership of our common stock;
•other factors beyond our control; and
•other factors set forth under “Risk Factors” in this Annual Report.
4
PART I
Item 1. BUSINESS
Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. (collectively with its direct and indirect subsidiaries, “Life Time,” “we,” “our,” “us,” or the “Company”) is a holding company incorporated in the state of Delaware. Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. common stock trades on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the symbol “LTH.”
Initial Public Offering
On October 12, 2021, Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. consummated its initial public offering (“IPO”) of 39.0 million shares of its common stock at a public offering price of $18.00 per share, resulting in total gross proceeds of $702.0 million before deducting the underwriting discounts and other offering expenses. The shares of its common stock began trading on the NYSE under the symbol “LTH” on October 7, 2021. A registration statement on Form S-1 relating to the offering of these securities was declared effective by the SEC on October 6, 2021. Additionally, on November 1, 2021, Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. consummated the sale of nearly 1.6 million additional shares of its common stock at the IPO price of $18.00 per share pursuant to the partial exercise by the underwriters of their over-allotment option, resulting in total gross proceeds of approximately $28.4 million before deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions. For more information on the IPO, including with respect to our use of proceeds, see Note 1, Nature of Business and Basis of Presentation—Initial Public Offering, to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report.
Who We Are
Life Time, the “Healthy Way of Life Company,” is a leading lifestyle brand offering premium health, fitness and wellness experiences to a community of nearly 1.3 million individual members, who together comprise more than 724,000 memberships, as of December 31, 2021. Since our founding nearly 30 years ago, we have sought to continuously innovate ways for our members to lead healthy and happy lives by offering them the best places, programs and performers. We deliver high-quality experiences through our omni-channel physical and digital ecosystem that includes more than 150 centers—distinctive, resort-like athletic destinations—across 29 states in the United States and one province in Canada. Our track record of providing differentiated experiences to our members has fueled our strong, long-term financial performance. In 2021, a year in which we saw an initial recovery from the impacts of COVID-19, we generated $1,318 million of revenue, a net loss of $579 million and $80 million in Adjusted EBITDA. In 2020, which was significantly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, we generated $948 million of revenue, a net loss of $360 million and $(63) million in Adjusted EBITDA. In 2019, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, we generated $1,900 million of revenue, net income of $30 million and $438 million in Adjusted EBITDA.
Our luxurious athletic centers, which are located in both affluent suburban and urban locations, total more than 15 million square feet in the aggregate. We offer expansive fitness floors with top-of-the-line equipment, spacious locker rooms, group fitness studios, indoor and outdoor pools and bistros, indoor and outdoor tennis courts, basketball courts, LifeSpa, LifeCafe and our childcare and Kids Academy learning spaces. Our premium service offering is delivered by approximately 30,000 Life Time team members, including over 7,800 certified fitness professionals, ranging from personal trainers to studio performers. Our members are highly engaged and draw inspiration from the experiences and community we have created, as demonstrated by the 69 million visits to our centers in 2021, 48 million visits to our centers in 2020 despite the COVID-19 pandemic and 92 million visits to our centers in 2019.
The table below displays the wide assortment of amenities, services, activities and events found at our centers:
| Amenities | Services | Activities and Events | ||||||||||||
|
Indoor and Outdoor Pools
Group Fitness Studios
Cycle Studios
Yoga & Pilates Studios
Indoor and Outdoor Tennis Courts
LifeCafe with Poolside Service
Bar and Lounge with Wi-Fi
Free Weight and Resistance Equipment
Cardiovascular Equipment
Steam Room and Sauna
Racquetball and Squash Spaces
Locker Rooms
Child Center and Kids Academy
Basketball/Volleyball Courts
Pickleball Courts
|
Personal and Small Group Training
Weight Loss Coaching
Nutrition Coaching
LifeSpa and Medi-spa
Physical Therapy and Chiropractic
Assessments and Lab Testing
Sport Specific Coaching
Endurance Coaching
Swim Lessons and Team Coaching
Towel and Locker Service
|
Athletic Leagues and Tournaments
Kids’ Birthday Parties
Summer and Vacation Camps for Kids
Sports Training Camps
Athletic Events
Social Events
Outdoor Group Runs
Outdoor Group Cycle Rides
Swim Meets
Charity Events
|
||||||||||||
5
Our footprint of premium athletic centers as of December 31, 2021:
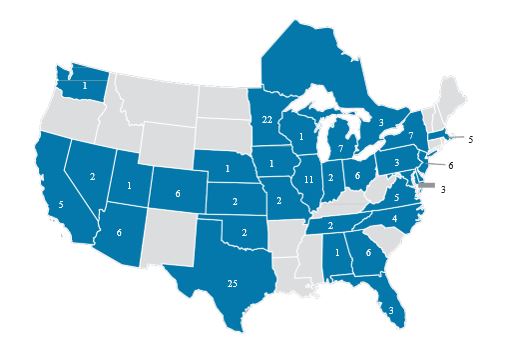
We believe that no other company in the United States delivers the same quality and breadth of health, fitness and wellness experiences as we deliver, which has enabled us to consistently grow our recurring membership dues and in-center revenues for 20 consecutive years, prior to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. As of December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, our recurring membership dues represented 68%, 67% and 63%, respectively, of our total revenue, while our in-center revenue, consisting of Life Time Training, LifeCafe, LifeSpa, Life Time Swim and Life Time Kids, among other services, represented 29%, 29% and 34%, respectively, of our total revenue. Between 2015 and 2019, we grew our average revenue per center membership from $1,883 to $2,172, a testament to the significant value that our members place on engaging with Life Time. While average revenue per center membership fell to $1,317 in 2020, we experienced a strong rebound in 2021, with $2,098 in average revenue per center membership.
Our Growth Strategies and Member Experience Initiatives
We have built a strong foundation with an engaged membership base in pursuit of a healthy way of living. We are executing on several strategies to grow our business and drive our memberships and revenue per center membership, including expanding the number of our premium centers in an asset-light model that targets higher income members, higher average annual revenue per center membership and higher returns on invested capital. We are also implementing new strategies to elevate our member experiences, including introducing new types of memberships, providing concierge-type member services, expanding our omni-channel offerings and improving our in-center services. We believe these strategies will allow us to reach our pre-COVID-19 center revenue more quickly than the recovery of our total center memberships.
Continue to Grow Our Membership Base
We believe we will continue to expand our membership base as consumer activity returns post-pandemic and by continuing to increase our member experiences and brand awareness, acquire new consumers and retain our current members longer. We expect to grow our consumer reach through the following initiatives:
•Data-driven, targeted marketing campaigns focused on personalized experiences. Employ targeted marketing campaigns driven by data analytics to increase personalized experiences, brand awareness and membership growth, as well as engage in consumer-focused marketing related to improving consumers’ health post-pandemic.
•Expand and elevate service offerings. Continue to expand and elevate our service offerings to attract and retain members of all ages, from extended childcare hours for kids, to new studio classes, to pickleball for the aging population. We believe extending and elevating our existing membership offerings with complementary or fee-based services and benefits will continue to drive broader appeal, higher memberships and longer member retention.
6
•Market share gains. Capture orphaned members from fitness centers that shut down during the pandemic. According to International Health, Racquet, and Sportsclub (“IHRSA”), from March 2020 when the pandemic began to December 31, 2021, approximately 25% of health clubs and fitness facilities and 30% of studios closed permanently. We believe we are well-positioned to capture a portion of these consumers within our markets.
We believe that employing these strategies will enable us to continue to grow our membership base over the long-term.
Increase Revenue per Center Membership
We expect to increase revenue from our members by executing on the following initiatives:
•Expand and elevate in-center offerings that generate incremental revenue. We nearly doubled our average in-center revenue per membership from 2007 to 2019. Although we saw a decline in average center revenue per membership during 2020, we experienced a recovery during 2021. We intend to continue to expand and elevate our health, fitness and wellness offerings to cater to all types of interests and levels, and to drive increased spend by members within our centers.
•Enhance membership pricing. We expect to increase spend from consumers by developing new premium centers in more affluent markets that drive higher membership dues, enhancing experiences at our existing centers to create more value and pricing opportunities and, over time, transitioning existing memberships to higher membership prices or tiers as we continue to add more value to their memberships.
Expanded National Footprint and Strategic Focus on Locations in Affluent Metropolitan Statistical Areas
We believe we have significant whitespace opportunity for our premium athletic centers across the United States and Canada, as well as internationally. Over the last five-plus years, we have expanded our footprint on the East and West coasts, and increased our presence in premium, urban and coastal areas such as Boston, Chicago, New York City and California. Our new center expansion initiatives are focused on strategic locations that will generate higher average dues, higher in-center revenue per membership and higher revenue per square foot. Our geographic and upscale expansion has been enabled by our flexible center formats, which can be modified to accommodate traditional suburban, vertical residential, urban and mall/retail locations.
Between 2016 and 2019, we opened eight new centers per year on average. After opening three new centers in 2020, we opened six new centers in 2021 and have a pipeline to open 22 or more new centers in 2022 and 2023. As we continue to focus on premium athletic centers in affluent areas, we closed four small under-performing centers in 2021, each of which was subject to a lease that we decided to let expire rather than renew. Our new centers historically have ramped to maturity over three to four years with a high level of consistency. As our annual number of new centers increases, we believe this ramping club dynamic will provide further support and predictability to our overall revenue and earnings growth.
We also intend to complement our organic growth through acquisitions. We have acquired, and expect to continue to acquire, athletic centers as well as services and experiences. Our acquisitions can be single assets or portfolios of assets. We take a disciplined approach to sourcing, acquiring and integrating high quality assets and/or locations and complementary businesses that can help us continue to expand into new geographic areas, acquire key talent and offer new services and experiences. Our post-acquisition integration process often involves significant investments in both the acquired physical assets and human capital to improve each acquired site and to rebrand the look and feel of the center to create the Life Time brand experience for our members.
Asset-light, Flexible Real Estate Strategy
Approximately 58% of our centers are now leased, including approximately 94% of our new centers opened within the last five years, versus a predominantly owned real estate strategy prior to 2015. Our focus on a flexible real estate strategy has enabled us to develop a business model that targets a new center return on invested capital of mid-to-upper thirties percent, more than double historical trends, grow the number of centers at a faster pace and enter attractive urban coastal markets with premium centers where the price of real estate had historically been a deterrent to entry.
Expanded Memberships and Omni-Channel Membership Offerings
We believe the importance of health, fitness and wellness coupled with the structural shift of consumer preferences toward experiential and proactive health and wellness spending creates new opportunities for us to leverage our “Healthy Way of Life” lifestyle brand. As our business model evolves and our membership base grows, we expect to leverage our brand reputation and use our deep understanding of membership needs to add a growing portfolio of products and services to our omni-channel
7
platform. We also believe that we can leverage our brand reputation to expand our operations internationally. While our operations are predominantly in the United States today, we continuously analyze our growth strategy and believe we have opportunities to expand our digital and physical ecosystem and healthy way of life internationally.
We continue to evolve our premium lifestyle brand in ways that elevate our members’ experiences and allow our members to more easily and regularly integrate health, fitness and wellness into their lives. We are introducing new memberships and communities, including our signature membership that includes unlimited small group training and priority registrations, and our new ARORA community focused on members aged 55 years and older. We are also focused on delivering a concierge experience to our members. As we enhance our member experiences and services, and further differentiate Life Time, we are able to adjust the pricing for our memberships and services accordingly.
We are also enhancing our digital platform to deliver a true omni-channel experience for our members. Our Life Time Digital offering delivers live streaming fitness classes, remote goal-based personal training, nutrition and weight loss support and curated award-winning health, fitness and wellness content. Through an agreement with Apple®, we also provide Apple Fitness+ to our members, which gives our members expanded content and wellness data monitoring on the go. In addition, our members are able to purchase a wide variety of equipment, wearables, apparel, beauty products and nutritional supplements via our digital health store. We are continuing to invest in our digital capabilities in order to strengthen our relationships with our members and more comprehensively address their health, fitness and wellness needs so that they can remain engaged and connected with Life Time at any time or place.
We are also expanding our “Healthy Way of Life” ecosystem in response to our members’ desire to more holistically integrate health and wellness into every aspect of their daily lives. In 2018, we launched Life Time Work, an asset-light branded co-working model, which offers premium work spaces in close proximity to our centers and integrates ergonomic furnishings and promotes a healthy working environment. We have eight Life Time Work locations open and operating, with plans to open more in the following years. Life Time Work members also receive access to all of our resort-like athletic destinations across the United States and Canada. Additionally, we opened our first Life Time Living location in 2021, another asset-light extension of our “Healthy Way of Life” ecosystem, which offers luxury wellness-oriented residences. While we are in the early stages of capitalizing on this opportunity, we believe integrating how and where consumers live, work, move and play is a promising opportunity that Life Time is uniquely positioned to capture. As we expand our footprint with new centers and nearby work and living spaces, as well as strengthen our digital capabilities, we expect to continue to grow our omni-channel platform to support the “Healthy Way of Life” journey of our members wherever they are.
Our Competitive Strengths
We believe that the following strengths power our brand and business model:
Authentic, Premium “Healthy Way of Life” Brand
We have built Life Time into a premier health, fitness and wellness lifestyle brand, earning the trust of our members for nearly 30 years to make their lives healthier and happier. We believe that consumers equate our brand with the uncompromising quality, luxury and “Healthy Way of Life” experiences that Life Time offers. We have built this credibility and robust brand equity through our continuous focus on high quality member experiences delivered through what we believe to be the best programs with the best performers in the best places. We believe our brand loyalty will allow us to continue to grow our core business as well as expand our omni-channel platform in digital, work, living and other health, fitness and wellness experiences.
Differentiated and Uncompromising Omni-Channel Experiences
Our omni-channel platform offers members an exceptional breadth of physical and digital experiences that meet or exceed our members’ expectations:
•Full Suite of Comprehensive Offerings: Life Time offers an expansive array of amenities, services and activities, thereby enabling members to enjoy a “Healthy Way of Life” across a diverse and varied set of offerings. Whether taking advantage of our state-of-the-art fitness equipment, partaking in summer camp for kids, competing in one of our sports leagues or relaxing in one of our award-winning spas, Life Time members enjoy a full end-to-end experience that can be utilized by the entire family and enable them to grow and develop, regardless of where they are in their health and wellness journey.
8
•World-Class Talent: We recruit, hire and certify those whom we believe are the best certified fitness professionals and performers in the industry to empower, educate and entertain our members. In addition, to enhance our member experiences and drive consistency in our hospitality and services, we have a strong focus on team member culture, training and certification. Life Time University, our in-house, proprietary education and certification division, offers curricula curated by over 20 dedicated professionals providing team members with online and in-person training and certification.
•Passionate Culture: Our focus on engagement among team members and performers attracts and fosters our multi-generational member base. We deeply value diversity, equity and inclusion at Life Time and strive to create a welcoming and inclusive culture. In addition, we foster community engagement through a wide range of events and activities, from parent-child dances to pool parties to charity runs. Since the start of 2019, we have organized approximately 15,000 events and served as a social and community hub for our members.
•Digital Offerings: Life Time Digital enables our members to experience some of our best offerings at their fingertips at any time and wherever they are located in the United States or Canada.
Loyal and Engaged Multi-Generational Membership Base with Attractive Demographics
Life Time’s breadth of premium services and offerings attracts anyone who wants to lead a healthier, happier life. The power of our lifestyle brand, attractive member demographics, breadth of amenities and services and high utilization of our centers allow us to build deeply meaningful connections with our members, which are difficult for others in our industry to replicate fully. From young children attending our swim lessons and Kids Academy classes, or teenagers engaged in our sports and agility training, to members of all ages participating in our iconic athletic events and variety of in-center activities, we have something for every generation. As of December 31, 2021, 75% of our members owned a home and had a median household income of $119,000 and approximately 59% of our members are part of a couples or family membership, and these members typically engage more fully within our centers. Approximately 62% of our members had at least a college education. Additionally, our gender mix is balanced and approximately 48% of our members are below 35 years of age and approximately 81% are under 55 years of age. On average, revenue per center membership was $1,317 and $2,172 at our centers during 2020 and 2019, respectively, and average visits per membership ranged from 69 and 108 times during the same periods, respectively. We experienced an improvement in these metrics during 2021, with average revenue per center membership of $2,098 at our centers and average visits of 113 times per membership.
Flexible Real Estate Strategy with Nationwide Footprint
We have a diversified portfolio of over 150 resort-like athletic destinations that are primarily located in affluent markets across 29 states and one Canadian province. Over the last five years, we have transitioned to an asset-light strategy through sale-leaseback transactions and have adopted more strategic and flexible center formats that can be modified to accommodate various settings, including traditional suburban, vertical residential, urban and mall/retail locations. Our focus on a flexible real estate strategy since 2015 has enabled us to develop a business model that targets a new center return on invested capital of mid-to-upper thirties percent, more than double historical trends, grow the number of centers at a faster pace and enter attractive urban and coastal markets with premium centers where the price of real estate had historically been a deterrent to entry. We also benefit from our in-house architecture, design and construction expertise that allows us to create sustainable and energy efficient centers. These efforts have helped us control the cost and pace of capital expenditures and have also ensured a consistent feel across our centers.
We have developed a disciplined and sophisticated process to evaluate markets and specific sites in those markets where we may want to build new centers. This dynamic process is based upon demographic, psychographic and competitive criteria generated from profiles of our most successful centers, and we continue to refine these criteria based upon the performance of our centers. We believe that the presence of a Life Time center benefits landlords and the value of the underlying property and surrounding neighborhoods. We seek to leverage this halo effect of our brand, as well as long-term relationships with landlords, to achieve favorable lease agreements and increased construction reimbursements from landlords to support our capital light expansion.
Recurring Revenue Model with Consistent Growth
Membership dues from our network of members create a recurring and relatively predictable revenue stream that has proven to be resilient for nearly 30 years and across economic cycles. Membership dues provide our largest source of revenue, representing 68%, 67% and 63% of our total revenue in 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
9
We have grown from $137 million, $4 million and $36 million in revenue, net income and Adjusted EBITDA, respectively, in 2001 to $1,900 million, $30 million and $438 million in revenue, net income and Adjusted EBITDA, respectively, in 2019. During that time period, we did not have a year-over-year decline in revenue or Adjusted EBITDA. While revenue, net income and Adjusted EBITDA did decline to $948 million, $(360) million and $(63) million, respectively, during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, we saw a recovery during 2021 as we re-opened our centers and began to emerge from the pandemic. During 2021, we generated $1,318 million, $579 million and $80 million in revenue, net loss and Adjusted EBITDA, respectively.
Passionate, Visionary, Founder-Led Management Team with Deep Industry Experience
Our unwavering commitment to excellence and a “Healthy Way of Life” culture is driven by our passionate management team, under the leadership of Bahram Akradi, our founder, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer. Life Time was founded by Mr. Akradi in 1992 with a goal of helping people achieve their health, fitness and wellness goals by delivering entertaining, educational and innovative experiences with uncompromising quality and unparalleled service. From the very beginning, Mr. Akradi has led the Company with a focus on serving members’ needs first and a belief that business results would naturally follow.
By building a strong and highly experienced executive leadership team, Life Time has continued to grow and consistently deliver exceptional experiences. Our executive leadership includes:
•Tom Bergmann, President & Chief Financial Officer. Mr. Bergmann has been with Life Time for more than six years and has more than 30 years of leadership experience across various industries, including as Chief Financial Officer at three companies including USF Corporation (prior to being acquired by Yellow Corporation), Amsted Industries and Harley Davidson.
•Jeff Zwiefel, President & Chief Operating Officer. Mr. Zwiefel has been with Life Time for over 20 years and has more than 35 years of experience in the health, fitness and wellness industry.
•Eric Buss, Executive Vice President & Chief Administrative Officer. Mr. Buss has been with Life Time for over 20 years and has served as a key executive leader in a variety of roles.
•Parham Javaheri, Executive Vice President & Chief Property Development Officer. Mr. Javaheri joined Life Time in 2004 and has over 20 years of experience in real estate development.
•RJ Singh, Executive Vice President & Chief Digital Officer. Mr. Singh joined Life Time in 2017 and oversees all digital and technology infrastructure, operations and initiatives.
Our team has an entrepreneurial spirit that we believe makes us highly adaptable, reflects an ownership mentality and allows us to navigate shifts in the health, fitness and wellness landscape, including as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. We believe the strength of our team, culture and organizational approach position us to continue to grow and deliver strong financial results.
Strong Financial Performance
Our compelling financial profile is distinguished by our long-term track record of consistent revenue growth prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, growth of new centers in attractive markets, a high percentage of predictable recurring membership revenue, increasing revenue per center membership and strong profitability.
•Long-Term Track Record of Revenue Growth. We believe the strength of our brand and the effective execution of our operating strategy have driven our long-term track record of growth. Prior to the impact of COVID-19 in 2020, we grew our revenue each year from 2000 through 2019.
10
Revenue ($ in millions)
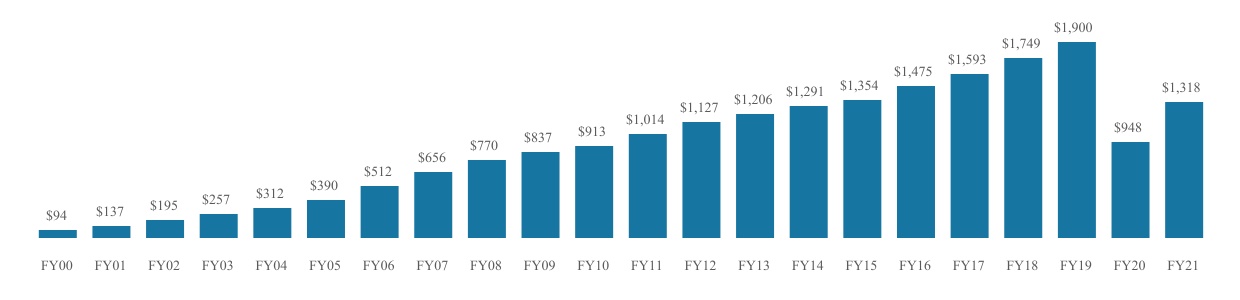
•Highly Successful New Center Openings. Our asset-light, flexible real estate strategy and compelling center economics have enabled us to successfully open new centers in attractive markets. From 2016 through December 31, 2021, we opened 40 new centers, increasing our total center count by 36.0%.
•Predictable Recurring Membership Revenue. Due to our strong membership base, our membership dues represent a predictable recurring revenue stream that provides stability to our business. Center memberships were approximately 649,000 at the end of 2021 compared to approximately 501,000 at the end of 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. Prior to the pandemic, Center memberships were approximately 854,000 at the end of 2019. With respect to the net increase of approximately 148,000 Center memberships during 2021, the percentage of that net increase attributable to members converting from Digital On-hold was approximately 66%, or 98,000 memberships. The proportion of our total revenue generated by the resulting recurring membership dues was 68%, 67% and 63% in 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
•Increasing Average Revenue Per Center Membership. Between 2015 and 2019, we grew our average revenue per center membership from $1,883 in 2015 to $2,172 in 2019, a testament to the significant value that our members place on engaging with Life Time. As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, average revenue per center membership fell to $1,317 in 2020 and recovered to $2,098 in 2021. As we emerge from the COVID-19 pandemic with a smaller membership balance, one of our strategies is to continue to increase our average revenue per center membership.
•Strong Profitability. We have maintained a highly profitable business model, achieving a 1.6% net income margin and 23.0% Adjusted EBITDA margin in 2019. These metrics were impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021, falling to a (38.0)% net loss margin and (6.6)% Adjusted EBITDA margin in 2020 and a (44.0)% net loss margin and 6.1% Adjusted EBITDA margin in 2021.
Impact of COVID-19 on Our Financial Performance
On March 16, 2020, we closed all of our centers based on orders and advisories from federal, state and local governmental authorities responding to the spread or threat of spread of COVID-19. While our centers were closed, we did not collect monthly access membership dues or recurring product charges from our members. We re-opened our first center on May 8, 2020 and continued to re-open our centers in accordance with evolving state and local governmental guidance. As of December 31, 2021, all of our 151 centers were open.
After the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, we prioritized the health and safety of our members and team members by developing and implementing robust COVID-19 operating protocols, while taking appropriate steps to ensure our financial stability, including by reducing operating expenses, delaying capital investments and securing additional debt financing. We continue to refine these protocols and may take further actions as governmental authorities require or recommend or as we determine to be in the interests of our members, team members, vendors and service providers as we operate in the evolving COVID-19 environment, including as a result of variants such as the Delta and Omicron variants. Despite the challenges presented by the governmental response to the COVID-19 pandemic with respect to the health, fitness and wellness industry, we have remained committed to our mission and our members and began our recovery in 2021.
Number of Centers. While our new center construction and growth was slowed as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, we have successfully opened nine new centers since the end of 2019 through December 31, 2021, seven of which opened after the onset of the pandemic. We have also continued our real estate development efforts after initially suspending them during the pandemic, and had 12 centers under construction as of December 31, 2021. We opened six new centers in 2021 and closed four small under-performing centers with expiring leases, and we have a pipeline to open 22 or more new centers in 2022 and 2023.
11
Revenue and Net Income (Loss). As a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, our total revenue fell from $1,900 million for 2019 to $948 million for 2020. This revenue loss resulted in a reduction of net income from approximately $30 million in 2019 to net losses of approximately $360 million in 2020. Our results began to recover in 2021 and we generated $1,318 million in total revenue but experienced net losses of approximately $579 million, which included tax-effected expenses of $269.1 million related to non-cash share-based compensation expense and $68.6 million of additional interest expense incurred as a result of a loss on the conversion of a related-party secured note into preferred stock, as well as costs incurred in connection with our debt refinancing and partial pay down of our Term Loan Facility.
Memberships. We define memberships for our centers as Center memberships and Digital On-hold memberships (as further detailed below under “—Our Membership Offering”). Both Center memberships and Digital On-hold memberships include Life Time Digital. Center memberships grew from approximately 814,000 at the end of 2018 to approximately 854,000 at the end of 2019. By the end of 2020, as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, Center memberships had declined to approximately 501,000 as we experienced more conversions of Center memberships to Digital On-hold memberships as well as a higher level of membership terminations. However, we saw significant improvement in our Center membership numbers during 2021 and had approximately 649,000 Center memberships as of December 31, 2021 due in large part to the conversion of Digital On-hold memberships back to Center memberships.
Our Membership Offering
We define a membership for our centers in two ways: Center memberships and Digital On-hold memberships. As of December 31, 2021, we had a total of 724,140 total memberships, comprised of 649,373 Center memberships and 74,767 Digital On-hold memberships. We also have Digital memberships that we began to offer in December 2020 for direct-to-consumer memberships that do not provide access to our centers.
Center Memberships. We offer a variety of convenient month-to-month memberships with no long-term contracts. Each Center membership is defined as one or more adults 14 years of age or older, plus any juniors under 14.
•Base Memberships. We offer base memberships that provide one or more individuals 14 years of age or older general access (with some amenities excluded) to a selected home center and all centers with the same or a lower base monthly dues rate. Our optimized pricing for a Center membership is determined center-by-center based on a variety of factors, including geography, market presence, demographic nature, population density, initial investment in the center and available services and amenities. Base memberships typically include locker and towel service, group fitness classes and access to the Life Time app.
•Junior Memberships. We offer junior memberships (as an add-on to a base membership) that provide one or more children 13 years of age or younger access to the child center, pools and gymnasiums at designated times, drop-off events and Kids Academy, which includes more in-depth programming focused on activity, learning and fitness. Junior memberships currently cost $10 to $90 per month depending upon the center. We do not count junior memberships as incremental in our membership count since they are already part of the Center membership.
•Other Memberships and Products. We offer several other recurring memberships and access-related products at select centers, including a Signature Membership that bundles a base membership with small group training, a Tennis Membership that bundles a base membership with tennis and a Pool Pass that provides access to the outdoor pool area at select centers.
Digital On-hold Memberships. We offer Digital On-hold memberships for members who do not currently wish to access our centers, but still want to maintain certain member benefits, including our Life Time Digital membership, and the right to convert to back to a Center membership without paying an enrollment fee. The majority of our Digital On-hold memberships cost $15 per month, which we may not charge from time to time, including during periods of the COVID-19 pandemic as a means to maintain member engagement.
Digital Memberships. We launched Life Time Digital direct-to-consumer in December 2020 to bring our “Healthy Way of Life” programs, services and content to consumers virtually. Life Time Digital features include live streaming fitness classes, remote goal-based personal training, nutrition and weight loss support, curated award-winning health, fitness and wellness content and access to Apple Fitness+. Currently, our digital membership is included with both our Center and Digital On-hold memberships at no additional charge or it can be purchased separately as a digital-only membership. We currently report our Digital memberships within our Digital On-hold membership totals.
12
Human Capital
As of December 31, 2021, we employed approximately 30,000 Life Time team members, including 21,000 part-time employees and over 7,800 certified fitness professionals, ranging from personal trainers to studio performers. On average, our centers are generally staffed with approximately 140 to 200 full-time and part-time employees depending on center activity levels.
Since our founding, we have believed that creating and sustaining a trusted community, where members know their experiences will always be exceptional, requires the highest levels of passion and commitment from our entire team. Our team members are dedicated to providing the best programs and experiences, in the best facilities, by the best people and performers. By consistently delivering extraordinary experiences, we have built a highly trusted, premium lifestyle brand that embraces all aspects of healthy living, healthy aging and healthy entertainment. Collectively, it is what we call “Healthy Way of Life,” or “HWOL.” This is a unique lens through which we can examine every aspect of our lives. It is a healthy perspective on physical, mental and social wellbeing.
To build our HWOL brand that is loved and trusted by members, we have dedicated ourselves to identifying, training and empowering team members who trust our Company like their own families. This was achieved naturally and intuitively at the start and, as our Company has grown, we have intentionally and systematically made it the foundation of what we call our “Culture of Care.” Creating and fostering this culture involves numerous critical details and initiatives – from casting, onboarding, training, certification and career path planning, to establishing supporting programs, such as our Life Time Foundation, Life Time University and Life Time Inclusion Council.
Inclusion, Diversity and Equity at Life Time
At Life Time, we are committed to inspiring healthy, happy lives for everyone in our communities. We embrace our responsibility to create healthy environments and workspaces that honor and champion all through inclusion, equity and diversity. We recognize, empower and celebrate the unique talents, backgrounds and perspectives of individuals so everyone feels welcomed, respected, supported and valued. We believe inclusion is at the heart of our team members’ and members’ sense of belonging. Our focus on making Life Time a “Place for Everyone” is a hallmark of our organization.
Delivering a “Place for Everyone” at Life Time is driven by our strategic pillars of developing an inclusive leader culture, introducing and growing mentoring and coaching for all, reaching out to our community to expand and support healthy communities, and monitoring our team member, member and community diversity. Our senior leadership, as well as our inclusion council and center-level ambassadors, play a critical role in delivering on our value of being a “Place for Everyone.” We also provide programs and development opportunities for all of our team members to grow and sustain the value of inclusion.
Development and Training
We recruit, hire and certify those whom we believe are the best certified fitness professionals and performers in the industry to empower, educate and entertain our members. All center team members are required to participate in a training and certification program that is specifically designed to promote a friendly and inviting environment with each member interaction, while upholding a consistent standard of performance across all of our centers. We provide comprehensive training through our Life Time Education platform that is comprised of both an externally licensed school branded as Life Time Academy (“LTA”) and an internal team member education and certification division that we call Life Time University (“LTU”). LTA offers a certification for entry-level professionals to prepare for a career with Life Time or within the health, fitness and wellness industry. LTU delivers world-class certification, learning, education and development opportunities for all team members. Life Time Education supports the culture of Life Time through enterprise-wide programs in service, inclusion and diversity and personal and professional growth. Team members also receive ongoing mentoring and continuing education, and we require an annual re-certification before any team member is permitted to work or to advance to other positions within our Company.
Our personal trainers, registered dietitians, massage therapists and cosmetologists are required to maintain a professional license or one of their industry’s top certifications.
Compensation and Benefits
We believe that supporting our team members and providing them the tools to be successful in their roles fosters our Culture of Care and enables them to provide extraordinary experiences to our members. We offer a wide range of benefits designed to holistically support our team members in all areas of their lives. In addition to paid time off, paid sick leave, adoption assistance, subsidized medical, dental and vision insurance, company paid life insurance, short and long-term disability, as well as a center membership, we also provide:
13
•Employee Assistance Program – Offers confidential assistance with personal, legal, work, financial and other life issues on a 24-hours-a-day, 7-days-a-week basis.
•Life Time Mind (“LT Mind”) - LT Mind is a holistic performance coaching program proprietary to Life Time aimed at helping team members optimize their performance, achieve their goals and enhance their well-being. Offerings for all team members include online training and virtual mental resiliency coaching.
We are not a party to a collective bargaining agreement with any of our employees. Our continued efforts on building a diverse, equitable, and inclusive environment centered around our Culture of Care for our team members has created a positive environment where our performers can thrive while delivering an uncompromising member experience, and we believe relations with our employees are good.
Information Systems
In addition to our standard operating and administrative systems, we use an integrated and proprietary member management system to manage the flow of member information within and between each of our centers and our corporate office. We have designed and developed our proprietary system to allow us to easily collect and process information. Our system enables us to, among other things, enroll new members with an electronic membership agreement, capture digital pictures of members for identification purposes and capture and maintain specific member information, including usage. The system allows us to streamline the collection of membership dues electronically, thereby offering additional convenience for our members while at the same time reducing our corporate overhead and accounts receivable. In addition, we use a customer relationship management system to enhance our marketing campaigns and management oversight regarding daily sales and marketing activities.
Competition
We consider the following groups to be the primary participants in the health, fitness and wellness industry:
•health center operators, including, but not limited to, Equinox Holdings, Inc., The Bay Club Company, ClubCorp, LA Fitness International, LLC and 24 Hour Fitness Worldwide, Inc.;
•the YMCA and similar non-profit organizations or community centers;
•physical fitness and recreational facilities established by local governments, hospitals and businesses;
•local salons, cafes and businesses offering similar ancillary services;
•small fitness clubs and studios and other boutique fitness offerings, including Anytime Fitness, Snap Fitness, Planet Fitness, Orange Theory, Barre3, Crunch Fitness and others;
•racquet, tennis and other athletic centers;
•rental unit and condominium amenity centers;
•country clubs;
•digital fitness and health services, including online personal training and fitness coaching;
•the home-use fitness equipment industry;
•athletic event operators and related suppliers; and
•providers of wellness and other health and wellness-orientated products and services.
The health, fitness and wellness industry is highly competitive. While competition in the industry varies from market to market, it may be impacted by various factors, including the breadth and price of membership offerings and other products and services, the flexibility of membership options, the overall quality of the offering, name or brand recognition and economies of scale. We believe that our brand, our comprehensive product offering and focus on services, amenities and value provide us with a distinct competitive advantage, positioning us well to compete in the health, fitness and wellness industry.
14
Intellectual Property
Our business depends on the quality and reputation of our brand. We file a substantial number of our trademarks and service marks with the United States Patent and Trademark Office, including for Life Time and many of our branded studio classes and service offerings. We consider our brand to be one of our most important assets and certain of our trademarks and service marks to be of material importance to our business and actively defend and enforce such trademarks and service marks. Examples include LIFE TIME®, EXPERIENCE LIFE®, LIFECAFE®, LIFESPA®, LIFE TIME HEALTHY WAY OF LIFE®, LIFE TIME WORK® and LIFE TIME LIVING®. Solely for convenience, our trademarks, service marks or tradenames may appear in this Annual Report without the corresponding ® or TM symbols, but such references are not intended to indicate in any way that we will not assert, to the fullest extent, our rights to such trademarks, service marks and tradenames.
Governmental Laws and Regulations
Our operations and business practices are subject to laws and regulations at federal, state, provincial and local levels, including consumer protection laws related to our advertising, marketing and sales efforts, health and safety regulations and licensing requirements related to our training, cafe, spa, aquatics, child care and ancillary health and fitness-related products and services, environmental laws and regulations, including those related to the handling, use, remediation and storage of hazardous materials, the emission, release and discharge of hazardous materials into the environment, and the health and safety of our employees, fair housing laws, accessibility laws, regulations related to the collection, use and security of personal information about our members, guests and purchasers, and wage and hour and other labor and employment laws. In addition, from time to time we have been required to investigate and remediate contamination at some of our sites under such environmental laws and regulations.
In particular, within the health, fitness and wellness industry, state statutes regulate the sale and terms of our membership contracts. State statutes often require that we:
•include certain terms in our membership contracts, including the right to cancel a membership, in most cases, within three to 10 days after joining, and receive a refund of enrollment fees paid;
•escrow funds received from pre-opening sales or post a bond or proof of financial responsibility; and
•adhere to price or financing limitations.
Seasonality of Business
Seasonal trends have an effect on our overall business. Generally, we have experienced greater membership growth at the beginning of the year. We also typically experience increased levels of membership in certain centers during the summer pool season. During the summer months, we also experience a slight increase in our in-center business activity with summer programming and operating expenses due to our outdoor aquatics operations and kids programming. We typically experience an increased level of membership attrition during the third and fourth quarters as the summer pool season ends and we enter the holiday season. This can lead to a sequential decline in memberships during those quarters.
Life Time Foundation
We believe in giving back to our communities in ways that empower people to live happy, healthy lives. In 2003, we formed the Life Time Foundation with a focus on inspiring healthier families. In 2010, we further focused on helping children reach their full potential by improving the nutrition, health, taste and overall quality of the meals served at schools which, for many children, is their sole source of food throughout the day. Specifically, the Life Time Foundation partners with schools to eliminate foods containing highly processed and artificial ingredients in favor of wholesome, real food alternatives and scratch cooking. As of December 31, 2021, the Life Time Foundation has benefited more than 35 school districts, including the largest school district in the United States (New York City), impacting over 3,600 schools with more than 265 million meals served to over 1.7 million students annually.
Available Information
We file annual, quarterly and special reports and other information with the SEC. Our filings with the SEC are available to the public on the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov. Those filings are also available to the public on, or accessible through, our investor relations website at www.ir.lifetime.life under the “Filings” tab. The information we file with the SEC or contained on or accessible through our corporate website or any other website that we may maintain is not part of this Annual Report.
15
Item 1A. RISK FACTORS
Risks Relating to Our Business Operations and Competitive Environment
COVID-19 has had and may continue to have a significant negative effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak of SARS-CoV-2, a novel coronavirus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (“COVID-19”), a pandemic, recommending containment and mitigation measures worldwide. On March 13, 2020, the United States declared a National Public Health Emergency with respect to COVID-19. On March 16, 2020, we closed all of our centers based on orders and advisories from federal, state and local governmental authorities regarding COVID-19. We re-opened our first center on May 8, 2020 and continued to re-open our centers as state and local governmental authorities permitted. As of December 31, 2021, all of our 151 centers were open (some of which were re-opened after being closed a second time by governmental authorities). Whether we will need to close any of our centers again and the duration of any such center closures that may occur, remain uncertain and are dependent on future developments that cannot be accurately predicted at this time. We did not collect any monthly Center membership dues or recurring product charges while our centers were closed, with limited exceptions where our members opted to continue to receive certain limited services, and we would expect to do the same if our centers need to close again. As a result, center closures have had and may continue to have a significant negative effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We expect our centers and in-center businesses will continue to be impacted differently based upon considerations such as their geographic location, vaccination rates, impacts of COVID-19 variants, applicable government restrictions and guidance and employee and member sentiment with respect to working in and/or using our centers. We continue to face more burdensome operating protocols in many of our center locations and have faced member and employee attrition in response to COVID-19. These events have negatively impacted and may continue to negatively impact our business, results of operations and financial condition. In addition, positive COVID-19 cases traced to any one of our centers or any negative publicity relating to health-related matters may affect members’ perceptions of our centers, reduce member and prospective member visits to our centers and negatively impact demand for our center offerings.
In addition to the significant reduction in revenue from our closed centers, we have experienced a reduction in membership levels and activity as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. As of December 31, 2021, total memberships were 724,140, a decrease of 24% compared to 950,183 at March 31, 2020, shortly following the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Center memberships were 649,373 as of December 31, 2021, a decrease of 23% compared to 847,161 at March 31, 2020. Digital On-hold memberships were 74,767 as of December 31, 2021, a decrease of 27% compared to 103,022 at March 31, 2020. If our memberships and in-center member activity do not return to pre-COVID-19 levels and if our strategy for delivering premium member services and increasing average revenue per center membership does not fully offset lower membership levels, our results of operations will continue to be negatively impacted.
COVID-19 also forced us to reduce our operating costs and preserve liquidity. Due to our significant fixed costs, we were not able to reduce our expenses commensurate with our reduced revenues. While we took swift and wide-ranging cash management actions to reduce our operating costs, defer rental payments and preserve liquidity, we experienced significant negative effects on our results of operations and financial condition. COVID-19 also impacted our ability to grow our business. We initially suspended virtually all construction capital spending and discontinued the development of a number of real estate projects. We have since returned to growing the number of our new centers with a plan to add 10 or more centers each year. We cannot be certain that we will not need to suspend or reduce the level of construction activities associated with these projects.
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused significant economic shifts across the United States, which may reduce or change consumer demand in our industry. We have experienced a material loss of members and revenue as a result of the necessary suspension of our operations mandated by governmental authorities to address the threat of the spread of COVID-19. We may continue to experience losses in members and/or revenue, including a higher loss of existing members, a lower conversion of Digital On-hold memberships to Center memberships than we have historically experienced and/or fewer new members joining our centers. We cannot predict the degree, or the time period, over which our business will be affected by COVID-19 and such impact is dependent on future developments that cannot be accurately predicted at this time. Therefore, the extent of the impact of COVID-19 on our financial position, results of operations, liquidity and cash flows is uncertain at this time.
16
We may be unable to attract and retain members and we may be unable to increase revenue per center membership, including if we are unable to anticipate and satisfy consumer preferences and shifting views of health, fitness and wellness, either of which could have a negative effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
The success of our business depends on our ability to attract and retain members, and there is no assurance that we will be successful in our efforts or that the membership levels at our centers will not decline, especially at those centers in operation for an extended period of time. All of our members are able to cancel their membership at any time upon providing advance notice. In addition, we experience attrition and must continually engage existing members and attract new members in order to maintain our membership levels and sales from in-center services. There are numerous factors that could lead to a decline in membership levels or sales of in-center services or that could prevent us from increasing membership and in-center service revenue. These factors include changing desires and behaviors of consumers, changing consumer confidence, changes in discretionary spending trends and general economic conditions, market maturity or saturation, a decline in our ability to deliver quality service, direct and indirect competition in our trade areas, advances in medical care that lead to less interest in health and fitness activities and a decline in the public’s interest in health and fitness, as well as social fears such as terror or health threats. Consumers’ preferences for health, fitness and wellness services could shift rapidly to different types of health and fitness centers or different channels of delivering those services, and we may be unable to anticipate and respond to shifts in consumer preferences. Failure to predict and respond to changes in public opinion, public research and consumer preferences could adversely impact our business and results of operations.
As detailed in the risk factor immediately above, we experienced a significant reduction in membership levels, sales of in-center services and center activity as a result of COVID-19. The full extent and duration of the impact of COVID-19 over the longer term on our membership levels, sales and center activity remains uncertain and is dependent on future developments that cannot be accurately predicted at this time. Additionally, our business could be particularly sensitive to reductions in discretionary consumer spending and in a depressed economic and consumer environment, consumers and businesses may postpone spending in response to tighter credit, negative financial news and/or declines in income or asset values, which could have a material negative effect on the demand for our services and products. We cannot be certain when our memberships levels will return to the levels that existed before COVID-19. We are executing on existing strategies to drive additional revenue per center membership, including expanding the number of our premium centers in an asset-light model that targets higher income members, higher average annual revenue per center membership and higher returns on invested capital. However, we may not be successful in optimizing price and mix or in adding new memberships at these new centers, and our growth in membership dues in these new centers may suffer as a result. We are also implementing new strategies to elevate our member experiences and drive additional revenue per center membership, including introducing new types of memberships, providing concierge-type member services, expanding our omni-channel offerings and improving our in-center services and products. Elevating our member experiences requires investment in our team members, programs, products, services and centers. These investments may impact our short-term results of operations and cash flows as our investments in our business may be made more quickly than we see the returns on our investments. Additionally, we cannot be certain that these strategies will attract and retain members or deliver higher revenue per center membership.
Our business could be adversely affected by strong competition in the highly competitive health, fitness and wellness industry.
We compete with numerous industry participants as detailed in “Item 1—Business—Competition” of this Annual Report. There is no assurance that our competitors will not attempt to copy our business model, or portions thereof, and that this will not erode our market share and brand recognition or impair our business and results of operations. It is also possible that competitors could introduce new products and services or news ways to provide those products and services that negatively impact consumer preference for our business model. Competitors, which may have greater name recognition and/or resources than we have, may compete with us to attract members in our markets. Non-profit and government organizations in our markets may be able to obtain land and construct centers at a lower cost and collect membership fees without paying taxes, thereby allowing them to charge lower prices. Additionally, consolidation in the health, fitness and wellness industry could result in increased competition among participants. Furthermore, due to the increased number of low-cost health center and fitness center alternatives, we may face increased competition during periods when we increase our prices, discretionary spending declines or unemployment increases. This competition may limit our ability to attract and retain members, each of which could materially and adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Events such as severe weather conditions, natural disasters, global pandemics or other health crises, hostilities, gun violence and social unrest, among others, can adversely affect our results of operations and prospects.
Severe weather conditions, natural disasters, global pandemics or other crises, hostilities, gun violence, social unrest, any shifting climate patterns or terrorist activities (or expectations about them) can adversely affect consumer spending and
17
confidence levels, supply availability and costs, as well as the local operations in impacted markets, all of which could have an adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. We may also be forced to temporarily close centers due to any number of unforeseen circumstances, including as a result of global pandemics or other health crises, fire, flood, technical difficulties, shortage of employees, loss of power, health and safety incident, social unrest, terrorist incident, natural disaster or an active shooting or other violence. The severity of, impact and duration of center closures could increase as the climate and social environment changes. Any prolonged closures may adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition and may also result in longer term reductions in revenue as a result of termination of memberships at the affected centers. Our receipt of proceeds under any insurance we maintain with respect to some of these risks may be delayed or the proceeds may be insufficient to cover our losses fully.
We operate multiple centers concentrated in various geographical locations across the country, with planned expansion in current and new markets. As a result, any prolonged disruption in the operations of our centers in any of these markets, whether due to technical difficulties, power failures, pandemics or epidemics, or destruction or damage to the centers as a result of a natural disaster, fire or any other reason, could harm our results of operations, as we have experienced and expect to continue to experience due to COVID-19. In addition, our concentration in these markets increases our exposure to adverse developments related to competition, as well as economic and demographic changes in these areas.
Our dependence on a limited number of suppliers for equipment and certain products and services could result in disruptions to our business and could adversely affect our revenues and gross profit.
Equipment and certain products and services used in our centers and businesses, including our exercise equipment and certain of our software and hardware, are sourced from third-party suppliers. Although we believe that adequate substitutes are currently available, we depend on these third-party suppliers in order for us to operate our business efficiently and consistently meet our business requirements. The ability of these third-party suppliers to successfully provide reliable and high-quality services is subject to technical and operational uncertainties that are beyond our control. Any disruption to our suppliers’ operations could impact our supply chain and our ability to service our centers. If we lose such suppliers or our suppliers encounter hardships unrelated to the demand for our equipment or other products or services, we may not be able to identify or enter into agreements with alternative suppliers on a timely basis and on acceptable terms, if at all. Transitioning to new suppliers could be time-consuming and expensive and may result in interruptions in our operations. If we should encounter delays or difficulties in securing the quantity of equipment, products or services we require, our suppliers encounter difficulties meeting our demands, our websites or applications experience delays or become impaired due to errors in the third-party technology or there is a deficiency, lack or poor quality of equipment, products or services provided or there is damage to the value of one or more of our suppliers’ brands, our ability to serve our members and to elevate our brand could be interrupted and/or negatively impacted. If any of these events occurs, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We may incur rising costs related to our business, including for construction of new centers, employees and maintenance and operation of our existing centers. If we are not able to pass these cost increases through to our members, our financial results may be adversely affected.
Our centers require significant upfront and ongoing investment. If our investment is higher than we had planned, or if our investment takes longer to execute due to any number of reasons, we may need to outperform our operational plan to achieve our targeted return. Over the longer term, we believe that we can offset cost increases by increasing our membership dues and other fees and improving profitability through cost efficiencies, but market and economic pressures and higher costs in regions where we are opening new centers may be difficult to offset in the short term.
Risks Relating to Our Brand
Our business depends on the quality and reputation of our brand, and any deterioration in the quality or reputation of our brand or the health, fitness and wellness industry could materially adversely affect our market share, business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our brand and our reputation are among our most important assets. Our ability to attract and retain members and expand our business depends, in part, upon the external perceptions of Life Time, the quality of our centers and services and our corporate and management integrity. Any adverse incidents, including any involving the potential safety of our members, guests or employees, physical or sexual abuse or other harm to a child at any of our children play areas or events or negative publicity regarding us, our competitors or the health, fitness and wellness industry, may damage our brand and our reputation, cause a loss of consumer confidence in Life Time and our industry and could have an adverse effect on our market share, business, results of operations and financial condition.
18
Use of social media platforms, and email, text messaging, phone and social media marketing may adversely impact our reputation, business, results of operations, and financial condition or subject us to fines or other penalties.
There has been a substantial increase in the use of social media platforms, including social media websites, blogs and other forms of internet-based communication, which allow individuals to access a broad audience of consumers and other interested persons. Negative commentary about us may be posted on social media platforms or similar devices at any time and may harm our brand, reputation or business. Consumers value readily available information about health, fitness and wellness and often act on such information without further investigation and without regard to its accuracy. The harm may be immediate without affording us an opportunity for redress or correction. In addition, social media platforms provide users with access to such a broad audience that collective action against our centers, such as boycotts, can be more easily organized. If such actions were organized, we could suffer reputational damage as well as physical damage to our centers, which could have a negative effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We also use email, text messaging, phone and social medial platforms as marketing tools. For example, we maintain Facebook, Instagram and Twitter accounts and communicate regularly with our members via email. As laws and regulations rapidly evolve to govern the use of these platforms and devices, the failure by us, our employees or third parties acting at our direction to abide by applicable laws and regulations in the use of these platforms and devices could adversely impact our business, results of operations and financial condition or subject us to fines or other penalties.
Our intellectual property rights may be inadequate to protect our business or may be infringed, misappropriated or challenged by others. We may also become involved in costly litigation or be required to pay royalties or fees.
We attempt to protect our intellectual property rights through a combination of patent, trademark, copyright and trade secret laws, as well as licensing agreements and third-party nondisclosure and assignment agreements. Our failure to obtain or maintain adequate protection of our intellectual property rights for any reason, whether in the United States or internationally, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We rely on our trademarks, trade names and brand names to distinguish our products and services from the products and services of our competitors, and we have registered or applied to register many of these trademarks. There is no assurance that our trademark applications will be approved in the United States or internationally. Third parties may also oppose our trademark applications, or otherwise challenge our use of the trademarks. In the event that our trademarks are successfully challenged, we could be forced to rebrand our products or services, which could result in loss of brand recognition, and could require us to devote resources to advertising and marketing new brands and to replacing products. In particular, although we own a United States federal trademark registration for use of the LIFE TIME® mark in the field of health and fitness centers, we are aware of entities in certain locations around the country and internationally that use LIFE TIME FITNESS, LIFE TIME or other similar marks in connection with goods and services related to health, fitness and wellness, including dietary food supplements. The rights of these entities in such marks may predate our rights. Accordingly, if we open any centers or otherwise operate in the areas in which these parties operate, we may be required to pay royalties or other fees or may be prevented from using the mark in such areas. Furthermore, if any third party were to successfully seek cancellation of our federal trademark registrations, we may be prevented from using such marks throughout the United States.
Further, there is no assurance that competitors or other businesses will not infringe on our trademarks or other intellectual property rights or that we will not have disputes with third parties to enforce our intellectual property rights, protect our trademarks, determine the validity and scope of the proprietary rights of others or defend ourselves from claims of infringement, invalidity, misappropriation or unenforceability. In the event of any such infringement or claimed infringement, the value of our brand may be harmed and we may be required to incur substantial costs and divert resources to pursue, or defend against, any claim. Additionally, any damage to our brand or reputation could cause membership levels to decline and make it more difficult to attract new members. If we were to fail to successfully defend a claim against us, we may have to pay significant fees (and fines and penalties) and enter into royalty or licensing agreements, we may be prevented from using the intellectual property within certain markets in connection with goods and services that are material to our business or we may be unable to prevent a third party from using our intellectual property. Any such failure to successfully protect our intellectual property rights, or to defend against any claims or infringement, invalidity, misappropriation or unenforceability, for any reason, could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
19
Risks Relating to the Growth of Our Business
If we are unable to identify and acquire or lease suitable sites for centers, our revenue growth rate and profits may be negatively impacted. Our center profitability may decline as we open new centers.
To successfully expand our business, we must identify and acquire or lease sites that meet the site selection criteria we have established. We may face significant competition for sites that meet our criteria, and as a result, we may lose those sites, our competitors could copy our format or we could be forced to pay significantly higher prices for those sites. If we are unable to cost-effectively identify and acquire sites for new centers, including due to the impact of COVID-19, our revenue growth rate and profits may be negatively impacted. Additionally, if our analysis of the suitability of a site is incorrect or if we do not anticipate all of the challenges relating to the expansion of our operations, we may not be able to expand profitably or recover our capital investment in developing and building the new center on the timeline or at the rate we expected. Any of these results could have a negative impact on our revenue growth rate and profits.
Our current focus for new centers is on wealthier demographic locations, including in urban and coastal markets and at mall/retail and residential tower locations, which may require higher costs of land, increased construction costs, higher lease payments and more luxurious amenities and features within the new centers. The higher gross invested capital and higher occupancy costs at these centers will require increases in the value of sale-leaseback transactions or higher operating profits per center to produce our targeted level of return. At the same time, however, a result of opening new centers is that our center operating margins may be lower than they have been historically while the centers build membership base. We expect both the increase in pre-opening expenses and the lower revenue volumes characteristic of newly opened centers to affect our operating margins at these new centers. As a result, our total center contribution and operating margins may be lower in future periods than they have been in the past, which could adversely affect our financial results.
Opening new centers in existing markets may attract some memberships away from other centers in those markets, thereby leading to diminished revenue and profitability. In addition, as a result of new center openings in existing markets, and because older centers will represent an increasing proportion of our center base over time, our same-center revenue increases may be lower in future periods than in the past.
Delays in new center openings could have an adverse effect on our growth.
In order to meet our objectives, it is important that we open new centers on schedule. A significant amount of time and expenditure of capital is required to develop and construct new centers. If we are forced to halt development or construction or if we are significantly delayed in opening new centers, we could face increased costs and our competitors may be able to open new centers in the same market before we open our centers or improve centers currently open. This change in the competitive landscape could negatively impact our pre-opening sales of memberships and increase our investment costs. In addition, delays in opening new centers could hurt our ability to meet our growth objectives and could have an adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. Our ability to open new centers on schedule and on budget or at all depends on a number of factors, many of which are beyond our control. These factors include:
•obtaining acceptable financing including executing sale-leaseback transactions to fund construction of new sites;
•obtaining entitlements, permits and licenses necessary to complete construction of the new center on schedule and to operate the center;
•securing access to labor and materials necessary to develop and construct our centers;
•delays due to material shortages, labor issues, weather conditions, acts of God, pandemics or epidemics, discovery of contaminants, accidents, deaths or injunctions;
•recruiting, training and retaining qualified employees; and
•general economic conditions.
Our growth and changes in the industry could place strains on our management, employees, information systems and internal controls, which may adversely impact our business.
Over the past several years before the impacts of COVID-19, we experienced growth in our business activities and operations, including an increase in the number of our centers, development of new businesses and memberships and acquisitions of other businesses. Our past expansion has placed, and our plans for current and future expansion and development may place, significant demands on our administrative, operational, financial, technological and other resources. Any failure to manage
20
growth and development effectively could seriously harm our business. To be successful, we will need to continue to implement management information systems and improve our operating, administrative, financial and accounting systems and controls. We will also need to train new employees and maintain close coordination among our executive, accounting, finance, legal, human resources, risk management and operations functions. These processes are time-consuming and expensive, increase management responsibilities and divert management attention.
In addition, changes in the industry affecting fitness memberships and payment for memberships may place significant demands on our administrative, operational, financial and other resources or require us to obtain different or additional resources. To be successful, we will need to continue to implement management information systems and improve our operating, administrative, financial and accounting systems and controls in order to adapt quickly to such changes. Any failure to effectively manage such changes or to implement necessary systems and controls could adversely affect our business.
We may incur significant costs in the development and implementation of new or re-imagined businesses with no guarantee of success.
In order to deliver member experiences, increase our revenue per membership, remain competitive, respond to consumer demands and expand our business, we have developed, and expect to continue to develop and re-imagine, in-center, digital and ancillary businesses as well as co-working and living spaces. We may incur significant costs in the development or refinement of these businesses, some of which may be outside of our core competency, and in the re-imagining of how we deliver and elevate our member experiences. In addition, we cannot guarantee that these businesses will be successful and contribute to earnings, and any of these businesses may lose money.
The growth and success of our omni-channel ecosystem may depend on numerous factors, including how much capital we commit to building our digital infrastructure and our ability to:
•deliver member experiences that are consistent with, and continue to elevate, our brand and in-center experiences;
•develop, implement, upgrade and/or license leading technologies, systems and use rights;
•secure and maintain the rights to use music in our content, which depends on the method we provide our content and may involve many third parties and navigating complex and evolving legal issues; and
•expand our business and potentially offer our digital membership in international markets, which would expose us to regulatory, economic and political risks in addition to those we already face in the United States and Canada.
Because our historical focus has been more on our in-center experiences, we cannot provide any assurances on the future prospects of our omni-channel ecosystem. Failure to execute on the factors above or to manage our future growth effectively could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and operating results.
We may be unable to successfully acquire suitable businesses or, if we do acquire them, the acquisition may disrupt our business, we may be unable to successfully integrate the businesses into our existing business or the acquired assets may be subject to impairment, any of which may have an adverse effect on our financial condition.
In order to remain competitive and to expand our business, we have acquired, and expect to continue to acquire, complementary businesses and centers. In the future, for any number of reasons including market conditions, we may not be able to find suitable acquisition candidates. If we do find suitable candidates, we may not be in a financial position to pursue the acquisitions or we may not be able to conduct effective due diligence or acquire the businesses on favorable terms or at all. We may also have to incur debt or issue equity securities to pay for any acquisition, which could adversely affect our financial condition or dilute our stockholders.
If we do acquire other businesses, integrating those businesses into our existing business may place significant demands on our administrative, operational, financial and other resources and may require significant management time, which may disrupt our other businesses. We may also need to invest significant capital into the acquired businesses or centers to deliver experiences consistent with the Life Time brand. Our ability to acquire and integrate larger or more significant companies is unproven. In addition, we cannot provide any assurances that we will be able to successfully integrate any acquired, or to be acquired, businesses into our existing business or achieve any goals relating to any such acquisition. Any such failure to integrate an acquired business or center into our existing business could have an adverse effect on our existing business, results of operations and financial condition.
21
Additionally, as we have acquired other businesses, we have recorded assets, liabilities and intangible assets at fair value at the time of acquisition. If the fair value of the long-lived assets or intangible assets were determined to be lower than the carrying value, the assets would be subject to impairment, which could adversely affect our financial results.
Risks Relating to Our Technological Operations
We rely on technology and may need to adapt to significant and rapid technological change in order to deliver connected and digital experiences and to compete effectively.
Technology is a key component of our business model and we regard it as crucial to our success moving forward. Our member interface has become increasingly reliant on technology, including for our new digital membership, the purchase of in-center services, through the use of online group exercise and other in-center reservations, virtual training and group lessons, live streaming, our mobile application and our payment systems. While we seek to offer our members best-in-class technology solutions to ensure a smooth customer experience, we operate in an environment that has undergone, and continues to experience, significant and rapid technological change. To remain competitive, we must continue to maintain, enhance and improve the functionality, capacity, accessibility, reliability and features of our automated member interfaces and other technology offerings.
In the future, our success will depend, in part, on our ability to develop and license leading technologies and use rights, to enhance existing platforms and services and create new platforms and services and to respond to member demands, technological advances and emerging industry standards and practices on a cost-effective and timely basis. The adoption of new technologies or market practices may require us to devote significant additional resources to improve and adapt our services. Keeping pace with these ever-increasing requirements can be expensive, and we may be unable to make these improvements to our technology infrastructure or obtain the necessary use rights in a timely manner or at all. If we are unable to anticipate and respond to the demand for new services, products and technologies on a timely and cost-effective basis, or to adapt to and leverage technological advancements and changing standards as successfully as our competitors, we may be unable to compete effectively, which could materially and adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. Furthermore, we may rely on the ability of our members to have the necessary hardware products (smartphones, tablets, watches, etc.) to support our new product offerings. To the extent our members are not prepared to invest or lack the necessary resources or infrastructure, the success of any new initiatives may be compromised.
If we fail to properly maintain the integrity and security of our data or the data of our members, guests and employees, to comply with applicable privacy laws, or to strategically implement, upgrade or consolidate existing information systems, our reputation and business could be adversely affected.
The integrity and security of our data and the data of our members, guests and employees is critical to us. Despite the security measures we have in place for compliance with applicable laws and rules, our facilities and systems, and those of our third-party service providers, may be vulnerable to security breaches, acts of cyber terrorism, demands for ransom, vandalism or theft, computer viruses, misplaced or lost data, programming and/or human errors or other similar events. Because such attacks are increasing in sophistication and frequently change in nature, we and our third-party service providers may be unable to anticipate these attacks or implement adequate preventative measures, and any compromise of our systems, or those of our third-party vendors, may not be discovered and remediated promptly. Changes in consumer behavior following a security breach or perceived breach, act of cyber terrorism or sabotage, vandalism or theft, computer viruses, loss or corruption of data or programming or human error or other similar event affecting us, a competitor, large retailer or financial institution may materially and adversely affect our business, which in turn may materially and adversely affect our reputation, results of operations and financial condition. Our receipt of proceeds under any insurance we maintain with respect to some of these risks may be delayed or the proceeds may be insufficient to cover our losses fully, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Additionally, the collection, maintenance, use, disclosure and disposal of individually identifiable data by our businesses are regulated at the federal, state and foreign levels as well as by certain financial industry groups, such as the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council, NACHA, Canadian Payments Association and individual credit card issuers. Federal, state and foreign regulators and financial industry groups may also consider from time to time new privacy and security requirements that may apply to our businesses. Compliance with evolving privacy and security laws, requirements and regulations may result in cost increases due to necessary systems changes, new limitations or constraints on our business models and the development of new administrative processes. They also may impose further restrictions on our collection, disclosure and use of individually identifiable information that are housed in one or more of our databases. Noncompliance with privacy laws, financial industry group requirements or a security breach involving the misappropriation, loss or other unauthorized disclosure of personal, sensitive and/or confidential information, whether by us or by one of our vendors, could have adverse effects on our business,
22
operations, brand, reputation and financial condition, including decreased revenue, fines and penalties, increased financial processing fees, compensatory, statutory, punitive or other damages, adverse actions against our licenses to do business and injunctive relief.
Disruptions and failures involving our information systems could cause member dissatisfaction and adversely affect our business.
We increasingly use electronic and digital means to interact with our members, provide services and products to our members and collect, maintain and store individually identifiable information, including, but not limited to, personal financial information, credit and debit card numbers, dates of birth and health-related information. In addition to our standard operating and administrative systems, we use an integrated and proprietary member management system to manage the flow of member information within each of our centers and between centers and our corporate office. Our system enables us to, among other things, enroll new members with an electronic membership agreement, streamline the collection of membership dues electronically, capture digital pictures of members for identification purposes and capture and maintain specific member information, including usage. We also have a customer relationship management system to enhance our marketing campaigns and management oversight regarding daily sales and marketing activities and a mobile application that tracks exercise and activity-related data, which may in the future track other personal information. Some of this data is sensitive and could be an attractive target of a criminal attack by malicious third parties with a wide range of motives and expertise.
Moreover, any failure or unforeseen issues, such as bugs, data inconsistencies, outages, fires, floods, changes in business processes and other interruptions with our systems or the systems of third-party vendors could adversely impact our business and member experiences and cause us to lose members. Disruptions or failures that affect our billing and other administrative functions could also have an adverse effect on our results of operations.
Correcting any disruptions or failures that affect our systems could be difficult, time-consuming and expensive. Additionally, if we need to move to different third-party systems, or otherwise significantly modify our systems, our operations and member experiences could be interrupted and negatively impacted.
Risks related to our acceptance of ACH, credit card, debit card and digital payments could harm our brand or our results of operations.
We accept payments through ACH, credit card, debit card and digital transactions. For such transactions, we pay interchange and other fees, which may increase over time. An increase in those fees would require us to either increase the prices we charge for our memberships, which could cause us to lose members, or suffer an increase in our operating expenses, either of which could harm our results of operations. In 2020, we began to surcharge our members for credit card transactions, which could cause us to lose members or negatively impact our brand or reputation.
If we or any of our processing vendors have problems with our billing software, or the billing software malfunctions, it could have an adverse effect on our member satisfaction and could cause one or more of the major credit card companies to disallow our continued use of their payment products. In addition, if our billing software fails to work properly and, as a result, we do not automatically charge our members’ credit cards, debit cards or bank accounts on a timely basis or at all, we could lose membership revenue, which would harm our results of operations.
If we fail to adequately control fraudulent ACH, credit card, debit card and digital transactions, we may face civil liability, diminished public perception of our security measures and significantly higher ACH, credit card and debit card related costs, each of which could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. The termination of our ability to process payments through ACH transactions or on any major credit or debit card would significantly impair our ability to operate our business.
Risks Relating to Our Capital Structure
Our substantial indebtedness and other obligations could adversely affect our financial condition and prevent us from growing our business or fulfilling our obligations under our indebtedness.
We have a significant amount of indebtedness and other obligations. As of December 31, 2021, we had total consolidated indebtedness outstanding of approximately $1,827 million, which includes $475 million of indebtedness under our 8.00% senior unsecured notes that mature in April 2026 (the “Unsecured Notes”), $925 million of indebtedness under our 5.75% senior secured notes that mature in January 2026 (the “Secured Notes”) and $274 million of indebtedness under the term loan portion of our senior secured credit facility (the “Term Loan Facility”), obligations under term notes that are secured by certain of our properties, mortgage notes that are secured by certain of our centers and obligations under capital leases and financing
23
leases and unused capacity under the revolving portion of our senior secured credit facility (the “Revolving Credit Facility” and together with the Term Loan Facility, the “Credit Facilities”) available to us of approximately $341.5 million, subject to a $100.0 million minimum liquidity requirement that ended on December 31, 2021. For the year ended December 31, 2021, our interest expense, net of interest income was $225 million, including non-cash interest related to loss on debt extinguishment of $41.0 million and write-off discounts and debt issuance costs of $28.6 million. Our annual debt service obligation is expected to be approximately $111.7 million for 2022, which includes interest payments under our Credit Facilities, Secured Notes and Unsecured Notes. We also have significant property lease obligations.
Specifically, our high level of indebtedness could have material consequences, including:
•making it more difficult for us to satisfy our obligations with respect to our indebtedness, and if we fail to comply with these requirements, an event of default could result;
•limiting our ability to obtain additional financing to fund future working capital, capital expenditures, our growth strategy including the development and construction of new centers, investments or acquisitions or other general corporate requirements or business opportunities;
•requiring a substantial portion of our cash flows to be dedicated to debt service instead of other purposes, thereby reducing the amount of cash flows available for working capital, capital expenditures, our growth strategy, investments or acquisitions and other general corporate purposes or business opportunities;
•increasing our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions;
•limiting our flexibility in planning for and reacting to changes in the industry in which we compete and to changing business and economic conditions;
•placing us at a disadvantage compared to other, less leveraged competitors and affecting our ability to compete; and
•increasing our cost of borrowing or limiting our ability to refinance indebtedness.
The occurrence of any one of these events could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and ability to grow our business or satisfy our obligations in respect of our outstanding debt.
Furthermore, borrowings under the Credit Facilities are at variable rates of interest and expose us to interest rate risk. If interest rates were to increase, our debt service obligations on the variable rate indebtedness would increase even though the amount borrowed remained the same, and our net income and cash flows, including cash available for servicing our indebtedness, would correspondingly decrease. Assuming no prepayments of the Term Loan Facility and that the Revolving Credit Facility is fully drawn (and to the extent that LIBOR is in excess of the floor rate applicable to the Term Loan Facility), each one percentage point change in interest rates would result in an approximately $7.5 million change in annual interest expense on the indebtedness under the Credit Facilities. In the future, we may enter into interest rate swaps that involve the exchange of floating for fixed rate interest payments in order to reduce interest rate volatility or risk. However, we may not maintain interest rate swaps with respect to any of our variable rate indebtedness, and any swaps we enter into may not fully or effectively mitigate our interest rate risk.
In addition, certain of our financial arrangements, including the Credit Facilities, use the London Interbank Offered Rate, or LIBOR (or metrics derived from or related to LIBOR), as a benchmark for establishing the interest rate. In July 2017, the Financial Conduct Authority (the authority that regulates LIBOR) announced its intent to stop compelling banks to submit rates for the calculation of LIBOR after 2021. Regulators across the world have proposed and/or endorsed alternative reference rates to use as the alternative to the applicable Interbank Offered Rate (“IBOR”) subject to that regulator’s supervision for use in derivatives and other financial contracts indexed to the applicable IBOR. These reforms and other pressures may cause LIBOR to disappear entirely or to perform differently than in the past. Market participants are currently working on industry wide and company-specific transition plans as it relates to derivatives and cash markets exposed to LIBOR. In March 2021, the Financial Conduct Authority announced that all LIBOR settings will either cease to be provided by any administrator or no longer be representative (a) immediately after December 31, 2021, in the case of all sterling, euro, Swiss franc and Japanese yen settings, and the one-week and two-month U.S. dollar setting and (b) immediately after June 30, 2023, in the case of the remaining U.S. dollar settings. The consequences of these developments cannot be entirely predicted and could have an adverse impact on the market value for or value of LIBOR-linked securities, loans and other financial obligations or extensions of credit held by or due to us. Changes in market interest rates may influence our financing costs, returns on financial investments and the valuation of derivative contracts and could reduce our earnings and cash flows.
24
The terms of the indentures governing our Unsecured Notes and Secured Notes and the credit agreement governing our Credit Facilities restrict our current and future operating flexibility, particularly our ability to respond to changes in the economy or our industry or to take certain actions, which could harm our long-term interests and may limit our ability to make payments on our indebtedness.
The indentures governing our Unsecured Notes and Secured Notes (collectively, the “Indentures”) and the credit agreement, dated as of June 10, 2015, governing our Credit Facilities (as amended, restated, modified and/or supplemented from time to time, the “Credit Agreement”) contain a number of covenants imposing significant restrictions on our business. These restrictions may affect our ability to operate our business and may limit our ability to take advantage of potential business opportunities as they arise. The restrictions these covenants place on us include limitations on our ability to:
•incur or guarantee additional indebtedness;
•make certain investments;
•pay dividends or make distributions on our capital stock;
•sell assets, including capital stock of restricted subsidiaries;
•agree to payment restrictions affecting our restricted subsidiaries;
•consolidate, merge, sell or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all of our assets;
•enter into transactions with our affiliates;
•incur liens; and
•designate any of our subsidiaries as unrestricted subsidiaries.
These restrictions might hinder our ability to grow in accordance with our strategy. These covenants could materially and adversely affect our ability to finance our future operations or capital needs. Furthermore, they may restrict our ability to expand, pursue our business strategies and otherwise conduct our business. Our ability to comply with these covenants may be affected by circumstances and events beyond our control, such as prevailing economic conditions, pandemics or epidemics and changes in regulations, and there is no assurance that we will be able to comply with such covenants. These restrictions also limit our ability to obtain future financings to withstand a future downturn in our business or the economy in general. In addition, complying with these covenants may also cause us to take actions that are not favorable to you and may make it more difficult for us to successfully execute our business strategy and compete against companies that are not subject to such restrictions.
We are also required to comply with a first lien net leverage ratio covenant under the revolving portion of the Credit Facilities. See Note 8—Debt, to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report.
A breach of the covenants under the Indentures or the Credit Agreement could result in an event of default under the applicable indebtedness. Such a default may allow the creditors to accelerate the related indebtedness and may result in the acceleration of any other indebtedness that is subject to an applicable cross-acceleration or cross-default provision. In addition, an event of default under the Credit Agreement would permit the lenders under the Credit Facilities to terminate all commitments to extend further credit under the facilities. Furthermore, if we were unable to repay the amounts due and payable under the Credit Facilities or the Secured Notes, those lenders or holders, as applicable, could proceed against the collateral granted to them, including our available cash, to secure that indebtedness, subject to the provisions of the applicable intercreditor agreement. In the event our lenders or holders of the Secured Notes or the Unsecured Notes accelerate the repayment of our borrowings, we and our subsidiaries may not have sufficient assets to repay that indebtedness.
We may not be able to generate sufficient cash to service all of our indebtedness and may be forced to take other actions to satisfy our obligations under our indebtedness, which may not be successful.
Our ability to make scheduled payments on or refinance our indebtedness depends on our financial condition and operating performance, which are subject to prevailing economic and competitive conditions and to certain financial, business, legislative, regulatory and other factors beyond our control, including the COVID-19 pandemic. Our inability to generate sufficient cash flows to satisfy our debt obligations, or to refinance our indebtedness on commercially reasonable terms or at all, would materially and adversely affect our business, financial position and results of operations. Additionally, if we cannot make scheduled payments on our debt we will be in default, and holders of the Secured Notes and the Unsecured Notes could declare
25
all outstanding principal and interest to be due and payable, the lenders under the Credit Facilities could terminate their commitments to loan additional money to us, the lenders could foreclose against the assets securing their borrowings and we could be forced into bankruptcy or liquidation.
We expect that we will need to refinance all or a portion of our indebtedness on or before maturity, including the need to repay, refinance, replace or otherwise extend the maturity of the Term Loan Facility and the Secured Notes before the maturity of the Unsecured Notes. We may not be able to refinance any of our indebtedness at comparable interest rates, on commercially reasonable terms or at all. If such refinancing indebtedness is not available at interest rates comparable to our existing indebtedness our interest expense could materially increase, which could have a negative impact on our results of operations. If we cannot timely refinance our indebtedness, we may have to take actions such as issuing additional equity and reducing, delaying or foregoing capital expenditures, strategic acquisitions and investments. There is no assurance that any such actions, if necessary, could be implemented on commercially reasonable terms or at all.
If our cash flows and capital resources are insufficient to meet our operating needs and fund our debt service obligations, we could face substantial liquidity problems and could be forced to reduce or delay investments and capital expenditures or to dispose of material assets or operations, seek additional debt or equity capital or restructure or refinance our indebtedness. We may not be able to effect any such alternative measures on commercially reasonable terms or at all and, even if successful, those alternative actions may not allow us to meet our operating needs or our scheduled debt service obligations. Our inability to generate sufficient cash flows or execute sale-leaseback transactions to satisfy our indebtedness or other obligations or to refinance our indebtedness or other obligations at comparable interest rates on commercially reasonable terms or at all, would materially and adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition and our ability to satisfy our obligations under our indebtedness.
Despite our level of indebtedness, we and our subsidiaries may still incur substantially more debt, including secured debt. This could further exacerbate the risks to our financial condition described above and impair our ability to operate our business.
We and our subsidiaries may incur significant additional indebtedness in the future. Although the Indentures and the Credit Agreement contain restrictions on the incurrence of additional indebtedness, these restrictions are subject to a number of qualifications and exceptions. The additional indebtedness we may incur in compliance with these restrictions could be substantial. These restrictions also will not prevent us from incurring obligations that do not constitute indebtedness. If such incremental indebtedness or other new indebtedness is added to our current indebtedness levels, the related risks that we now face would increase.
Risks Relating to Our Human Capital
If we cannot retain our key employees and hire additional highly qualified employees, we may not be able to successfully manage our businesses and pursue our strategic objectives. We may also face increased labor costs that could reduce our profitability.
We are highly dependent on the services of our senior management team and other key employees at both our corporate headquarters and our centers, and on our ability to recruit, retain and motivate key employees. Competition for such employees is intense. Our inability to attract and retain the additional qualified employees required to expand our activities and to operate as a public company, or the loss of current key employees, could reduce member satisfaction, harm our brand and reputation and adversely affect our operating efficiency and financial results. Staffing shortages, including for our centers and for key corporate and technology resources, could also hinder our ability to implement our business strategy. Because payroll costs are a major component of the operating expenses at our centers, a shortage of skilled labor or changes in the labor market could also require higher wages that would increase our labor costs, which would reduce our profitability. Increases in minimum wage rates could also result in increased costs for us, which may adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition. Additionally, when a significant percentage of our current equity awards granted to our key employees becomes exercisable in April 2022, it may be more difficult or costly to retain such employees.
Attempts by labor organizations to organize groups of our employees or changes in labor laws could disrupt our operations or increase our labor costs.
Although none of our employees are currently covered under collective bargaining agreements, we may become subject to collective bargaining agreements, similar agreements or regulations enforced by governmental entities in the future. Changes in the federal regulatory scheme could make it easier for unions to organize groups of our employees. Unionization could hinder our ability to cross-train and cross-promote our employees due to prescribed work rules and job classifications. Labor regulations could also lead to higher wage and benefit costs, changes in work rules that raise operating expenses and legal costs,
26
and limit our ability to take cost saving measures during economic downturns. If relationships with our employees or other personnel become adverse, our centers could experience labor disruptions such as strikes, lockouts and public demonstrations. These or similar agreements, legislation or changes in regulations could disrupt our operations, reduce our profitability or interfere with the ability of our management to focus on executing our business and operating strategies.
Risks Relating to Legal Compliance and Risk Management
We are subject to extensive governmental laws and regulations, and changes in these laws and regulations could have a negative effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Our operations are subject to various United States and foreign national, federal, state, provincial and local laws and regulations, including but not limited to the following:
•consumer protection laws related to the advertising, marketing and sale of our products and services;
•statutes that regulate the sale and terms of our membership contracts;
•health or safety regulations related to various center operations, such as Life Time Training, LifeCafe, LifeSpa, Life Time Swim and Life Time Kids;
•regulation of ancillary health, fitness and wellness-related products and services;
•licensing or other regulation of our service providers, such as cosmetologists, massage therapists and registered dietitians;
•environmental laws and regulations;
•laws and regulations on fair housing and accessibility;
•laws and regulations governing privacy and security of information; and
•wage and hour or other employment related laws and regulations.
Any changes in such laws or regulations or any failure by us to comply with such laws or regulations could have an adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
We could be subject to claims related to the construction or operation of our facilities and in the use or condition of our premises, facilities, equipment, services, activities or products, which could have a negative effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Use of our premises, facilities, equipment, services, activities or products pose potential health or safety risks to members and guests. Claims may be asserted against us for loss, injury or death suffered by someone (including a minor child) using our premises, facilities, equipment, services, activities or products. We could also face claims in connection with the construction and remodel of our centers and other facilities, as well as claims related to environmental matters or remediation. While we carry insurance generally applicable to such claims, we face exposure for losses within any self-insured retention or for uninsured damages.
We could also face claims for economic or other damages by members, guests or employees, including consumer protection, wage and hour, health center contract, or other statutory or common law claims arising from our business operations. Such claims may be uninsured or the proceeds of our insurance coverages for such claims may be insufficient to cover our losses fully. Depending upon the outcome, these matters may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We could be subject to claims related to our health, fitness and wellness-related offerings or other claims, and the value and reputation of our brand may suffer.
We have offered and continue to offer directly or through third parties a variety of health, fitness and wellness-related products and services, such as nutritional products, blood screenings and other fitness assessments, health and fitness content and services through various digital methods, chiropractic services and medi-spa services. These products and services are, or may be subject to, legal and regulatory requirements. There is no assurance that there will be no claims against us, including those regarding the ingredients in, manufacture of or results of using our nutritional products, or our provision of other health, fitness
27
and wellness-related services or our relationships with third parties. Furthermore, there is no assurance that any rights we have under indemnification provisions and/or insurance policies will be sufficient to cover any losses that might result from such claims. Any publicity surrounding such claims may negatively impact the value of our brand.
We may also be exposed to other claims from time to time, including class action claims, that may have significant adverse effects upon us. See “Item 3—Legal Proceedings” in this Annual Report. In the ordinary course of conducting our business, we are exposed to claims that can have significant adverse effects upon our financial position, results of operations and cash flows. At any given time, there may be one or more civil actions initiated against us. If one or more of these pending lawsuits, or any lawsuits in the future, are adjudicated in a manner adverse to our interests, or if a settlement of any lawsuit requires us to pay a significant amount, the result could have an adverse impact on our financial position, results of operations and cash flows. In addition, any litigation, regardless of the outcome, may distract our management from the operation of our business.
We may not be able to maintain the required level of insurance coverage on acceptable terms or at an acceptable cost.
We may not be able to maintain general liability and/or property insurance on acceptable terms in the future or maintain a level of insurance that would provide adequate coverage against potential third-party liability, health and safety and other claims. An increase in the number of claims against health and fitness center operators generally or against us in particular may cause the cost of insurance for the industry as a whole or us in particular to rise, and comprehensive insurance coverage may become more difficult to attain. Any increase in the cost of insurance may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Risks Relating to Our Financial Performance
We may be materially adversely affected by risks associated with leases on certain of our centers.
We have and will continue to have significant lease obligations. As of December 31, 2021, we had 149 leased properties, including 110 center leases (of which 11 are ground leases) and centers under construction. Of our 110 center leases, 54 are long-term leases resulting from sale-leaseback transactions. The average remaining term on our center leases is approximately 15.9 years and we typically have certain rights to renew our leases. Assuming the exercise of our renewal options, the average remaining term on our center leases is 36.2 years. For leases with renewal options, several of them provide for our unilateral option to renew for additional rental periods at increased rental rates. Our ability to negotiate favorable terms on an expiring lease or to negotiate favorable terms on leases with renewal options, or conversely for a suitable alternate location, could depend on conditions in the real estate market, competition for desirable sites and our relationships with current and prospective landlords or other factors that are not within our control. We may not be able to renew our leasehold interests on their expiration or to renew them on terms that are as favorable as the current terms. Any or all of these factors and conditions could negatively impact our results of operations. In addition to future minimum lease payments, some of our center leases provide for additional rental payments based on a percentage of net sales, or “percentage rent,” if sales at the respective centers exceed specified levels, as well as the payment of common area maintenance charges, real property insurance and real estate taxes. Many of our leases also have defined escalating rent provisions over the initial term and any extensions.
A number of our leases, including those pursuant to the sale-leaseback transactions, may be terminated in the event of a breach and certain other circumstances. Moreover, we expect to lease, rather than own, the majority of our new centers in the future, and our obligations under the leases may require us to dedicate a portion of our cash flow from operations to making rent payments, thereby reducing our flexibility and the availability of our cash flow to fund working capital, capital expenditures and other general corporate purposes. We depend on cash flow from operations to pay our lease expenses. If our business does not generate sufficient cash flow from operating activities to fund these expenses, we may not be able to service our lease expenses, which could materially harm our business. In addition, since as a lessee we do not completely control the land and improvements underlying our operations, we may not be able to take certain actions that we desire or the lessors under our leases could take certain actions to disrupt our rights in the centers we lease. There can be no assurance that we will be able to comply with our obligations under the leases and the termination of the leases on any of our properties could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
In addition, our substantial operating lease obligations could have significant negative consequences, including those listed in the risk factor above under “—Risks Relating to Our Capital Structure—Our substantial indebtedness and other obligations could adversely affect our financial condition and prevent us from growing our business or fulfilling our obligations under our indebtedness.”
28
Our results of operations are subject to seasonal and quarterly variations in our revenues and net income.
We have experienced, and expect to continue to experience, seasonal and quarterly variations in our revenues and net income. These variations are primarily related to increased membership during the first quarter, as members tend to exercise more regularly at the beginning of each calendar year as a part of achieving goals that were set for the upcoming year. We also experience increased membership in certain centers during the summer pool season and a slight increase in in-center business activity with summer programming and operating expenses due to our outdoor operations. We then typically experience decreased membership and in-center business activity in the third and fourth quarters.
Our quarterly results of operations may also fluctuate significantly as a result of a variety of other factors, including the timing of new center openings, changes in pricing and revenues mix and changes in operating expenses. As a result of these seasonal and quarterly fluctuations, we believe that comparisons of our operating results between different quarters within a single year are not necessarily meaningful and that these comparisons cannot be relied upon as indicators of our future performance.
Delayed payment or failure to pay by our members and difficulties negotiating and collecting amounts due from members could have an adverse effect on our business.
Most of our members pay their membership fees on a monthly basis by direct debit or charges to their debit cards or credit cards. There is a risk of such scheduled payments being declined, resulting in such membership fees remaining unpaid. In the ordinary course of our business, we aim to resolve claims for unpaid membership fees through discussion with our members. An increase of declined or delinquent payments and difficulties in recovering unpaid membership fees could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Adverse developments in applicable tax laws could have a material and adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Our effective tax rate could also change materially as a result of various evolving factors, including changes in income tax law or changes in the scope of our operations.
We are subject to taxation in the United States at the federal level and by certain states and municipalities and foreign jurisdictions because of the scope of our operations. While our existing operations have been implemented in a manner we believe is in compliance with current prevailing laws, one or more taxing jurisdictions could seek to impose incremental or new taxes on us. In addition, jurisdictions in which we operate are actively considering significant changes to current tax laws, including increasing the corporate income tax rate in the United States. Any adverse developments in tax laws or regulations, including legislative changes, judicial holdings or administrative interpretations, could have a material and adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Finally, changes in the scope of our operations, including expansion to new products or new geographies, could increase the amount of taxes to which we are subject, and could increase our effective tax rate.
Risks Relating to Ownership of Our Common Stock
Our share price may change significantly, and stockholders may not be able to resell our common stock at or above the price per share paid or at all.
The stock market has experienced volatility and the trading price of our common stock may also be volatile. Stock volatility often has been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of particular companies. Additionally, we cannot predict the extent to which investor interest in us will lead to the development of a trading market on the NYSE or otherwise or how active and liquid that market may become. If an active and liquid trading market does not develop or continue, stockholders may have difficulty selling any of the shares of common stock that they purchased. Stockholders may also not be able to resell the Company’s common stock at or above the price per share paid due to a number of factors, such as those listed in other portions of this “Risk Factors” section and the following:
•results of operations that vary from the expectations of securities analysts and investors;
•if securities analysts do not publish research or reports about our business, or if they downgrade our common stock or our industry;
•results of operations that vary from those of our competitors;
•changes in expectations as to our future financial performance and growth, including financial estimates and investment recommendations by securities analysts and investors;
•changes in the perception of our brand or industry;
29
•declines in the market prices of stocks generally;
•strategic actions by us or our competitors;
•announcements by us or our competitors of significant contracts, new products, acquisitions, joint marketing relationships, joint ventures, other strategic relationships or capital commitments;
•changes in general economic or market conditions or trends in our industry or markets;
•changes in business or regulatory conditions;
•additions or departures of key management personnel;
•future sales of our common stock or other securities by us or our existing stockholders, or the perception of such future sales;
•investor perceptions of the investment opportunity associated with our common stock relative to other investment alternatives;
•the public’s response to press releases or other public announcements by us or third parties, including our filings with the SEC;
•announcements relating to litigation;
•guidance, if any, that we provide to the public, any changes in this guidance or our failure to meet this guidance;
•the development and sustainability of an active trading market for our common stock;
•changes in accounting principles; and
•other events or factors, including those resulting from natural disasters, pandemics, epidemics, war, acts of terrorism or responses to these events.
These broad market and industry fluctuations may materially adversely affect the market price of our common stock, regardless of our actual operating performance. In addition, price volatility may be greater if the public float and trading volume of our common stock are low.
In the past, following periods of market volatility, stockholders have instituted securities class action litigation. If we were involved in securities litigation, it could have a substantial cost and divert resources and the attention of executive management from our business regardless of the outcome of such litigation.
We are controlled by certain of our stockholders, whose interests may not be aligned with yours.
Certain of our existing stockholders who were stockholders before the IPO, and who we collectively refer to as the “Voting Group,” are party to an amended and restated stockholders agreement with the Company (the “Stockholders Agreement”) and collectively hold approximately 84.5% of the voting power of our common stock. The Voting Group includes investment funds affiliated with Leonard Green & Partners, L.P. and its affiliates (“LGP”) and TPG Global, LLC and its affiliates (“TPG”), which collectively hold approximately 52.7% of the voting power of our common stock. Pursuant to the terms of the Stockholders Agreement, certain members of the Voting Group will be entitled to designate individuals to be included in the slate of nominees recommended by our board of directors for election to our board of directors, subject to certain stock ownership thresholds set forth in the Stockholders Agreement, and the members of the Voting Group will agree to vote their shares of our common stock in favor of the election of such nominees. As a result, the Voting Group will have the ability to elect all of the members of our board of directors, and thereby, control our management and affairs. The directors so elected will have the authority, subject to the terms of our indebtedness and applicable rules and regulations, to issue additional stock, implement stock repurchase programs, declare dividends and make other decisions. We anticipate that the Voting Group will, for the foreseeable future, have this significant influence over our corporate management and affairs, and will be able to control virtually all matters requiring stockholder approval. Even if the Voting Group were to own or control less than a majority of our total outstanding shares of common stock, they will be able to influence the outcome of corporate actions so long as they own a significant portion of our total outstanding shares of common stock.
30
It is possible that members of the Voting Group may have interests that are different from other stockholders and may vote in a way with which other stockholders may disagree and that may be adverse to other stockholders’ interests. Further, members of the Voting Group may have differing views from each other, none of which may align with other stockholders’ interests. In addition, the Voting Group’s concentration of ownership could have the effect of delaying or preventing a change in control or otherwise discouraging a potential acquirer from attempting to obtain control of us, which could cause the market price of our common stock to decline or prevent our stockholders from realizing a premium over the market price for their common stock.
Additionally, certain of the members of the Voting Group are in the business of making investments in companies and may from time to time acquire interests in businesses that directly or indirectly compete with certain portions of our business or supply us with goods and services. Such members of the Voting Group may also pursue acquisition opportunities that may be complementary to our business and, as a result, those acquisition opportunities may not be available to us or may be more expensive for us to pursue.
We are a “controlled company” within the meaning of the NYSE rules and the rules of the SEC. As a result, we qualify for and are currently relying on exemptions from certain corporate governance requirements that provide protection to stockholders of other companies.
As a result of the Voting Group owning a majority of our common stock, we are a “controlled company” within the meaning of the corporate governance standards of the NYSE. Under these rules, a “controlled company” may elect not to comply with certain corporate governance requirements, including:
•the requirement that a majority of our board of directors consist of “independent directors” as defined under the rules of the NYSE;
•the requirement that we have a compensation committee that is composed entirely of directors who meet the NYSE independence standards for compensation committee members with a written charter addressing the committee’s purpose and responsibilities;
•the requirement that our director nominations be made, or recommended to our full board of directors, by our independent directors or by a nominations committee that consists entirely of independent directors and that we adopt a written charter or board resolution addressing the nominations process; and
•the requirement for an annual performance evaluation of the nominating and corporate governance and compensation committees.
We are currently relying on certain of the exemptions listed above, including that we do not currently have a nominating and corporate governance committee or compensation committee that consists entirely of independent directors and such committees may not be subject to annual performance evaluations. We may also elect to rely on additional exemptions for so long as we remain a “controlled company.” As a result, in the future our board of directors and those committees may have more directors who do not meet the NYSE’s independence standards than they would if those standards were to apply. The independence standards are intended to ensure that directors who meet those standards are free of any conflicting interest that could influence their actions as directors. Accordingly, stockholders may not have the same protections afforded to stockholders of other companies that are subject to all of the corporate governance requirements of the NYSE.
Future sales, or the perception of future sales, by us or our existing stockholders in the public market could cause the market price for our common stock to decline.
The sale of our common stock in the public market, or the perception that such sales could occur, could harm the prevailing market price of our common stock. These sales, or the possibility that these sales may occur, also might make it more difficult for us to sell equity securities in the future at a time and at a price that we deem appropriate.
As of December 31, 2021, we had a total of 193,059,949 shares of common stock outstanding and the Voting Group held 163,229,907 shares, or approximately 84.5%, of our common stock. The shares of our common stock held by the Voting Group are “restricted securities” under Rule 144 of the Securities Act and subject to certain restrictions on resale. Restricted securities may be sold in the public market only if they are registered under the Securities Act or are sold pursuant to an exemption from registration such as Rule 144.
Our directors, executive officers and the Voting Group have also agreed with the underwriters of the IPO, subject to certain exceptions, not to dispose of or hedge any of our common stock or securities convertible into or exchangeable for our common stock until April 5, 2022 at the earliest, except with the prior written consent of Goldman Sachs & Co. LLC and Morgan
31
Stanley & Co. LLC, on behalf of the underwriters. Upon the expiration of the contractual lock-up agreements, the shares of common stock held by our directors, executive officers and the Voting Group will be eligible for sale in the public market but will be subject to volume, manner of sale and other limitations under Rule 144. The Voting Group has certain registration rights under the Stockholders Agreement. Registration of any of these outstanding shares of common stock would result in such shares becoming freely tradable without compliance with Rule 144 upon effectiveness of the registration statement.
As restrictions on resale end or if these stockholders exercise their registration rights, the market price of our common stock could drop significantly if the holders of these shares sell them or are perceived by the market as intending to sell them. These factors could also make it more difficult for us to raise additional funds through future offerings of our common stock or other securities.
In addition, our shares of common stock reserved for future issuance under our 2021 Incentive Award Plan and our 2021 Employee Stock Purchase Plan will become eligible for sale in the public market once those shares are issued, subject to provisions relating to various vesting agreements, lock-up agreements and Rule 144, as applicable.
In the future, we may also issue our securities in connection with investments or acquisitions. The amount of our common stock issued in connection with an investment or acquisition could constitute a material portion of our then-outstanding common stock. Any issuance of additional securities in connection with investments or acquisitions may result in additional dilution to our stockholders and the securities issued may have rights that are senior to our common stock.
Our ability to raise capital in the future may be limited.
Our business and operations may consume resources faster than we anticipate. In the future, we may need to raise additional funds through the issuance of new equity securities, debt or a combination of both. Additional financing may not be available on favorable terms, or at all. If adequate funds are not available on acceptable terms, we may be unable to fund our capital requirements. If we issue new debt securities, the debt holders would have rights senior to common stockholders to make claims on our assets, and the terms of any debt could restrict our operations, including our ability to pay dividends on our common stock. If we issue additional equity securities, existing stockholders will experience dilution, and the new equity securities could have rights senior to those of our common stock. Because our decision to issue securities in any future offering will depend on market conditions and other factors beyond our control, we cannot predict or estimate the amount, timing or nature of our future offerings. Thus, our stockholders bear the risk of our future securities offerings reducing the market price of our common stock and diluting their interest.
Some provisions of our charter documents and Delaware law may have anti-takeover effects that could discourage an acquisition of us by others, even if an acquisition would be beneficial to our stockholders, and may prevent attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management.
Provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and our amended and restated bylaws, as well as provisions of the Delaware General Corporation Law (the “DGCL”), could make it more difficult for a third party to acquire us or increase the cost of acquiring us, even if doing so would benefit our stockholders, including transactions in which stockholders might otherwise receive a premium for their shares. These provisions include:
•establishing a classified board of directors such that not all members of the board are elected at one time;
•allowing the total number of directors to be determined exclusively (subject to the rights of holders of any series of preferred stock to elect additional directors) by resolution of our board of directors and granting to our board the sole power (subject to the rights of holders of any series of preferred stock or rights granted pursuant to the Stockholders Agreement) to fill any vacancy on the board;
•limiting the ability of stockholders to remove directors without cause;
•authorizing the issuance of “blank check” preferred stock by our board of directors, without further stockholder approval, to thwart a takeover attempt;
•prohibiting stockholder action by written consent (and, thus, requiring that all stockholder actions be taken at a meeting of our stockholders), if the Voting Group collectively ceases to own, or no longer has the right to direct the vote of, at least 50% of the voting power of our common stock;
32
•eliminating the ability of stockholders to call a special meeting of stockholders, except for LGP and TPG, so long as the Voting Group collectively owns, or has the right to direct the vote of, at least 50% of the voting power of our common stock;
•establishing advance notice requirements for nominations for election to the board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon at annual stockholder meetings;
•requiring the approval of the holders of at least two-thirds of the voting power of all outstanding stock entitled to vote thereon, voting together as a single class, to amend or repeal our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or amended and restated bylaws if the Voting Group collectively ceases to own, or no longer has the right to direct the vote of, at least 50% of the voting power of our common stock; and
•electing not to be governed by Section 203 of the DGCL.
These provisions could discourage, delay or prevent a transaction involving a change in control of our Company. They could also discourage proxy contests and make it more difficult for stockholders to elect directors of their choosing and cause us to take corporate actions other than those which the stockholders desire.
We are exposed to risks relating to evaluations of controls required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act.
As a privately-held company, we were not required to evaluate our internal control over financial reporting in a manner that met the standards of publicly traded companies required by Section 404(a) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (“Section 404” and the “Sarbanes-Oxley Act,” respectively). As a public company, we now have significant requirements for enhanced financial reporting and internal controls. Our internal control over financial reporting is currently managed by an internal financial reporting team with support from a third-party service provider. The process of designing and implementing effective internal controls that we manage is a continuous effort that requires us to anticipate and react to changes in our business and the economic and regulatory environments and to expend significant resources to maintain a system of internal controls that is adequate to satisfy our reporting obligations as a public company. If we are unable to establish or maintain appropriate internal financial reporting controls and procedures, it could cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations on a timely basis, result in material misstatements in our consolidated financial statements and harm our results of operations. In addition, we will be required, pursuant to Section 404, to furnish a report by management on, among other things, the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting in the annual report for the year ended December 31, 2023. This assessment will need to include disclosure of any material weaknesses identified by our management in our internal control over financial reporting. The rules governing the standards that must be met for our management to assess our internal control over financial reporting are complex and require significant documentation, testing and possible remediation. Testing our internal controls may divert our management’s attention from other matters that are important to our business. Our independent registered public accounting firm may be required to issue an attestation report on effectiveness of our internal controls.
In connection with the implementation of the necessary procedures and practices related to our internal control over financial reporting, we may identify deficiencies that we may not be able to remediate in time to meet the deadline imposed by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act for compliance with the requirements of Section 404. In addition, we may encounter problems or delays in completing the remediation of any deficiencies identified by our independent registered public accounting firm in connection with the issuance of their attestation report.
Our testing, or the subsequent testing by our independent registered public accounting firm, may reveal deficiencies in our internal control over financial reporting that are deemed to be material weaknesses. A material weakness in our internal controls could result in our failure to detect a material misstatement of our annual or quarterly consolidated financial statements or disclosures. We may not be able to conclude on an ongoing basis that we have effective internal control over financial reporting in accordance with Section 404. If we are unable to conclude that we have effective internal control over financial reporting, investors could lose confidence in our reported financial information, which could have a material adverse effect on the trading price of our common stock.
We became a public company in October 2021 and will incur increased costs as a result of operating as a publicly traded company, and our management will be required to devote substantial time to new compliance initiatives.
As a publicly traded company, we will incur additional legal, accounting, insurance and other expenses that we did not previously incur. Although we are currently unable to estimate these costs with any degree of certainty, they may be material in amount. In addition, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act and the rules of the SEC, and the stock exchange on which our common stock is listed, have imposed various requirements on public companies. Our management and other personnel will need to devote a substantial amount of time to these compliance
33
initiatives as well as investor relations. Moreover, these rules and regulations will increase our legal and financial compliance costs and will make some activities more time-consuming and costly. For example, these rules and regulations made it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and we were required to incur additional costs to maintain the same or similar coverage.
Our ability to use our net operating loss carryforwards and certain other tax attributes may become subject to limitation.
As of December 31, 2021, we had U.S. federal and state net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $554.4 million ($116.4 million tax effected) and $436.1 million ($25.4 million tax effected), respectively, and disallowed interest expense carryforwards under Section 163(j) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), of approximately $133.5 million ($34.2 million tax effected). Our ability to utilize our federal net operating carryforwards and disallowed interest expense carryforwards (the “Tax Attributes”) may become limited under Section 382 of the Code. The limitation applies if we experience an “ownership change,” which is generally defined as a greater than 50 percentage point change (by value) in the ownership of our equity by certain stockholders over a rolling three-year period. The amount of the annual limitation is generally equal to the product of the applicable long-term tax exempt-rate (as published by the Internal Revenue Service for the month in which the “ownership change” occurred) and the value of our outstanding stock immediately prior to the “ownership change.” If we have a net unrealized built-in gain in our assets immediately prior to the “ownership change,” the annual limitation may be increased as certain gains are, or are treated as, recognized during the five-year period beginning on the date of the “ownership change.” Similar provisions of state tax law may also apply to limit the use of our state net operating loss carryforwards. We may undergo an “ownership change” due to future transactions in our stock, which may be outside of our control, and we cannot predict whether any future “ownership change” would result in a significant limitation on our ability to use our Tax Attributes to offset our taxable income and adversely affect our future cash flows.
Non-U.S. holders who own more than 5% of our common stock may be subject to U.S. federal income tax on gain realized on the sale or other taxable disposition of such stock.
Because we have significant ownership of real property located in the United States, we may be a “United States real property holding corporation” (“USRPHC”) for U.S. federal income tax purposes, but we have made no determination to that effect. There can be no assurance that we do not currently constitute or will not become a USRPHC. As a result, any beneficial owner of our common stock that is neither a “U.S. person” nor an entity treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes (a “Non-U.S. Holder”) may be subject to U.S. federal income tax on gain realized on a sale or other taxable disposition of our common stock if such Non-U.S. Holder has owned, actually or constructively, more than 5% of our common stock at any time during the shorter of the five-year period ending on the date of the sale or other taxable disposition or the Non-U.S. Holder’s holding period in such stock.
Item 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
Item 2. PROPERTIES
We operate distinctive, resort-like athletic destinations in both affluent suburban and urban locations centered around major metropolitan areas in the United States and Canada. As of December 31, 2021, we operated 151 centers in 29 states and one Canadian province, 63 of which were owned (including ground leases) and 88 of which were leased. During 2021, we opened six new centers and closed four small under-performing centers, each of which was subject to a lease that we decided to let expire rather than renew. Our luxurious athletic centers total more than 15,000,000 square feet in the aggregate and measure approximately 100,000 square feet on average. They offer expansive fitness floors, spacious locker rooms, group fitness studios, indoor and outdoor pools and bistros, indoor and outdoor tennis courts, basketball courts, LifeSpa personal care services, LifeCafe healthy restaurants and child care and Kids Academy learning spaces. Excluding renewal options, the terms of our leased centers, including ground leases, expire at various dates from January 2024 through December 2049. Including renewal options, only four of our 88 leases expire in the next 15 years. The majority of our leases have renewal options and a few grant us the right to purchase the property.
Our corporate headquarters, located in Chanhassen, Minnesota next to our Chanhassen center, is comprised of two 105,000 square foot, free-standing, three-story buildings that we own.
34
The table below contains information about our centers as of December 31, 2021:
| Number of Owned Centers |
Number of Leased Centers |
Total Number of Centers |
Aggregate Square Feet |
||||||||||||||||||||
United States: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Alabama |
0 | 1 | 1 | 103,647 | |||||||||||||||||||
Arizona |
2 | 4 | 6 | 638,776 | |||||||||||||||||||
California |
3 | 2 | 5 | 453,933 | |||||||||||||||||||
Colorado |
3 | 3 | 6 | 657,557 | |||||||||||||||||||
Florida |
1 | 2 | 3 | 209,933 | |||||||||||||||||||
Georgia |
3 | 3 | 6 | 585,601 | |||||||||||||||||||
Illinois |
7 | 4 | 11 | 1,235,464 | |||||||||||||||||||
Indiana |
2 | 0 | 2 | 122,956 | |||||||||||||||||||
Iowa |
0 | 1 | 1 | 110,376 | |||||||||||||||||||
Kansas |
1 | 1 | 2 | 222,190 | |||||||||||||||||||
Maryland |
0 | 3 | 3 | 305,826 | |||||||||||||||||||
Massachusetts |
0 | 5 | 5 | 637,568 | |||||||||||||||||||
Michigan |
4 | 3 | 7 | 682,638 | |||||||||||||||||||
Minnesota |
13 | 9 | 22 | 1,997,354 | |||||||||||||||||||
Missouri |
0 | 2 | 2 | 236,990 | |||||||||||||||||||
Nebraska |
0 | 1 | 1 | 115,030 | |||||||||||||||||||
Nevada |
1 | 1 | 2 | 261,673 | |||||||||||||||||||
New Jersey |
1 | 5 | 6 | 683,135 | |||||||||||||||||||
New York |
2 | 5 | 7 | 536,886 | |||||||||||||||||||
North Carolina |
1 | 3 | 4 | 375,252 | |||||||||||||||||||
Ohio |
1 | 5 | 6 | 508,297 | |||||||||||||||||||
Oklahoma |
0 | 2 | 2 | 237,769 | |||||||||||||||||||
Pennsylvania |
0 | 3 | 3 | 310,170 | |||||||||||||||||||
Tennessee |
0 | 2 | 2 | 228,625 | |||||||||||||||||||
Texas |
14 | 11 | 25 | 2,466,528 | |||||||||||||||||||
Utah |
0 | 1 | 1 | 108,925 | |||||||||||||||||||
Virginia |
1 | 4 | 5 | 510,131 | |||||||||||||||||||
Washington |
0 | 1 | 1 | 39,597 | |||||||||||||||||||
Wisconsin |
0 | 1 | 1 | 126,423 | |||||||||||||||||||
Canada: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Ontario |
3 | 0 | 3 | 400,435 | |||||||||||||||||||
Total Centers |
63 | 88 | 151 | 15,109,685 | |||||||||||||||||||
In a few of our centers, we sublease space to third parties. The square footage figures above include those subleased areas. The center square footage figures exclude areas used for tennis courts, outdoor swimming pools, outdoor play areas and stand-alone Life Time Work, Life Time Sport and Life Time Swim locations.
In addition to the centers listed in the table above, as of December 31, 2021, we had 12 centers under construction and $340 million of capital expenditures invested in future center development, including our 12 centers under construction. We also operate four facilities that we classify as satellite locations. These include tennis-only facilities that we own in Oakdale, Minnesota, Centennial, Colorado and Plano, Texas, along with a leased small center in Austin, Texas.
35
Other Property Data:
| As of December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| (Number of centers) | |||||||||||||||||
| Center age: | |||||||||||||||||
| Open 1 to 12 months | 6 | 3 | 9 | ||||||||||||||
| Open 13+ months | 145 | 146 | 137 | ||||||||||||||
| Total centers | 151 | 149 | 146 | ||||||||||||||
| Center ownership: | |||||||||||||||||
| Own | 33 | 34 | 39 | ||||||||||||||
| Own/ground lease | 11 | 11 | 11 | ||||||||||||||
| Own/mortgaged outside of Credit Facilities | 18 | 18 | 18 | ||||||||||||||
| Joint venture | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Leased | 88 | 85 | 77 | ||||||||||||||
| Total centers | 151 | 149 | 146 | ||||||||||||||
Item 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
Life Time, Inc. et al. v. Zurich American Insurance Company — On August 19, 2020, Life Time, Inc., several of its subsidiaries and a joint venture entity, Bloomingdale Life Time Fitness LLC (collectively, the “Life Time Parties”), filed a complaint against Zurich American Insurance Company (“Zurich”) in the Fourth Judicial District of the State of Minnesota, County of Hennepin (Case No. 27-CV-20-10599) (the “Action”), seeking declaratory relief and damages under a property/business interruption insurance policy with respect to Zurich’s failure to provide certain coverage to the Life Time Parties related to the closure or suspension by governmental authorities of their business activities due to the spread or threat of spread of COVID-19. On March 15, 2021, certain of the Life Time Parties filed a First Amended Complaint in the Action adding claims against Zurich under a Builders’ Risk policy related to the suspension of multiple construction projects. The parties are currently in discovery. This Action is subject to many uncertainties, and the outcome of the matter is not predictable with any assurance.
Other Legal Proceedings—We are also engaged in other proceedings incidental to the normal course of business. Due to their nature, such legal proceedings involve inherent uncertainties, including but not limited to, court rulings, negotiations between affected parties and governmental intervention. We will establish reserves for matters that are probable and estimable in amounts we believe are adequate to cover reasonable adverse judgments. Based upon the information available to us and discussions with legal counsel, it is our opinion that the outcome of the various legal actions and claims that are incidental to our business will not have a material adverse impact on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. Such matters are subject to many uncertainties, and the outcomes of individual matters are not predictable with assurance.
Item 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information
Our common stock is listed on the NYSE under the symbol “LTH” and began trading on October 7, 2021. Prior to that date, there was no public market for our common stock.
36
Holders
As of March 7, 2022, there were 30 holders of record of our common stock. The number of holders of record is based upon the actual number of holders registered at such date and does not include holders of shares in “street name” or persons, partnerships, associates, corporations or other entities identified in security position listing maintained by depositories.
Dividends
We do not currently expect to pay any cash dividends on our common stock for the foreseeable future. Instead, we anticipate that all of our earnings in the foreseeable future will be used to support our operations and to finance the growth and development of our business. Any determination to declare or pay dividends in the future will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend upon our results of operations, cash requirements, financial condition, contractual restrictions, restrictions imposed by applicable laws and other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant. In addition, our business is conducted through our subsidiaries. Dividends, distributions and other payments from, and cash generated by, our subsidiaries will be our principal sources of cash to repay indebtedness, fund operations and pay dividends. Accordingly, our ability to pay dividends to our stockholders is dependent on the earnings and distributions of funds from our subsidiaries. The covenants in the Credit Agreement and the Indentures significantly restrict the ability of our subsidiaries to pay dividends or otherwise transfer assets to us.
Purchases of Equity Securities
During the fourth quarter of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021, we did not purchase any of our equity securities that are registered under Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act.
Stock Performance Graph
The following graph compares the change in total cumulative stockholder return on our common stock for the period from the close of trading on October 7, 2021, which was the first day our common stock began to trade publicly on the NYSE, to the end of fiscal 2021 relative to the performance of the S&P 500 Index, the S&P 400 Index and the Russell 2000 (Total Return) Index. We include a comparison against the Russell 2000 (Total Return) Index because there is no published industry or line-of-business index for our industry and we do not have a readily definable peer group that is publicly traded. The graph assumes $100.00 is invested at the closing price of $17.75 for our common stock on October 7, 2021.
The stock price performance shown below is not indicative of future performance. The performance graph shall not be deemed “soliciting material” or considered to be “filed” with the SEC for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act or otherwise subject to the liabilities under that Section, and shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any of the Company’s filings under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act.
37
Sales of Unregistered Securities
During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2021, we granted the following securities under the LTF Holdings, Inc. 2015 Equity Incentive Plan which were not registered under the Securities Act at the time of grant: (i) stock options to purchase an aggregate of 3,189,205 shares of our common stock, which options had an exercise price per share of $19.32 when issued, and (ii) an aggregate of 610,351 restricted stock units. We also granted 500,000 shares of our restricted Series A Preferred Stock, which automatically converted into 595,049 restricted shares of our common stock in connection with the IPO. In addition, on January 22, 2021, we issued an aggregate of 5,429,570 shares of our Series A Preferred Stock upon contribution of the outstanding principal and interest owed by us under a loan agreement, dated as of June 24, 2020, among LT Co-Borrower, LLC, LT Canada Co-Borrower, LP, and the lenders party thereto, which automatically converted into 6,687,219 shares of our common stock in connection with the IPO.
The issuances of these stock options, restricted stock units and shares of common stock, restricted preferred stock and preferred stock were deemed to be exempt from registration under the Securities Act in reliance upon Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act or Regulation D promulgated thereunder, or Rule 701 promulgated under Section 3(b) of the Securities Act, as transactions by an issuer not involving any public offering or pursuant to benefit plans and contracts relating to compensation as provided under Rule 701. Individuals who purchased shares as described above represented their intention to acquire the common stock for investment only and not with a view to or for sale in connection with any distribution thereof, and appropriate legends were affixed to the shares issued in such transactions, if applicable. None of the foregoing transactions involved any underwriters, underwriting discounts or commissions or any public offering.
Item 6. [RESERVED]
Item 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations together with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes and other financial information included elsewhere in this Annual Report. Some of the information included in this discussion and analysis or set forth elsewhere in this Annual Report, including information with respect to our plans and strategy for our business, includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. You should review the “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and “Risk Factors” sections of this Annual Report for a discussion of important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the following discussion and analysis.
Overview
Initial Public Offering
On October 12, 2021, Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. consummated its initial public offering (“IPO”) of 39.0 million shares of its common stock at a public offering price of $18.00 per share, resulting in total gross proceeds of $702.0 million before deducting the underwriting discounts and other offering expenses. The shares of its common stock began trading on the NYSE under the symbol “LTH” on October 7, 2021. A registration statement on Form S-1 relating to the offering of these securities was declared effective by the SEC on October 6, 2021. Additionally, on November 1, 2021, Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. consummated the sale of nearly 1.6 million additional shares of its common stock at the IPO price of $18.00 per share pursuant to the partial exercise by the underwriters of their over-allotment option, resulting in total gross proceeds of approximately $28.4 million before deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions.
Business
Life Time, the “Healthy Way of Life Company,” is a leading lifestyle brand offering premium health, fitness and wellness experiences to a community of nearly 1.3 million individual members, who together comprise more than 724,000 memberships, as of December 31, 2021. Since our founding nearly 30 years ago, we have sought to continuously innovate ways for our members to lead healthy and happy lives by offering them the best places, programs and performers. We deliver high-quality experiences through our omni-channel physical and digital ecosystem that includes more than 150 centers—distinctive, resort-like athletic destinations—across 29 states in the United States and one province in Canada. Our track record of providing differentiated experiences to our members has fueled our strong, long-term financial performance. In 2021, a year in which we experienced an initial recovery from the impacts of COVID-19, we generated $1,318 million of revenue, a net loss of $579 million and $80 million in Adjusted EBITDA. In 2020, which was significantly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, we generated $948 million of revenue, a net loss of $360 million and $(63) million in Adjusted EBITDA. In 2019, prior to
38
the COVID-19 pandemic, we generated $1,900 million of revenue, net income of $30 million and $438 million in Adjusted EBITDA.
Our luxurious athletic centers, which are located in both affluent suburban and urban locations, total more than 15 million square feet in the aggregate. As of December 31, 2021, we had 12 new centers under construction and we believe we have significant opportunities to continue expanding our portfolio of premium centers with 10 or more planned new centers annually for the foreseeable future in increasingly affluent markets. We offer expansive fitness floors with top-of-the-line equipment, spacious locker rooms, group fitness studios, indoor and outdoor pools and bistros, indoor and outdoor tennis courts, basketball courts, LifeSpa, LifeCafe and our childcare and Kids Academy learning spaces. Our premium service offering is delivered by approximately 30,000 Life Time team members, including over 7,800 certified fitness professionals, ranging from personal trainers to studio performers. As we continue to emerge from the COVID-19 pandemic and grow our business with more team members and more centers, we may be impacted by broader market conditions such as inflation and pressure on labor costs and labor availability.
Our members are highly engaged and draw inspiration from the experiences and community we have created, as demonstrated by the 69 million visits to our centers in 2021, 48 million visits to our centers in 2020 despite the COVID-19 pandemic and 92 million visits to our centers in 2019. We believe that no other company in the United States delivers the same quality and breadth of health, fitness and wellness experiences that we deliver, which has enabled us to consistently grow our recurring membership dues and in-center revenues for 20 consecutive years, prior to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. As of December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, our recurring membership dues represented 68%, 67% and 63%, respectively, of our total revenue, while our in-center revenue, consisting of Life Time Training, LifeCafe, LifeSpa, Life Time Swim and Life Time Kids, among other services, represented 29%, 29% and 34%, respectively, of our total revenue. Between 2015 and 2019, we grew our average revenue per center membership from $1,883 to $2,172, a testament to the significant value that our members place on engaging with Life Time. While average revenue per center membership fell to $1,317 in 2020, we saw a strong rebound in 2021, with $2,098 in average revenue per center membership. As we have delivered and continued to enhance premium experiences for our members, we have strategically increased our membership dues across most of our new and existing centers in 2021. We believe we can continually refine our pricing as we deliver exceptional experiences and find the optimal balance among the number of memberships per center, the member experience and maximizing our return for each center. We expect average revenue per center membership to continue to increase as we acquire new members and open new centers in increasingly affluent markets, which will allow us to generate additional revenue even if total memberships are slower to return due to the continued impacts of COVID-19.
We offer a variety of convenient month-to-month memberships with no long-term contracts. We define a membership for our centers in two ways: Center memberships and Digital On-hold memberships. A Center membership is defined as one or more adults 14 years of age or older, plus any juniors under the age of 14. Our base memberships provide individuals general access (with some amenities excluded) to a selected home center and all centers with the same or a lower base monthly dues rate. Our optimized pricing for a Center membership is determined center-by-center based on a variety of factors, including geography, market presence, demographic nature, population density, initial investment in the center and available services and amenities. Digital On-hold memberships do not provide access to our centers and are for those members who want to maintain certain member benefits including our Life Time Digital membership and the right to convert to Center membership without paying enrollment fees.
We continue to evolve our premium lifestyle brand in ways that elevate our member experiences and allow our members to more easily and regularly integrate health, fitness and wellness into their lives. We are introducing new types of Center memberships and communities, including our signature membership that includes unlimited small group training and priority registrations, and our new ARORA community focused on members aged 55 years and older. We are also enhancing our digital platform to deliver a true omni-channel experience for our members. Our Life Time Digital offering delivers live streaming fitness classes, remote goal-based personal training, nutrition and weight loss support and curated award-winning health, fitness and wellness content. Through an agreement with Apple®, we also provide Apple Fitness+ to our members, which gives our members expanded content and wellness data monitoring on the go. In addition, our members are able to purchase a wide variety of equipment, wearables, apparel, beauty products and nutritional supplements via our digital health store. We are continuing to invest in our digital capabilities in order to strengthen our relationships with our members and more comprehensively address their health, fitness and wellness needs so that they can remain engaged and connected with Life Time at any time or place. Elevating our member experiences and delivering a connected and digital environment requires investment in our team members, programs, products, services and centers. These investments may impact our short-term results of operations and cash flows as our investments in our business may be made more quickly than we see the returns on our investments.
39
We are also expanding our ecosystem in response to our members’ desire to more holistically integrate health and wellness into every aspect of their daily lives. In 2018, we launched Life Time Work, an asset-light branded co-working model that offers premium work spaces in close proximity to our centers and integrates ergonomic furnishings and promotes a healthy working environment. Life Time Work members also receive access to all of our resort-like athletic destinations across the United States and Canada. Additionally, we opened our first Life Time Living location in 2021, another asset-light extension of our “Healthy Way of Life” ecosystem, which offers luxury wellness-oriented residences. As we expand our footprint with new centers and nearby work and living spaces, as well as strengthen our digital capabilities, we expect to continue to grow our omni-channel platform to support the “Healthy Way of Life” journey of our members.
Components of Our Results of Operations
Total revenue
Total revenue consists of center revenue and other revenue (each defined below).
Center revenue
Center revenue consists of membership dues, enrollment fees and revenue generated within a center, which we refer to as in-center revenue. In-center revenue includes fees for personal training, aquatics and kids programming and other member services, as well as sales of products at our cafés, and sales of products and services offered at our spas and tennis programs.
Other Revenue
Other revenue includes revenue generated from our businesses outside our centers, which are primarily media, athletic events and related services. Our media revenue includes our magazine, Experience Life®, our athletic events revenue includes endurance activities such as running, cycling and triathlons, and our related services revenue includes revenue from our race registration and timing businesses. Other revenue also includes revenue generated from our Life Time Work locations.
Center operations expenses
Center operations expenses consist of direct expenses related to the operation of our centers, such as salaries, commissions, payroll taxes, benefits, real estate taxes and other occupancy costs (excluding rent), utilities, repairs and maintenance, supplies and pre-opening expenses.
Rent expense
Rent expense consists of both cash and non-cash expense related to our operating leases booked on straight-line basis over the lease term in accordance with GAAP.
Non-cash rent expense
Non-cash rent expense reflects the non-cash portion of our annual GAAP operating lease expense that is greater or less than the cash operating lease payments. Non-cash rent expense for our open properties represents non-cash expense associated with properties that were operating at the end of each period presented. Non-cash rent expense for our properties under development represents non-cash expense associated with properties that are still under development at the end of each period presented.
General, administrative and marketing expenses
General, administrative and marketing expenses include:
•Costs relating to our centralized support functions, such as accounting, information systems, procurement, real estate and development and member relations, as well as share-based compensation expense.
•Marketing expenses, which primarily consist of marketing department costs and media and advertising costs to support and grow Center membership levels, in-center businesses, new center openings and our businesses outside of our centers.
•Indirect support costs related to the operation of our centers, including payroll-related expenses associated with our regional center management structure and in-center business support.
40
Depreciation and Amortization
Consists of depreciation and amortization for our depreciable long-live assets, including assets related to our owned centers.
Other operating expenses
Consists primarily of expenses related to our other revenue, which is generated from our businesses outside of our centers. In addition, we record other non-recurring operating expenses that we believe are not indicative of our core operating performance, as a component of other operating expenses.
Interest expense, net of interest income
Interest expense, net of interest income consists primarily of cash interest expense on borrowings and non-cash interest expense which includes the amortization of debt issuance costs, partially offset by interest earned.
Equity in (loss) earnings of affiliate
Includes investments in unconsolidated subsidiaries which we account for using the equity method of accounting.
(Benefit from) provision for income taxes
The (benefit from) provision for income taxes consists of an estimate for U.S. federal, state and foreign income taxes based on enacted rates, as adjusted for allowable credits, deductions, uncertain tax positions, changes in deferred tax assets and liabilities and changes in the tax law.
Net (loss) income
Net (loss) income consists of our total revenue, less our total operating expenses, and then adjusted for other (expense) income and (benefit from) provision for income taxes, as set forth on our consolidated statements of operations.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
This discussion and analysis includes certain financial measures that are not presented in accordance with the generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“GAAP”), including Adjusted EBITDA and free cash flow before growth capital expenditures and ratios related thereto. These non-GAAP financial measures are not based on any comprehensive set of accounting rules or principles and should not be construed as an inference that our future results will be unaffected by unusual or non-recurring items. In addition, these non-GAAP financial measures should be read in conjunction with our financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. The reconciliations of the Company’s non-GAAP financial measures to the corresponding GAAP measures should be carefully evaluated. We use Adjusted EBITDA as an important performance metric for the Company. In addition, free cash flow before growth capital expenditures is an important liquidity metric we use to evaluate our ability to make principal payments on our indebtedness and to fund our capital expenditures and working capital requirements.
Adjusted EBITDA
We define Adjusted EBITDA as net (loss) income before interest expense, net, (benefit from) provision for income taxes and depreciation and amortization, excluding the impact of share-based compensation expense, loss (gain) on sale-leaseback transactions, capital transaction costs, legal settlements, asset impairment, severance and other items that are not indicative of our ongoing operations, including incremental costs related to COVID-19.
Management uses Adjusted EBITDA to evaluate the Company’s performance. We believe that Adjusted EBITDA is an important metric for management, investors and analysts as it removes the impact of items that we do not believe are indicative of our core operating performance and allows for consistent comparison of our operating results over time and relative to our peers. We use Adjusted EBITDA to supplement GAAP measures of performance in evaluating the effectiveness of our business strategies, and to establish annual budgets and forecasts. We also use Adjusted EBITDA or variations thereof to establish short-term incentive compensation for management.
41
Free Cash Flow Before Growth Capital Expenditures
We define free cash flow before growth capital expenditures as net cash provided by (used in) operating activities less center maintenance capital expenditures and corporate capital expenditures. We believe free cash flow before growth capital expenditures assists investors and analysts in evaluating our liquidity and cash flows, including our ability to make principal payments on our indebtedness and to fund our capital expenditures and working capital requirements. Our management considers free cash flow before growth capital expenditures to be a key indicator of our liquidity and we present this metric to our board of directors. Additionally, we believe free cash flow before growth capital expenditures is frequently used by analysts, investors and other interested parties in the evaluation of companies in our industry. We also believe that investors, analysts and rating agencies consider free cash flow before growth capital expenditures as a useful means of measuring our ability to make principal payments on our indebtedness and evaluating our liquidity, and management uses this measurement for one or more of these purposes.
Adjusted EBITDA and free cash flow before growth capital expenditures should be considered in addition to, and not as a substitute for or superior to, financial measures calculated in accordance with GAAP. These are not measurements of our financial performance under GAAP and should not be considered as alternatives to net (loss) income or any other performance measures derived in accordance with GAAP or as an alternative to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities as a measure of our liquidity and may not be comparable to other similarly titled measures of other businesses. Adjusted EBITDA and free cash flow before growth capital expenditures have limitations as analytical tools, and you should not consider these measures in isolation or as a substitute for analysis of our operating results or cash flows as reported under GAAP. Furthermore, we compensate for the limitations described above by relying primarily on our GAAP results and using Adjusted EBITDA and free cash flow before growth capital expenditures only for supplemental purposes. See our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report for our GAAP results.
Non-GAAP Measurements and Key Performance Indicators
We prepare and analyze various non-GAAP performance metrics and key performance indicators to assess the performance of our business and allocate resources. We analyze these key performance indicators to assess the performance of our business and allocated resources. For more information regarding our non-GAAP performance metrics, see “—Non-GAAP Financial Measures” above. These are not measurements of our financial performance under GAAP and should not be considered as alternatives to any other performance measures derived in accordance with GAAP.
42
Set forth below are certain GAAP and non-GAAP measurements and key performance indicators for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019. The following information has been presented consistently for all periods presented.
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands, except for Average Center revenue per center membership data) | |||||||||||||||||
| Membership Data | |||||||||||||||||
| Center memberships | 649,373 | 500,948 | 853,748 | ||||||||||||||
| Digital On-hold memberships | 74,767 | 248,641 | 90,299 | ||||||||||||||
| Total memberships | 724,140 | 749,589 | 944,047 | ||||||||||||||
| Revenue Data | |||||||||||||||||
| Membership dues and enrollment fees | 70.5% | 70.0% | 65.3% | ||||||||||||||
| In-center revenue | 29.5% | 30.0% | 34.7% | ||||||||||||||
| Total Center revenue | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | ||||||||||||||
| Membership dues and enrollment fees | $ | 907,111 | $ | 651,116 | $ | 1,208,365 | |||||||||||
| In-center revenue | 379,523 | 278,850 | 642,980 | ||||||||||||||
| Total Center revenue | $ | 1,286,634 | $ | 929,966 | $ | 1,851,345 | |||||||||||
Average Center revenue per center membership (1)
|
$ | 2,098 | $ | 1,317 | $ | 2,172 | |||||||||||
Comparable center sales (2)
|
35.3% | (52.2)% | 2.7% | ||||||||||||||
| Center Data | |||||||||||||||||
Net new center openings (3)
|
2 | 3 | 5 | ||||||||||||||
Total centers (end of period) (3)
|
151 | 149 | 146 | ||||||||||||||
Total center square footage (end of period) (4)
|
15,000,000 | 14,800,000 | 14,600,000 | ||||||||||||||
| GAAP and Non-GAAP Financial Measures | |||||||||||||||||
| Net (loss) income | $ | (579,369) | $ | (360,192) | $ | 30,049 | |||||||||||
Net (loss) income margin (5)
|
(44.0) | % | (38.0) | % | 1.6 | % | |||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA (6)
|
$ | 80,299 | $ | (62,966) | $ | 437,933 | |||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA margin (6)
|
6.1 | % | (6.6) | % | 23.0 | % | |||||||||||
Center operations expense |
$ | 844,098 | $ | 660,046 | $ | 1,041,133 | |||||||||||
Pre-opening expenses (7)
|
7,021 | 7,463 | 14,282 | ||||||||||||||
Rent |
209,823 | 186,257 | 165,965 | ||||||||||||||
Non-cash rent expense (open properties)
|
9,959 | 24,480 | 15,717 | ||||||||||||||
| Non-cash rent expense (properties under development) | 12,643 | 12,625 | 6,804 | ||||||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities |
(20,029) | (95,981) | 358,718 | ||||||||||||||
Free cash flow before growth capital expenditures (8)
|
(143,630) | (197,441) | 177,479 | ||||||||||||||
(1) We define Average Center revenue per center membership as Center revenue less Digital On-hold revenue, divided by the average number of Center memberships for the period, where the average number of Center memberships for the period is an average derived from dividing the sum of the total Center memberships outstanding at the beginning of the period and at the end of each month during the period by one plus the number of months in each period.
(2) We measure the results of our centers based on how long each center has been open as of the most recent measurement period. We include a center, for comparable center sales purposes, beginning on the first day of the 13th full calendar month of the center’s operation, in order to assess the center’s growth rate after one year of operation.
43
(3) Net new center openings is the number of centers that opened for the first time to members during the period, less any centers that closed during the period. Total centers (end of period) is the number of centers operational as of the last day of the period. As of December 31, 2021, all of our 151 centers were open.
(4) Total center square footage (end of period) reflects the aggregate fitness square footage, which we use as a metric for evaluating the efficiencies of a center as of the end of the period. The square footage figures exclude areas used for tennis courts, outdoor swimming pools, outdoor play areas and stand-alone Work, Sport and Swim locations. These figures are approximations.
(5) Net (loss) income margin is calculated as net (loss) income divided by total revenue.
(6) We present Adjusted EBITDA as a supplemental measure of our performance. We define Adjusted EBITDA as net (loss) income before interest expense, net, (benefit from) provision for income taxes and depreciation and amortization, excluding the impact of share-based compensation expense, loss (gain) on sale-leaseback transactions, capital transaction costs, legal settlements, asset impairment, severance and other items that are not indicative of our ongoing operations, including incremental costs related to COVID-19.
Adjusted EBITDA margin is calculated as Adjusted EBITDA divided by total revenue.
The following table provides a reconciliation of net (loss) income, the most directly comparable GAAP measure, to Adjusted EBITDA:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||||||
| Net (loss) income | $ | (579,369) | $ | (360,192) | $ | 30,049 | |||||||||||
Interest expense, net of interest income (a)
|
224,516 | 128,394 | 128,955 | ||||||||||||||
| (Benefit from) provision for income taxes | (140,344) | (127,538) | 10,080 | ||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 235,124 | 247,693 | 220,468 | ||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation expense (b)
|
334,339 | — | 24,152 | ||||||||||||||
COVID-19 related (credits) expenses (c)
|
(1,589) | 49,183 | — | ||||||||||||||
Loss (gain) on sale-leaseback transactions (d)
|
2,380 | (7,235) | (157) | ||||||||||||||
Capital transaction costs (e)
|
2,904 | 96 | 6,297 | ||||||||||||||
Legal (recoveries) settlements (f)
|
(44) | 345 | 8,359 | ||||||||||||||
Asset impairments (g)
|
— | 7,475 | 10,127 | ||||||||||||||
Other (h)
|
2,382 | (1,187) | (397) | ||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 80,299 | $ | (62,966) | $ | 437,933 | |||||||||||
(a)During the year ended December 31, 2021, we incurred a non-cash expense of $41.0 million related to the extinguishment of our related party secured loan and $28.6 million related to write-off discounts and debt issuance costs of our prior term loan facility, our previous senior unsecured notes and our related party secured loan. In June 2020, we closed on an approximate $101.5 million secured loan from an investor group comprised solely of our stockholders or their affiliates. The secured loan carried an interest rate of 12.0% and was scheduled to mature in June 2021. In January 2021, we extinguished the related party secured loan plus accrued interest with a book value of $108.6 million by converting the loan into approximately 5.4 million shares of our Series A Preferred Stock, which had a fair value of $149.6 million, as determined by an independent third-party valuation, at the time of conversion. Accordingly, we booked a $41.0 million loss upon conversion.
(b)A significant portion of the share-based compensation expense that we recognized during the year ended December 31, 2021 is associated with stock options that were granted prior to 2021. As of the effective date of the IPO in October 2021, these stock options became fully vested, and they either became immediately exercisable or they will become exercisable no later than April 4, 2022, subject to continued service through such date. Accordingly, during the period from the effective date of the IPO through December 31, 2021, we recognized share-based compensation expense associated with these stock options in an amount equal to the proportion of the total service period that has passed from the respective grant dates associated with each of these stock option awards through December 31, 2021. Because the vesting and exercisability of these stock options was contingent upon the occurrence of a change of control or an initial public offering, no share-based compensation expense associated with these stock options was recognized prior to the IPO.
44
(c) Represents the incremental net (credits) expenses we recognized related to the COVID-19 pandemic. We adjust for these costs as they do not represent costs associated with our normal ongoing operations. We believe that adjusting for these costs provides a more accurate and consistent representation of our actual operating performance from period to period. The net credits we recognized during 2021 consist primarily of the recovery of certain qualifying expenses recovered under the CARES Act, partially offset by COVID-19 legal-related costs. For the year ended December 31, 2020, COVID-19 related expenses consisted of $27.0 million for project cost write-offs for sites no longer deemed viable as a result of the economic downturn caused by COVID-19, $12.0 million for the employee portion of health care coverage which is normally paid by employees but was paid by us during this period on behalf of our employees, and $10.2 million of emergency leave and non-working payroll, which includes subsequent recovery of certain expenses under the CARES Act, severance and charitable contributions made to support our employees who were directly impacted by COVID-19.
(d) We adjust for the impact of gains or losses on the sale-leaseback of our properties as they do not reflect costs associated with our ongoing operations.
(e) Represents one-time costs related to capital transactions, including debt and equity offerings that are non-recurring in nature but excluding direct costs related to the IPO which were netted against the proceeds.
(f) We adjust for the impact of large class action and unusual legal settlements paid or recoveries received. These are non-recurring in nature and do not reflect costs associated with our normal ongoing operations.
(g) Represents non-cash asset impairments of our long-lived and intangible assets.
(h) Includes costs associated with large corporate restructuring charges, executive level involuntary terminations and other transactions, which are unusual and non-recurring in nature. For the year ended December 31, 2021, other expenses consisted of $1.6 million of incremental expenses related to a winter storm resulting in historical freezing temperatures affecting our Texas region, and $0.8 million of executive level severance.
(7) Represents non-capital expenditures associated with opening new centers which are incurred prior to the commencement of a new center opening. The number of centers under construction or development, the types of centers and our costs associated with any particular center opening can vary significantly from period to period.
(8) Free cash flow before growth capital expenditures, a non-GAAP financial measure, is calculated as net cash (used in) provided by operating activities less center maintenance capital expenditures and corporate capital expenditures.
The following table provides a reconciliation from net cash (used in) provided by operating activities to free cash flow before growth capital expenditures:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
| ($ in thousands) | 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities | $ | (20,029) | $ | (95,981) | $ | 358,718 | |||||||||||
| Center maintenance capital expenditures | (61,932) | (32,111) | (107,612) | ||||||||||||||
| Corporate capital expenditures | (61,669) | (69,349) | (73,627) | ||||||||||||||
| Free cash flow before growth capital expenditures | $ | (143,630) | $ | (197,441) | $ | 177,479 | |||||||||||
Factors Affecting the Comparability of our Results of Operations
Impact of COVID-19 on our Business
Overview
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak of a novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19 a pandemic and recommended containment and mitigation measures worldwide. On March 13, 2020, the United States declared a National Public Health Emergency with respect to COVID-19. On March 16, 2020, in compliance with orders and advisories from federal, state and local governmental authorities regarding COVID-19, we closed all of our centers. Throughout this Annual Report, including this “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” when we refer to “COVID-19,” such as when we describe the “impact of COVID-19” on our operations, we mean the coronavirus-related orders issued by governmental authorities affecting our operations and/or the presence of coronavirus in our centers, including COVID-19 positive members or team members.
While our centers were closed, in consultation with an epidemiologist (MD/PhD) with a wide range of experience in clinical, occupational and environmental medicine, we developed processes and protocols for the operation of our centers in
45
the COVID-19 environment. These protocols, which have varied at our centers across the United States and Canada, have included physical distancing, restricting certain equipment and amenities, occupancy limits, required appointments, touchless interactions, facial coverings, cleaning, sanitation, hygiene, air circulation and filtering, screening, contact tracing and educational awareness. We may take further actions as government authorities require or recommend, including implementing vaccine mandates or negative testing, or as we determine to be in the interests of our members, guests, team members, vendors and service providers, including in response to emerging variants of the COVID-19 virus, such as the Delta and Omicron variants. We continue to refine these processes and protocols as we operate in the evolving COVID-19 environment.
With a focus on providing a healthy and clean environment for our members and team members, we began re-opening our centers in May 2020 and continued to re-open our centers as governmental authorities permitted. During the second half of 2020 and into 2021, we were able to re-open all of our centers; however, these re-openings were staggered and many of our centers were required to be closed again after re-opening for some period of time as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and related restrictions. For instance, during the three months ended June 30, 2020, September 30, 2020 and December 31, 2020, 149, 43 and 31 of our centers, respectively, were closed for some period of time. The performance of our centers after we were able to re-open them has varied depending on various factors, including how early we were able to re-open them in 2020, whether we were required to close them again, their geographic location and applicable governmental restrictions. The performance of our centers was also impacted in 2021 as a result of the Delta variant and then again later in 2021 and into 2022 with the Omicron variant.
We have experienced a slightly faster recovery in our membership dues revenue compared to our in-center revenue as our centers have re-opened. We expect membership dues revenue to remain a higher percentage of our total revenue in the near term and return to more historical levels over time. While we are encouraged by the trends of increased vaccination rates, reduced COVID-19 infections and hospitalizations and reduced operating restrictions in many of the regions where our centers operate, we continue to operate under governmental restrictions at many of our centers and the full extent of the impact of COVID-19, including the Delta and Omicron variants, remains uncertain and is dependent on future developments that cannot be accurately predicted at this time. Considering this uncertainty, the extent of the impact of COVID-19 on our financial position, results of operations, liquidity and cash flows is uncertain at this time.
Operations
As of December 31, 2021, all of our 151 centers were open. As of December 31, 2021, total memberships were 724,140, a decrease of 3.4% compared to 749,589 at December 31, 2020. Center memberships were 649,373, an increase of 29.6% compared to 500,948 at December 31, 2020. Digital On-hold memberships were 74,767, a decrease of 69.9% compared to 248,641 at December 31, 2020. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, Center memberships and Digital On-hold memberships were 853,748 and 90,299, respectively, at December 31, 2019.
We continue to monitor governmental orders regarding the operations of our centers, as well as our center operating processes and protocols. We expect we may need to continue to adjust such processes and protocols as facts and circumstances change, including as a result of variants of the COVID-19 virus, such as the Delta and Omicron variants.
We also expect our centers and in-center businesses will continue to be impacted differently based upon considerations such as their geographic location, vaccination rates, impacts of variants, applicable government restrictions and guidance, and team member and member sentiment with respect to our center operating processes and protocols and working in and/or using our centers. For example, we have seen an increase in Center memberships and center utilization in various regions when government restrictions have been lifted.
Given increasing demand for online engagement with consumers, we have increased our focus on delivering a digitized in-center experience through our omni-channel ecosystem. We continue to expand our Digital membership offering, bringing our “Healthy Way of Life” programs, services and content to consumers virtually. This omni-channel experience is designed to deliver health, fitness and wellness where, when and how members want it by offering online reservations registrations, virtual training, live streaming and on-demand classes, virtual events and more.
Cash Flows and Liquidity
In response to the impact of COVID-19 on our business, we took swift cash management actions to reduce our operating costs and preserve liquidity. These actions included: initially furloughing over 95% of our employees; undertaking two corporate restructuring events to right size overhead relative to the current business; initially suspending virtually all construction capital spending; negotiating rent reductions and deferrals with many of our landlords; evaluating the CARES Act and receiving the employee retention credit, the deferment of the employer’s portion of social security tax payments and the various income tax-related benefits; and completing sale-leaseback transactions associated with six properties.
46
Although there is uncertainty related to the impact of COVID-19 on our financial position, results of operations, liquidity and cash flows, much of which is dependent on the length and severity of the pandemic and the related measures taken, we believe that the combination of our current cash position, our availability under the revolving portion of the Credit Facilities, the recent actions we have taken to refinance our debt and strengthen our balance sheet, as well as the actions we have taken to reduce our cash outflows, leave us well-positioned to manage our business through this pandemic. If our available liquidity were not sufficient to meet our operating and debt service obligations as they come due, we would need to pursue alternative arrangements through additional debt or equity financing to meet our cash requirements. There can be no assurance that any such financing would be available on commercially acceptable terms, or at all.
There may be developments outside of our control requiring us to adjust our operating plan, including additional required center closures. As such, given the dynamic nature of our current operating environment, we cannot reasonably estimate the impacts of COVID-19 on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows in the future.
Investment in Business
As we recover from the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic, we are investing in our business to elevate our member experiences and drive additional revenue per center membership, including introducing new types of memberships, providing concierge-type member services, expanding our omni-channel offerings and improving our in-center services and products. Elevating our member experiences requires investment in our team members, programs, products, services and centers. These investments may impact our short-term results of operations and cash flows as our investments in our business may be made more quickly than we achieve additional revenue per center membership.
Impact of our Asset-light, Flexible Real Estate Strategy on Rent Expense
Our asset-light, flexible real estate strategy has allowed us to expand our business by leveraging operating leases and sale-leaseback transactions. Approximately 58% of our centers are now leased, including approximately 94% of our new centers opened within the last five years, versus a predominantly owned real estate strategy prior to 2015. Rent expense, which includes both cash and non-cash rent expense, will continue to increase as we lease more centers and will therefore impact the comparability of our results of operations. The impact of these increases is dependent upon the timing of our centers under development and the center openings and terms of the leases for the new centers or sale-leaseback transactions.
Share-Based Compensation
During the year ended December 31, 2021, we recognized share-based compensation expense associated with stock options, restricted Series A Preferred Stock, restricted stock and restricted stock units totaling approximately $334.3 million, a significant portion of which is associated with stock options that were granted prior to 2021. As of the effective date of the IPO, these stock options became fully vested, and they either became immediately exercisable or they will become exercisable no later than April 4, 2022, subject to continued service through such date. Accordingly, during the period from the effective date of the IPO through December 31, 2021, we recognized share-based compensation expense associated with these stock options in an amount equal to the proportion of the total service period that has passed from the respective grant dates associated with each of these stock option awards through December 31, 2021. Because the vesting and exercisability of these stock options was contingent upon the occurrence of a change of control or an initial public offering, no share-based compensation expense associated with these stock options was recognized prior to the IPO. For more information on our share-based compensation arrangements, see Note 10, Stockholders’ Equity, to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Ultimate results could differ from those estimates. In recording transactions and balances resulting from business operations, we use estimates based on the best information available. We revise the recorded estimates when better information is available, facts change or we can determine actual amounts. These revisions can affect operating results. We have identified below the following accounting policies and estimates that we consider to be critical.
Impairment of Goodwill and Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
We assess the recoverability of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets, such as our Life Time trade name, on an annual basis, or more often if circumstances warrant. We assess the recoverability of goodwill by estimating the fair value of the
47
reporting unit to which the goodwill relates and comparing this fair value to the net book value of the reporting unit. We assess the recoverability of the Life Time trade name through the use of the relief from royalty valuation method. If the fair value of goodwill or indefinite-lived intangible assets is less than net book value, we reduce the book value accordingly and record a corresponding impairment loss. Our policy is to test goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment on October 1 of each year. The valuation of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets requires assumptions and estimates of many critical factors, including revenue and market growth, operating margins, membership trends, strategic initiatives, royalty rates and discount rates. A significant change in the factors noted above could cause us to reduce the estimated fair value of some or all of our reporting units or indefinite-lived intangible assets and recognize a corresponding impairment of our goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets in connection with a future impairment test. Adverse changes in strategy, market conditions or assumed market capitalization may result in an impairment of goodwill. Based upon our review and analysis, no material impairments of goodwill or indefinite-lived intangible assets were deemed to have occurred during any of the periods presented.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
We test long-lived asset groups for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the net book value of the asset group may not be recoverable. A long-lived asset group may include property and equipment, finite-lived intangible assets and/or operating lease right-of-use assets. We consider a history of consistent and significant operating losses, or the inability to recover net book value over the remaining useful life, to be our primary indicators of potential impairment. Judgments regarding existence of impairment indicators are based on factors such as operational performance (including revenue and expense growth rates), market conditions and expected holding period of the primary asset associated with each asset group. We evaluate long-lived asset groups for impairment at the lowest levels for which there are identifiable cash flows, which is generally at an individual center or ancillary business level. The determination of whether impairment has occurred is based on an estimate of undiscounted future cash flows directly related to that center or ancillary business, compared to the carrying value of the related assets. If an impairment has occurred, the amount of impairment recognized is determined by estimating the fair value of these assets and recording a loss if the carrying value is greater than the fair value. Worsening operational performance, market conditions or change in expected holding periods of each asset may cause us to re-evaluate the assumptions used in management’s analysis. Based upon our review and analysis, no material impairments of long-lived assets were deemed to have occurred during any of the periods presented.
48
Results of Operations
Year Ended December 31, 2021 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2020
The following table sets forth our consolidated statements of operations data (amounts in thousands) and data as a percentage of total revenue for the periods indicated:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| As a Percentage of Total Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Revenue: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Center revenue |
$ | 1,286,634 | $ | 929,966 | 97.6 | % | 98.1 | % | |||||||||||||||
Other revenue |
31,419 | 18,413 | 2.4 | % | 1.9 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Total revenue |
1,318,053 | 948,379 | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Operating expenses: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Center operations |
844,098 | 660,046 | 64.0 | % | 69.6 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Rent |
209,823 | 186,257 | 15.9 | % | 19.6 | % | |||||||||||||||||
General, administrative and marketing |
480,543 | 149,898 | 36.5 | % | 15.8 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
235,124 | 247,693 | 17.9 | % | 26.1 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Other operating |
43,653 | 63,634 | 3.3 | % | 6.7 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Total operating expenses |
1,813,241 | 1,307,528 | 137.6 | % | 137.8 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Loss from operations |
(495,188) | (359,149) | (37.6) | % | (37.8) | % | |||||||||||||||||
Other income (expense): |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net of interest income |
(224,516) | (128,394) | (17.0) | % | (13.5) | % | |||||||||||||||||
Equity in loss of affiliate |
(9) | (187) | 0.0 | % | — | % | |||||||||||||||||
Total other expense |
(224,525) | (128,581) | (17.0) | % | (13.5) | % | |||||||||||||||||
Loss before income taxes |
(719,713) | (487,730) | (54.6) | % | (51.3) | % | |||||||||||||||||
Benefit from income taxes |
(140,344) | (127,538) | (10.6) | % | (13.3) | % | |||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (579,369) | $ | (360,192) | (44.0) | % | (38.0) | % | |||||||||||||||
Total revenue. The $369.7 million increase in Total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 primarily reflects the adverse economic impact that our center closures had on our business during the year ended December 31, 2020 and the timing of the subsequent reopening of our centers, as well as pricing initiatives we implemented at the majority of our centers during the year ended December 31, 2021, which have resulted in higher average Center membership dues being charged to new members during the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020.
With respect to the $356.6 million increase in Center revenue for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020:
•71.8% was from membership dues and enrollment fees, which increased $256.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020. This increase reflects the adverse economic impact that our center closures, which resulted from COVID-19, had on our business during the year ended December 31, 2020 and the timing of the subsequent reopening of our centers, as well as pricing initiatives we implemented at the majority of our centers during the year ended December 31, 2021, which have resulted in higher average Center membership dues being charged to new members during the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020; and
•28.2% was from in-center revenue, which increased $100.6 million as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020. This increase was recognized across all of our primary in-center businesses and reflects the adverse economic impact that our center closures, which resulted from COVID-19, had on our business during the year ended December 31, 2020 as well as the timing of the subsequent reopening of our centers.
49
The $13.0 million increase in Other revenue for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily driven by our athletic events business, as we were able to produce several of our iconic events during the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 when COVID-19 restrictions forced the cancellation of most of our events.
Center operations expenses. The $184.1 million increase in Center operations expenses for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily driven by increased staffing requirements resulting from the subsequent reopening of our centers and the addition of six new centers. Center operations expenses for the year ended December 31, 2021 also includes $12.9 million of share-based compensation expense, a significant portion of which is associated with stock options that were granted prior to 2021. For more information regarding share-based compensation expense that we recognized during the year ended December 31, 2021, see “—General, administrative and marketing expenses” below.
Rent expense. The $23.5 million increase in Rent expense for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily driven by the sale leaseback of two centers occurring during the year ended December 31, 2021, the sale leaseback of three centers that occurred during the fourth quarter of 2020, and our taking possession of nine properties during the year ended December 31, 2021 for future centers where we started incurring GAAP rent expense, most of which is non-cash.
General, administrative and marketing expenses. The $330.6 million increase in General, administrative and marketing expenses for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily driven by a $316.8 million increase in share-based compensation expense, a $16.4 million increase in general and administrative costs, primarily driven by the return of corporate team members who were furloughed during the year ended December 31, 2020 as well as other costs to support revenue growth, and a $5.7 million increase in marketing expenses, partially offset by a $9.9 million decrease in corporate COVID-19-related expenses. A significant portion of the share-based compensation expense that we recognized during the year ended December 31, 2021 is associated with stock options that were granted prior to 2021. As of the effective date of the IPO, these stock options became fully vested, and they either became immediately exercisable or they will become exercisable no later than April 4, 2022, subject to continued service through such date. Accordingly, during the period from the effective date of the IPO through December 31, 2021, we recognized share-based compensation expense associated with these stock options in an amount equal to the proportion of the total implied service period that has passed from the respective grant dates associated with each of these stock option awards through December 31, 2021. Because the vesting and exercisability of these stock options was contingent upon the occurrence of a change of control or an initial public offering, no share-based compensation expense associated with these stock options was recognized prior to the IPO.
Depreciation and amortization. The $12.6 million decrease in Depreciation and amortization for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 consists of $9.3 million and $3.3 million lower depreciation and amortization, respectively. The decrease in depreciation for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily driven by the timing of sale-leaseback transactions, as well as the reduction in the carrying value of certain fixed assets associated with some of our leased centers and some of our ancillary businesses that resulted from impairment charges that we recognized during the fourth quarter of 2020.
Other operating expenses. The $19.9 million decrease in Other operating expenses for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily attributable to $30.3 million of project cost write-offs recognized during the year December 31, 2020 for sites that were no longer deemed viable for construction as a result of COVID-19, partially offset by approximately $6.0 million higher costs associated with our athletic events business during the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 as well as a $4.6 million increase in share-based compensation expense. The increase in costs associated with our athletic events resulted from our ability to produce several of our iconic events during the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 when COVID-19 restrictions forced the cancellation of most of our events. A significant portion of the share-based compensation expense is associated with stock options that were granted prior to 2021. For more information regarding share-based compensation expense that we recognized during the year ended December 31, 2021, see “—General, administrative and marketing expenses” above.
Interest expense, net. The $96.1 million increase in Interest expense, net of interest income for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily driven by a $41.0 million non-cash expense recognized related to the conversion of our related party secured loan into Series A Preferred Stock, write-offs of debt issuance costs and original issuance discount costs associated with extinguished debt instrument totaling $28.6 million and $5.7 million prepayment penalty related to partial pay down of our Term Loan Facility. Additionally, the increase also reflects a relatively higher effective weighted average interest rate on an increased average level of outstanding borrowings during the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020.
50
Benefit from income taxes. The benefit from income taxes was $140.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to $127.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. The effective tax rate was 19.5% and 26.1% for those same periods, respectively. The change in benefit from income taxes was primarily attributable to: (i) an increase in our loss before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020; (ii) a $41.0 million loss related to the extinguishment of our related party secured loan that we recognized for GAAP purposes during the year ended December 31, 2021 that is not recognized for tax purposes; and (iii) the recognition during the year ended December 31, 2021 of an increase in the valuation allowance to reduce the deferred tax asset associated with our net operating losses.
Net loss. As a result of the factors described above, net loss increased by $219.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020.
Year Ended December 31, 2020 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2019
The following table sets forth our consolidated statements of operations data (amounts in thousands) and data as a percentage of total revenue for the periods indicated:
| Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| As a Percentage of Total Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Revenue: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Center revenue |
$ | 929,966 | $ | 1,851,345 | 98.1 | % | 97.4 | % | |||||||||||||||
Other revenue |
18,413 | 49,026 | 1.9 | % | 2.6 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Total revenue |
948,379 | 1,900,371 | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Operating expenses: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Center operations |
660,046 | 1,041,133 | 69.6 | % | 54.8 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Rent |
186,257 | 165,965 | 19.6 | % | 8.7 | % | |||||||||||||||||
General, administrative and marketing |
149,898 | 227,684 | 15.8 | % | 12.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
247,693 | 220,468 | 26.1 | % | 11.6 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Other operating |
63,634 | 76,842 | 6.7 | % | 4.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Total operating expenses |
1,307,528 | 1,732,092 | 137.8 | % | 91.1 | % | |||||||||||||||||
(Loss) income from operations |
(359,149) | 168,279 | (37.8) | % | 8.9 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Other income (expense): |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net of interest income |
(128,394) | (128,955) | (13.5) | % | (6.8) | % | |||||||||||||||||
Equity in (loss) earnings of affiliate |
(187) | 805 | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Total other expense |
(128,581) | (128,150) | (13.5) | % | (6.8) | % | |||||||||||||||||
(Loss) income before income taxes |
(487,730) | 40,129 | (51.3) | % | 2.1 | % | |||||||||||||||||
(Benefit from) provision for income taxes |
(127,538) | 10,080 | (13.3) | % | 0.5 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income |
(360,192) | 30,049 | (38.0) | % | 1.6 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
— | 24 | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income attributable to Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. |
$ | (360,192) | $ | 30,025 | (38.0) | % | 1.6 | % | |||||||||||||||
Total revenue. The $952.0 million decrease in Total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 reflects the adverse economic impact that our center closures, which resulted from COVID-19, had on our business as well as the timing of the subsequent reopening of our centers.
With respect to the $921.4 million decrease in Center revenue for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019:
•60.5% was from membership dues and enrollment fees, which decreased $557.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 due to the adverse economic impact that our center closures, which resulted from COVID-19, had on our business as well as the timing of the subsequent reopening of our centers; and
51
•39.5% was from in-center revenue, which decreased $364.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 due to a decline across all of our primary in-center businesses, as a result of our center closures, which resulted from COVID-19, as well as the timing of the subsequent reopening of our centers.
The $30.6 million decrease in Other revenue for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 was primarily driven by athletic event cancellations caused by COVID-19, which had a negative impact on sales of media, race and timing-related technology, as well as event-related registration fees.
Center operations expenses. The $381.1 million decrease in Center operations expenses for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 was primarily the result of $290.7 million in decreased labor costs, $38.8 million in decreased cost of goods sold, $23.2 million in reduced facility costs and $17.8 million in reduced credit card fees as a result of center closures and lower Center revenue, which resulted from COVID-19.
Rent expense. The $20.3 million increase in Rent expense for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 was primarily driven by the sale-leaseback transactions that were consummated during 2020, as well as the timing of other property leases that commenced during 2020 and the prior year.
General, administrative and marketing expenses. The $77.8 million decrease in General, administrative and marketing expenses for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 was primarily driven by a reduction of expenses of $26.9 million, which was primarily the result of lower salaries and wages associated with our furloughed employees, as well as corporate headcount reduction actions that we took during 2020, and a reduction in our advertising and marketing spend of approximately $22.7 million as a result of our continued efforts to control expenses in light of COVID-19. In addition, in 2019, we incurred $23.0 million of additional share-based compensation as part of a voluntary stock option purchase offer, as well as $5.2 million of costs related to the sale of newly issued common stock to a minority investor group.
Depreciation and amortization. The $27.2 million increase in Depreciation and amortization for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 consists of $31.4 million higher depreciation, partially offset by $4.2 million lower amortization.
Other operating expenses. The $13.2 million decrease in Other operating expenses for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 was primarily attributable to the decline in sales of race and timing-related technology, as well as the decline in media sales, which was driven by the cancellation of athletic events as a result of COVID-19.
Interest expense, net. The $0.6 million decrease in Interest expense, net for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 reflects the decrease in the LIBOR during the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019, partially offset by interest associated with new borrowings under a secured loan with related parties during 2020 and a relatively lower level of capitalized interest on lower construction spending during the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019.
(Benefit from) provision for income taxes. The benefit from income taxes was $127.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the $10.1 million provision for income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2019. The benefit from income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily driven by the loss before income taxes. The effective tax rate was 26.1% and 25.1% for the year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The change in effective tax rate for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 reflects an increase in the overall effective state rate during the year ended December 31, 2020.
Net (loss) income. As a result of the factors described above, net loss was $360.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, compared to net income of $30.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest. Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest, which represents the stated dividends associated with the underlying preferred shares of Massage Retreat & Spa, Inc. (“MR&S”), was $0.0 million and less than $0.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
52
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Liquidity
Our principal liquidity needs include the development of new centers, debt service and lease requirements, investments in technology and expenditures necessary to maintain and update our centers and associated fitness equipment and member experiences. We have primarily satisfied our historical liquidity needs with cash flow from operations, drawing on the revolving portion of the Credit Facilities and through sale-leaseback transactions.
We have taken significant actions to improve our liquidity and during 2021, we refinanced a significant portion of our outstanding debt. Specifically, we: (i) refinanced in full the outstanding balances associated with our then existing senior secured credit facility as well as our then existing senior unsecured notes; (ii) converted our related party secured loan into Series A Preferred Stock, which were automatically converted into our common stock in connection with the IPO; and (iii) increased the commitments under the revolving portion of our Credit Facilities to $475 million and extended their maturity. Additionally, we completed a sale-leaseback transaction associated with two properties. For information regarding the refinancing actions we took during 2021, see Note 8, Debt, to our consolidated financial statements in this Annual Report. For more information regarding the sale-leaseback transaction that was consummated during 2021, see Note 9, Leases, to our consolidated financial statements in this Annual Report.
On October 12, 2021, we completed our IPO of 39.0 million shares of our common stock at a public offering price of $18.00 per share, resulting in total gross proceeds of $702.0 million before deducting the underwriting discounts and other offering expenses. Additionally, on November 1, 2021, we consummated the sale of nearly 1.6 million additional shares of our common stock at the IPO price of $18.00 per share pursuant to the partial exercise by the underwriters of their over-allotment option, resulting in total gross proceeds of approximately $28.4 million before deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions. On October 13, 2021, we paid down $575.7 million (including a $5.7 million pre-payment penalty) of our Term Loan Facility with a portion of the net proceeds we received from the IPO. We intend to use the remaining net proceeds from the IPO, along with the additional net proceeds of approximately $27.1 million from the sale of the additional nearly 1.6 million shares of common stock, for general corporate purposes.
As the opportunity arises or as our business needs require, we may seek to raise capital through additional debt financing or through equity financing. There can be no assurance that any such financing would be available on commercially acceptable terms, or at all. To date, we have not experienced difficulty accessing the credit and capital markets; however, volatility in these markets, particularly in light of the impacts of COVID-19 and the potential for rising interest rates, may increase costs associated with issuing debt instruments or affect our ability to access those markets, which could have an adverse impact on our ability to raise additional capital, to refinance existing debt and/or to react to changing economic and business conditions. In addition, it is possible that our ability to access the credit and capital markets could be limited at a time when we would like, or need, to do so.
As of December 31, 2021, there were no outstanding borrowings under our Revolving Credit Facility and there were $33.5 million of outstanding letters of credit, resulting in total availability under our Revolving Credit Facility, subject to a $100.0 million minimum liquidity requirement that ended on December 31, 2021, of $341.5 million. Total cash and cash equivalents at December 31, 2021 was $31.6 million, resulting in total cash and availability under our Revolving Credit Facility of $373.1 million.
The following table sets forth our consolidated statements of cash flows data (amounts in thousands):
| For the Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities |
$ | (20,029) | $ | (95,981) | $ | 358,718 | |||||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities |
(269,919) | (6,115) | (477,814) | ||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities |
288,399 | 87,395 | 133,316 | ||||||||||||||
Effect of exchange rate on cash and cash equivalents |
(9) | (55) | 208 | ||||||||||||||
(Decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents |
$ | (1,558) | $ | (14,756) | $ | 14,428 | |||||||||||
53
Operating Activities
The $76.0 million decrease in net cash used in operating activities for the year December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily the result of higher profitability, before the impact of non-cash share-based compensation expense, due to the recovery from the impact of COVID-19 on our business during 2020.
The $454.7 million increase in net cash used in operating activities for the year December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 was primarily due to lower center profitability as a result of center closures, which reflects the adverse economic impact that COVID-19 has had on our business.
Investing Activities
Investing activities consist primarily of purchasing real property, constructing new centers, acquisitions and purchasing new fitness equipment. In addition, we invest in capital expenditures to maintain and update our existing centers. We finance the purchase of our property and equipment through operating cash flows, proceeds from sale-leaseback transactions, construction reimbursements and draws on our Revolving Credit Facility.
The $263.8 million increase in net cash used in investing activities for the year December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily driven by a relatively higher level of new center construction activity and lower amount of proceeds we received from landlords for sale-leaseback transactions during the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020. Cash used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2021 also includes a $9.1 million payment we made in connection with the acquisition of the assets associated with an outdoor enthusiast and bicycling event.
The $471.7 million decrease in net cash used in investing activities for the year December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 was primarily driven by a relatively lower level of new center construction activity, as well as a relatively higher amount of proceeds that we received from sale-leaseback transactions during the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019. Additionally, we received $23.0 million of proceeds from the sale of land held for sale during the year ended December 31, 2020.
The following schedule reflects capital expenditures by type of expenditure (in thousands):
| For the Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Growth capital expenditures (new center land and construction, growth initiatives, major remodels of acquired centers and the purchase of previously leased centers), net of construction reimbursements |
$ | 205,308 | $ | 164,157 | $ | 442,778 | |||||||||||
Center maintenance capital expenditures |
61,932 | 32,111 | 107,612 | ||||||||||||||
Corporate capital expenditures |
61,669 | 69,349 | 73,627 | ||||||||||||||
Total capital expenditures |
$ | 328,909 | $ | 265,617 | $ | 624,017 | |||||||||||
The $63.3 million increase in total capital expenditures for the year ended December 31, 2021 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily driven by higher growth capital expenditures for new centers and center maintenance capital expenditures due to the reopening of our centers after the COVID-19 pandemic and our desire to deliver the best places for our members as they return.
The $358.4 million decrease in total capital expenditures for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 reflects actions we took during the year ended December 31, 2020 to reduce our cash outflows in light of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Financing Activities
The $201.0 million increase in net cash provided by financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily driven by the $702 million of gross proceeds we received in connection with the IPO, offset by repayments of our Term Loan Facility and Revolving Credit Facility.
The $45.9 million decrease in net cash provided by financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019 was primarily driven by net repayments made on our then existing senior secured credit facility during the year ended December 31, 2020, partially offset by proceeds from new borrowings which we received during
54
the year ended December 31, 2020. During the year ended December 31, 2020, we received approximately $101.5 million of proceeds associated with a secured loan from an investor group that is comprised solely of our stockholders or their affiliates, and $15.1 million of proceeds associated with a loan secured by a mortgage on one location.
Cash Requirements
Our cash requirements within the next twelve months include accounts payable, construction accounts payable, accrued expenses and other current liabilities.
Our cash requirements greater than twelve months from various contractual obligations and commitments include:
Debt Obligations and Interest Payments
Refer to Note 8, Debt, to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report for further detail of our debt and the timing of expected future principal and interest payments. We expect to pay approximately $118.5 million of interest in the next 12 months and approximately $381.5 million of interest beyond 12 months.
Operating and Finance Leases
Refer to Note 9, Leases, to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report for further detail of our lease obligations and the timing of expected future payments.
Deferred Compensation Obligations
Refer to Note 14, Executive Nonqualified Plan, to our consolidated financial statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report for further detail of our deferred compensation plans.
Contracted Services
Contracted services include agreements with third-party service providers for software licenses and support, and marketing services. We expect to pay approximately $8.5 million for contracted services in the next 12 months and approximately $12.0 million beyond 12 months.
Capital Expenditures
Our primary capital expenditure requirements include growth capital expenditures, which include new center land and construction, growth initiatives and major remodels of acquired centers, as well as maintenance capital expenditures to keep our centers operational and meeting our standards. As of December 31, 2021, we had 12 centers under construction and $340 million of capital expenditures invested in future center development.
We expect to satisfy our short-term and long-term obligations through a combination of cash on hand, funds generated from operations, sale-leaseback transactions and the borrowing capacity available under our Revolving Credit Facility.
Item 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are exposed to market risks in the ordinary course of our business that include changes in interest rates and changes in foreign currency exchange rates. Information relating to quantitative and qualitative disclosures about these market risks is set forth below.
Interest rate risk
Our cash consists primarily of an interest-bearing account at a large U.S. bank with limited interest rate risk. At December 31, 2021, we held no investments in marketable securities.
We incur interest at variable rates under the revolving portion of our Credit Facilities. At December 31, 2021, there were no outstanding borrowings on the Revolving Credit Facility and there were $33.5 million of outstanding letters of credit, resulting in total revolver availability, subject to a $100.0 million minimum liquidity requirement that ended on December 31, 2021, of $341.5 million, which was available at intervals ranging from 30 to 180 days at interest rates ranging from LIBOR plus 4.25% or base rate plus 3.25%. Our Term Loan Facility is also subject to variable rates of LIBOR plus 4.75% or base rate plus 3.75% and had an outstanding balance of $273.6 million at December 31, 2021.
55
Assuming no prepayments of the Term Loan Facility and that the Revolving Credit Facility is fully drawn (and that LIBOR is in excess of the floor rate applicable to the Term Loan Facility), each one percentage point change in interest rates would result in an approximately $7.5 million change in annual interest expense on the indebtedness under the Credit Facilities.
Foreign currency exchange risk
We operate primarily in the United States with three centers operating in Canada. Given the limited amount of operations outside of the United States, fluctuations due to changes in foreign currency exchange rates would not have a material impact on our business.
56
Item 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Page | |||||
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (PCAOB ID No. |
F- 2 |
||||
| Consolidated Financial Statements | |||||
F- 4 |
|||||
F- 5 |
|||||
F- 6 |
|||||
F- 7 |
|||||
F- 8 |
|||||
F- 9 |
|||||
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the stockholders and the Board of Directors of Life Time Group Holdings, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive (loss) income, stockholders' equity, and cash flows, for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2021, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2021, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Sale-Leaseback Transactions—Refer to Notes 2 and 9 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
As described in Note 9 to the Company’s consolidated financial statements, the Company entered into two sale-leaseback transactions, involving two properties, with unrelated third parties during the year ended December 31, 2021. Under these transactions, the Company sold property with a net book value of $85.8 million for cash proceeds of $76.0 million, which was reduced by transactions costs of $2.0 million, for net cash proceeds of $74.0 million. The estimated fair value of the properties sold was $85.5 million. Accordingly, the aggregate sales price associated with these arrangements was increased, for accounting purposes, by a total of $9.5 million, which resulted in the recognition of an aggregate loss of $2.3 million on these transactions. The Company determined that the transactions qualified as sale-leaseback transactions in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 842, Leases.
We identified management’s evaluation of whether the sale-leaseback transactions transferred control, was recognized timely, and at fair value, as a critical audit matter. Management applies judgment in assessing relevant lease terms, provisions, and other conditions, including repurchase rights, included in the Company’s sale and lease agreements to determine whether or not
F-2
the control of the real estate property has transferred from the Company, the timing of the transaction, and the determination of fair value. Auditing these assessments made by management involved challenging auditor judgment due to the extent of specialized skills or knowledge required.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures related to sale-leaseback transactions included the following, among others:
•Utilizing professionals with skills and knowledge to assist in: (i) assessing management’s application of ASC Topic 842 and (ii) evaluating relevant lease terms, provisions and other conditions included in the Company’s sale-leaseback agreements to assess the appropriateness of the conclusion that a transfer of control has occurred.
•Evaluating whether the Company appropriately accounted for the sale by recognizing the transaction price for the sale at the time control is transferred, derecognizing the carrying amount of the asset, and accounting for the lease in accordance with ASC Topic 842.
•Utilizing professionals with specialized skills and knowledge in valuation to assist, for certain transactions, with assessing whether the overall transaction was at fair value.
•Recalculating the operating lease right-of-use asset and liability based on the terms of the agreement and calculated incremental borrowing rate.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
March 10, 2022
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2002.
F-3
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except per share data)
| December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||
ASSETS |
|||||||||||
Current assets: |
|||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | $ | |||||||||
Accounts receivable, net |
|||||||||||
Center operating supplies and inventories |
|||||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|||||||||||
Income tax receivable |
|||||||||||
Total current assets |
|||||||||||
Property and equipment, net |
|||||||||||
Goodwill |
|||||||||||
Operating lease right-of-use assets |
|||||||||||
Intangible assets, net |
|||||||||||
Other assets |
|||||||||||
Total assets |
$ | $ | |||||||||
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|||||||||||
Current liabilities: |
|||||||||||
Accounts payable |
$ | $ | |||||||||
Construction accounts payable |
|||||||||||
Deferred revenue |
|||||||||||
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities |
|||||||||||
Current maturities of debt |
|||||||||||
Current maturities of operating lease liabilities |
|||||||||||
Total current liabilities |
|||||||||||
Long-term debt, net of current portion |
|||||||||||
Operating lease liabilities, net of current portion |
|||||||||||
Deferred income taxes |
|||||||||||
Other liabilities |
|||||||||||
Total liabilities |
|||||||||||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 12) |
|||||||||||
Stockholders’ equity: |
|||||||||||
Common stock, $ |
|||||||||||
Additional paid-in capital |
|||||||||||
Stockholder note receivable |
( |
||||||||||
Accumulated deficit |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Total stockholders’ equity |
|||||||||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | $ | |||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-4
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In thousands, except per share data)
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Revenue: |
|||||||||||||||||
Center revenue |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
Other revenue |
|||||||||||||||||
Total revenue |
|||||||||||||||||
Operating expenses: |
|||||||||||||||||
Center operations |
|||||||||||||||||
Rent |
|||||||||||||||||
General, administrative and marketing |
|||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
|||||||||||||||||
Other operating |
|||||||||||||||||
Total operating expenses |
|||||||||||||||||
(Loss) income from operations |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Other (expense) income: |
|||||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net of interest income |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
Equity in (loss) earnings of affiliate |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Total other expense |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
(Loss) income before income taxes |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
(Benefit from) provision for income taxes |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
|||||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income attributable to Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
(Loss) earnings per common share – basic and diluted |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding – basic and diluted |
|||||||||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-5
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE (LOSS) INCOME
(In thousands)
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of tax of $ |
|||||||||||||||||
Comprehensive (loss) income |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest |
|||||||||||||||||
Comprehensive (loss) income attributable to Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-6
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(In thousands)
| Common Stock | Additional Paid-in Capital |
Stockholder Note Receivable |
Retained Earnings/ (Accumulated Deficit) |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
Noncontrolling Interest |
Total Equity |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2018 |
$ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Partial forgiveness of stockholder note receivable | — | — | ( |
— | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock, net of issuance costs | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Purchases of stock options | — | — | ( |
— | — | — | — | ( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of noncontrolling interest | — | — | — | — | — | ( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2019 |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | — | ( |
— | — | ( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2020 |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | — | — | — | — | ( |
— | — | ( |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Settlement of accrued compensation liabilities through the issuance of share-based compensation awards | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock in connection with the IPO and over-allotment exercise, net of offering costs | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock in connection with Series A Preferred Stock conversion | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of restricted stock in connection with restricted Series A Preferred Stock conversion | ( |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cancellation of stockholder note receivable | — | — | ( |
— | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2021 |
$ | $ | $ | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-7
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: |
|||||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) income to net cash (used in) provided by operating activities: |
|||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
|||||||||||||||||
Deferred income taxes |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation |
|||||||||||||||||
Non-cash rent expense |
|||||||||||||||||
Impairment charges associated with long-lived assets |
|||||||||||||||||
Loss (gain) on disposal of property and equipment, net |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
| Loss on debt extinguishment | |||||||||||||||||
| Write-off of discounts and debt issuance costs | |||||||||||||||||
Amortization of debt issuance costs |
|||||||||||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities |
|||||||||||||||||
Other |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: |
|||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
Acquisitions, net of cash acquired |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
Proceeds from sale-leaseback transactions |
|||||||||||||||||
Proceeds from the sale of land held for sale |
|||||||||||||||||
Other |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: |
|||||||||||||||||
Proceeds from borrowings |
|||||||||||||||||
Repayments of debt |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
Proceeds from senior secured credit facility |
|||||||||||||||||
Repayments on senior secured credit facility |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
Repayments of finance lease liabilities |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
Proceeds from the issuance of common stock, net of issuance costs |
|||||||||||||||||
Purchases of stock options |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Increase in debt discounts and issuance costs |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|||||||||||||||||
Effect of exchange rate on cash and cash equivalents |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
(Decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents – beginning of period |
|||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents – end of period |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-8
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
1.Nature of Business and Basis of Presentation
Nature of Business
Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. (collectively with its direct and indirect subsidiaries, “Life Time,” “We,” “Our,” or “the Company”) is a holding company incorporated in the state of Delaware. Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. changed its name from LTF Holdings, Inc. effective on June 21, 2021. As a holding company, Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. does not have its own independent assets or business operations, and all of our assets and business operations are through Life Time, Inc. and its direct and indirect subsidiaries. We are primarily dedicated to providing premium health, fitness and wellness experiences at our athletic resort destinations and via our comprehensive digital platform and portfolio of iconic athletic events – all with the objective of inspiring healthier, happier lives. We design, build and operate our athletic resort destinations that are distinctive and large, multi-use sports and athletic, professional fitness, family recreation and spa centers in a resort-like environment. As of December 31, 2021, we operated 151 centers in 29 states and one Canadian province.
COVID-19 Impact
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak of a novel coronavirus (“COVID-19”) as a pandemic and recommended containment and mitigation measures worldwide. On March 13, 2020, the United States declared a National Public Health Emergency with respect to COVID-19. On March 16, 2020, we closed all of our centers based on orders and advisories from federal, state and local governmental authorities regarding COVID-19, during which time we did not draft or collect monthly access membership dues or recurring product charges from our members. We re-opened our first center on May 8, 2020 and continued to re-open our centers as state and local governmental authorities permitted.
As of December 31, 2021, all of our 151 centers were open. We are collecting monthly access membership dues and recurring product charges from active members associated with all of our centers. Whether we will need to close any of our centers, and the duration of any such future center closures that may occur, remains uncertain and is dependent on future developments that cannot be accurately predicted at this time.
Initial Public Offering
On October 12, 2021, Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. consummated its initial public offering (“IPO”) of 39.0 million shares of its common stock at a public offering price of $18.00 per share, resulting in total gross proceeds of $702.0 million, which was reduced by underwriting discounts and other offering and issuance expenses of $27.7 million, for net proceeds of $674.3 million. The shares of the Company's common stock began trading on the New York Stock Exchange (the “NYSE”) under the symbol “LTH” on October 7, 2021. A registration statement on Form S-1 relating to the offering of these securities was declared effective by the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) on October 6, 2021.
Upon consummation of the IPO, the 5.4 million shares of Series A Preferred Stock (as defined in Note 10, Stockholders’ Equity) then outstanding automatically converted into approximately 6.7 million shares of common stock of Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. Also upon consummation of the IPO, the 0.5 million shares of restricted Series A Preferred Stock then outstanding converted into approximately 0.6 million restricted shares of common stock of Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. For more information regarding the Series A Preferred Stock, see Note 10, Stockholders’ Equity.
On October 13, 2021, we used a portion of the $674.3 million of net proceeds we received in connection with the IPO to pay down $575.7 million (including a $5.7 million prepayment penalty) of our Term Loan Facility (as defined in Note 8, Debt). For more information regarding our Term Loan Facility, see Note 8, Debt.
On November 1, 2021, Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. consummated the sale of nearly 1.6 million additional shares of its common stock at the IPO price of $18.00 per share pursuant to the partial exercise by the underwriters of their over-allotment option, resulting in total gross proceeds of approximately $28.4 million, which was reduced by underwriting discounts and other offering expenses of $1.3 million, for net proceeds of $27.1 million. We intend to use these net proceeds, as well as the remaining portion of the net proceeds we received in connection with the IPO after the partial pay down of our Term Loan Facility, for general corporate purposes.
F-9
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Basis of Presentation
In December 2019, we formed both a Delaware limited liability company named Dallas-Montfort Holdings, LLC (“D-M Holdings”) and a Delaware limited liability company named Dallas-Montfort Property, LLC, which is a wholly owned subsidiary of D-M Holdings. Also in December 2019, we and an unrelated organization each became a holder of 50 % of the membership interests in D-M Holdings in exchange for a cash capital contribution of approximately $16.2 million. These capital contributions were made in connection with the acquisition of a property in Texas. See “Other Assets” within Note 2 below for additional information.
In 1999, we, together with two unrelated organizations, formed an Illinois limited liability company named Bloomingdale LIFE TIME Fitness L.L.C. (“Bloomingdale LLC”) for the purpose of constructing and operating a center in Bloomingdale, Illinois. We account for our interest in Bloomingdale LLC using the equity method. See “Other Assets” within Note 2 below for additional information.
2.Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Segment Reporting
Use of Estimates in the Preparation of Financial Statements
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
Leases
In February 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standard Update (“ASU”) 2016-02, “Leases,” as a new topic, ASC 842 (“ASC 842”). The new guidance supersedes previous lease accounting guidance and requires the recognition of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities for all leases with lease terms greater than one year. Effective January 1, 2019, we adopted ASC 842 using the “Comparatives Under 840 Option” approach to transition. Under this method, financial information related to periods prior to adoption are reported under the previous standard - ASC 840, “Leases.” The effects of adopting ASC 842 were recognized as a cumulative-effect adjustment to retained earnings as of January 1, 2019. We elected the package of practical expedients in transition for leases that commenced prior to January 1, 2019, including not needing to reassess whether existing contracts are (or contain) leases, whether the lease classification for existing leases would differ under ASC 842 or whether initial direct costs associated with any expired or existing leases qualify for capitalization under ASC 842. We did not elect the hindsight practical expedient in determining the lease term for existing leases as of January 1, 2019. The adoption of ASC 842 did not materially impact our results of operations and had no impact on our consolidated cash flows. Upon our adoption of ASC 842, we elected the short-term lease recognition exemption, whereby
F-10
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recognized on our consolidated balance sheet. In addition, for all lease agreements entered into or reassessed after January 1, 2019, we have elected not to separate (and allocate consideration to) lease and non-lease components. Instead, we have chosen to combine lease and non-lease components and account for them as a single lease component.
In April 2020, the FASB staff issued a question-and-answer document (the “Lease Modification Q&A”) that focused on the application of lease accounting guidance to lease concessions provided as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. Under ASC 842, economic relief that is agreed to or negotiated outside of the original lease agreement is typically considered a lease modification, in which case both the lessee and lessor are required to apply the respective lease modification framework, in order to determine how to account for the relief. However, if the lessee is entitled to the economic relief because of either contractual or legal rights that explicitly exist within the original lease agreement, the relief is to be accounted for outside of the lease modification framework. The Lease Modification Q&A established a different framework to account for certain lease concessions granted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. For lease concessions related to the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic that result in the total payments required by the modified contract being substantially the same as or less than the total payments required by the original contract, the Lease Modification Q&A allows an entity to make an accounting policy election to account for these lease concessions consistent with how those concessions would be accounted for under ASC 842 as though enforceable rights and obligations for those concessions exist within the original lease agreement (regardless of whether those enforceable rights and obligations for the concessions explicitly exist within the original lease agreement). Such accounting policy election is required to be applied consistently to leases with similar characteristics and similar circumstances.
Beginning in the second quarter of 2020, due to the disruption caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, we began negotiating lease concessions with many of our landlords. The concessions we were able to obtain from these landlords primarily consisted of full or partial rent payment deferrals, with scheduled repayments due at various dates through December 2021. Although these rent deferrals affect the timing of lease payments, the total amount of consideration we are required to pay under the terms of each of the renegotiated lease agreements is substantially the same as that required under the applicable original lease agreement. Consistent with the guidance provided in the Lease Modification Q&A, we made an accounting policy election to account for each of these lease concessions as if no changes had been made to the original lease agreement. Accordingly, as it relates to each of these leases, we continued to recognize rent expense each month during the deferral period in an amount equal to that which was recognized in accordance with the original lease agreement.
For more information regarding leases, see “—Leases” within this footnote as well as Note 9, Leases.
Other Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, “Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments.” ASU 2016-13 will replace today’s “incurred loss” approach with an “expected loss” model for instruments measured at amortized cost. The guidance requires companies to record an allowance for expected credit losses over the contractual term of certain financial assets, including trade receivables and contract assets. We adopted ASU 2016-13 as of January 1, 2020. The adoption of this guidance did not materially impact our results of operations and financial position and had no impact on our cash flows.
In December 2019, the FASB issued ASU 2019-12, “Simplifying the Accounting for Income Taxes (Topic 740).” This ASU simplifies the accounting for income taxes by eliminating certain exceptions to the guidance in ASC 740 related to the approach for intraperiod tax allocation, the methodology for calculating income taxes in an interim period and the recognition of deferred tax liabilities for outside basis differences. The standard also simplifies aspects of the accounting for franchise taxes and enacted changes in tax laws or rates and clarifies the accounting for transactions that result in a step-up in the tax basis of goodwill. This ASU was effective for us effective January 1, 2021. The adoption of this ASU did not have any impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In January 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-01, “Investments—Equity Securities (Topic 321), Investments—Equity Method and Joint Ventures (Topic 323), and Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815).” The amendments in this ASU clarify the interaction between the accounting for investments in equity securities, investment in equity method and certain derivatives instruments. The ASU is expected to reduce diversity in practice and increase comparability of the accounting for these interactions. The Company adopted the new standard effective January 1, 2021. The adoption of this ASU did not have any impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
F-11
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
New Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted
In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-04, “Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848): Facilitation of the Effects of Reference Rate Reform on Financial Reporting.” ASU 2020-04 provides optional expedient and exceptions for applying generally accepted accounting principles to contracts, hedging relationships, and other transactions affected by reference rate reform if certain criteria are met. In response to the concerns about structural risks of interbank offered rates (“IBORs”) and, particularly, the risk of cessation of the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”), regulators in several jurisdictions around the world have undertaken reference rate reform initiatives to identify alternative reference rates that are more observable, or transaction based and less susceptible to manipulation. The ASU provides companies with optional guidance to ease the potential accounting burden associated with transitioning away from reference rates that are expected to be discontinued. In January 2021, the FASB issued ASU 2021-01, “Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848): Scope,” which provides implementation guidance associated with ASU 2020-04 and clarifies certain optional expedients in Topic 848. This guidance in ASU 2020-04 is effective for all entities as of March 12, 2020 and may be applied through December 31, 2022. We are currently evaluating the effect the adoption of ASU 2020-04 may have on our consolidated financial statements.
In November 2021, the FASB issued ASU 2021-10, “Government Assistance (Topic 832): Disclosures by Business Entities about Government Assistance,” to increase the transparency of government assistance including the disclosure of the types of assistance an entity receives, an entity’s method of accounting for government assistance, and the effect of the assistance on an entity’s financial statements. The guidance in this ASU will be effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2021, with early adoption permitted. The amendments are to be applied prospectively to all transactions within the scope of the amendments that are reflected in financial statements at the date of initial application and new transactions that are entered into after the date of initial application or, retrospectively to those transactions. We are currently evaluating the effect the adoption of this ASU may have on our disclosures.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue is recognized when control of the promised goods or services is transferred to our customers, in an amount that reflects the transaction price consideration that we expect to receive in exchange for those goods or services. We defer the revenue associated with any unsatisfied performance obligation until the obligation is satisfied (i.e., when control of the product is transferred to the customer or a service has been completed).
Center Revenue
Center revenue consists of center membership and digital membership dues, enrollment fees and revenue generated within a center, which we refer to as in-center revenue. In-center revenue includes fees for personal training, aquatics, and kids programming, as well as sales of products at our cafés, and sales of products and services offered at our spas and tennis programs.
Revenue from product sales is generally recognized at the point of sale to the customer; however, revenue from our various service offerings received in advance of service delivery is deferred and subsequently recognized when the services are provided. Personal training revenue received in advance of training sessions, as well as the related sales commissions, are initially deferred and subsequently recognized when the sessions are delivered. Upon recognition, sales commissions associated with personal training sessions are included in Center operations in our consolidated statements of operations. Throughout the estimated redemption period associated with prepaid sessions, we also recognize personal training breakage revenue and the related commissions, using a method that is proportionate to the pattern of redemptions. We estimate breakage based on historical redemption patterns.
Generally, we receive a one-time enrollment fee at the time a member joins. The enrollment fees are nonrefundable after seven days. Enrollment fees and related direct expenses are deferred and recognized on a straight-line basis over an estimated average membership life, which is based on historical membership experience. If the direct expenses related to the enrollment fees exceed the enrollment fees for any center in a month, the amount of direct expenses in excess of the enrollment fees are expensed in the current period instead of deferred over the estimated average membership life.
F-12
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Other Revenue
Other revenue includes revenue generated outside of our centers, which are primarily media, athletic events and related services. Our media revenue includes our magazine, Experience Life®, and the related advertising revenue is recognized over the duration of the advertising placement. Our athletic events revenue includes endurance activities such as running, cycling and triathlons, and our related services revenue includes revenue from our race registration and timing businesses. Athletic event revenue and race registration revenue is recognized upon the completion of the event. Other revenue also includes revenue generated from our digital memberships and our Life Time Work locations.
For more information regarding revenue, see Note 6, Revenue.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Accounts Receivable
Inventories
Property and Equipment
Property, equipment and leasehold improvements are recorded at cost. Improvements are capitalized while repair and maintenance costs are charged to operations when incurred.
Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Leasehold improvements are amortized using the straight-line method over the shorter of the lease term or the estimated useful life of the improvement. Accelerated depreciation methods are used for tax reporting purposes.
Site development capitalization commences when acquisition of a particular property is deemed probable by management. Should a specific project be subsequently deemed not viable for construction, any capitalized costs related to that project are charged to operations at the time of that determination. Upon completion of a project, the site development costs are classified as property and depreciated over the useful life of the asset. We capitalize interest during the construction period of our centers and this capitalized interest is included in the cost of the building. Unpaid construction costs are included in Construction accounts payable on our consolidated balance sheets.
Business Combinations and Asset Acquisitions
F-13
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The temporary closure of our centers during 2020 due to COVID-19, as well as the continued uncertainty of the extent of the impact of COVID-19 on our business, is an impairment trigger. As a result of the impact of COVID-19 on our business during 2021 and 2020, and for other reasons during 2019, we determined that certain projects were no longer deemed viable for construction, and that the previously capitalized site development costs associated with these projects were impaired. During 2020, we also determined that the operating lease right-of-use assets and certain of the fixed assets associated with some of our leased centers and some of our ancillary businesses were also impaired. During 2019, we also determined that the operating lease right-of-use assets and fixed assets associated with the business operations of MR&S were impaired. Accordingly, we recognized impairment charges of $2.1 million, $37.8 million and $3.9 million associated with these long-lived assets during the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively, which are included in Other operating in our consolidated statements of operations.
Goodwill
Based upon our review and analysis, no 3.3 million goodwill impairment charge during the year ended December 31, 2019, which is included in Other operating in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019. For more information on goodwill, see Note 5, Goodwill and Intangibles.
Leases
F-14
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Lease Cost
Lease cost associated with operating leases and short-term leases is recognized on a straight-line basis from the date we take possession of the property through the end of the lease term. Finance lease right-of-use assets are amortized on a straight-line basis over the shorter of the estimated useful life of the underlying assets or the lease term. Interest associated with finance lease liabilities is recognized using the effective interest rate method. Variable lease payments not recognized in the measurement of operating and finance lease liabilities are expensed as incurred. For more information regarding lease cost included in our consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, see Note 9, Leases.
Operating Lease Right-of-Use Assets and Liabilities
Upon our adoption of ASC 842 effective on January 1, 2019, we recognized operating lease right-of-use assets and liabilities of $1,235.1 million and $1,300.5 million, respectively, on our consolidated balance sheet. The measurement of each operating lease liability we recognized upon our adoption of ASC 842 represents the present value of the remaining minimum lease payments over the remaining lease term, discounted using an appropriate incremental borrowing rate, determined as of the ASC 842 adoption date. The measurement of each operating lease liability associated with leases commencing during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 represents the present value of the full amount of the remaining lease payments over the remaining lease term, discounted using an appropriate incremental borrowing rate, determined as of the lease commencement date.
The measurement of each operating lease right-of-use asset we recognized upon our adoption of ASC 842 represents the related operating lease liability measurement increased by, as applicable, prepaid rent, leasehold right and favorable lease asset balances and decreased by, as applicable, unfavorable lease liability and deferred rent balances, as well as tenant allowances previously received or due from landlords. In addition, certain operating lease right-of-use assets were reduced by pre-tax impairment charges, which were recognized as a cumulative effect adjustment to beginning retained earnings. The measurement of each operating lease right-of-use asset associated with leases that commenced during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 represents the related operating lease liability measurement increased by, as applicable, prepaid rent and decreased by, as applicable, lease incentives.
For more information regarding the operating lease right-of-use assets and liabilities that are recognized on our December 31, 2021 and 2020 consolidated balance sheets, see Note 9, Leases.
Finance Lease Right-of-Use Assets and Liabilities
The measurement of each finance lease right-of-use asset we recognized upon our adoption of ASC 842 represents the aggregate of the carrying value of the related capital lease asset that we recognized under previous lease accounting rules. The measurement of each finance lease liability we recognized upon our adoption of ASC 842 represents the carrying value of the related capital lease obligation we recognized under previous lease accounting rules. The measurement of each finance lease right-of-use asset and liability associated with leases that commenced during the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 represents the present value of the full amount of the remaining payments associated with the arrangement (i.e., lease and non-lease components are combined and accounted for as a single lease component) over the remaining lease term, discounted using an appropriate incremental borrowing rate, determined as of the lease commencement date.
Finance lease right-of-use assets and liabilities are included in Prepaid expenses and other current assets and Accrued expenses and other current liabilities, respectively, on our consolidated balance sheets. For more information regarding the finance lease right-of-use assets and liabilities that are recognized on our December 31, 2021 and 2020 consolidated balance sheets, see Note 9, Leases.
Sale-Leaseback Transactions
Under lease accounting guidance in effect prior to our adoption of ASC 842, we assessed each sale-leaseback transaction to determine if each such transaction qualified as a sale or if it was required to be treated as a financing transaction. Prior to our adoption of ASC 842, a sale-leaseback transaction associated with one of our constructed centers qualified as a sale and we initially deferred a gain on that successful sale. Upon our adoption of ASC 842, this deferred gain was recognized as a cumulative pre-tax increase in beginning retained earnings.
F-15
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Prior to our adoption of ASC 842, we also had several sale-leaseback transactions that we were required to account for as financing transactions due to a prohibited form of continuing involvement with the applicable property. Upon our adoption of ASC 842, we reassessed each of these sale-leaseback transactions and determined that each of them qualified as a sale under the new lease guidance. As a result, financing accounting was discontinued, and we began accounting for each arrangement as an operating lease. Accordingly, the carrying value of the property and the related financing obligation associated with each of these arrangements was derecognized and an operating lease right-of-use asset and a related operating lease liability was recognized. Upon derecognition of the property and related financing obligations, we recognized a cumulative pre-tax increase in beginning retained earnings.
Since our adoption of ASC 842, we account for sale-leaseback transactions with unrelated third parties at fair value and we account for sale-leaseback transactions with related parties at their contractually stated terms. We typically engage third-party appraisal firms to assist us in determining the estimated fair value of each property sold. Property valuations generally involve the use of the cost approach, the sales comparison approach and the income approach, each of which requires management to make assumptions and to apply judgment to determine the estimated fair value of the property. These assumptions and judgments include, but are not limited to, replacement cost estimates, comparable sales adjustments, projected net operating income estimates and capitalization rates.
For more information regarding sale-leaseback transactions that occurred during the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, see Note 9, Leases.
Build-to-Suit Lease Arrangements
For some of our centers, we enter into build-to-suit lease arrangements related to the design and construction of a new center on the property. Under lease accounting guidance in effect prior to our adoption of ASC 842, due to our involvement with the property, we were considered the owner of some construction projects associated with build-to-suit lease arrangements. As a result, we were required to account for each of these arrangements as a financing transaction. Upon our adoption of ASC 842, we reassessed each of these build-to-suit lease arrangements and determined that we did not control any of the underlying assets that were either already constructed or under construction. As a result, financing accounting was discontinued, and we began accounting for each arrangement as an operating lease. Accordingly, the carrying value of the assets that we did not own and the related financing obligation associated with each of these arrangements was derecognized and an operating lease right-of-use asset and related operating lease liability was recognized.
Since our adoption of ASC 842, we evaluate build-to-suit lease arrangements by first determining whether or not we control the underlying asset being constructed prior to the commencement date of the lease. If we determine that we do not control the underlying asset during the construction period, we account for the arrangement as either an operating lease or a finance lease. If we determine that we control the underlying asset during the construction period, we initially account for the arrangement as a financing transaction. For each build-to-suit arrangement that we have entered into since our adoption of ASC 842, we have determined that we either: (1) do not control the underlying asset currently under construction as of December 31, 2021; or (2) we did not control the underlying constructed asset prior to the commencement date of the lease. Accordingly, we have accounted for each build-to-suit arrangement that we have entered into since our adoption of ASC 842 as an operating lease.
Intangible Assets
Intangible assets at December 31, 2021 and 2020 include trade names, member relationships, customer relationships and a facility license associated with an outdoor enthusiast and bicycling event. For more information on intangible assets, see Note 5, Goodwill and Intangibles.
Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
Intangible assets that are determined to have an indefinite useful life, such as trade names, are not amortized but instead tested for impairment at least annually. Our policy is to test indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment on October 1 of each year. We also evaluate these assets for impairment between annual tests if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of an indefinite-lived intangible asset below its carrying amount. If such a review should indicate that the carrying amount of indefinite-lived intangible assets is not recoverable, we reduce the carrying amount of such assets to fair value. Based upon our review and analysis, no
F-16
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Finite-Lived Intangible Assets
Finite-lived intangible assets are stated at cost, net of accumulated amortization, which is recorded on a straight-line or accelerated basis over the life of the asset. We review finite-lived intangible assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may not be recoverable. If such a review should indicate that the carrying amount of finite-lived intangible assets is not recoverable, we reduce the carrying amount of such assets to fair value. Based upon our review and analysis, no
Other Assets
Other assets at December 31, 2021 and 2020 primarily consists of our executive nonqualified plan assets, our investment in Bloomingdale LLC, our investment in D-M Holdings, rent deposits and unamortized debt issuance costs associated with the revolving portion of our senior secured credit facility.
Investment in Unconsolidated Subsidiary
In December 2019, we formed both D-M Holdings and a Delaware limited liability company named Dallas-Montfort Property, LLC, which is a wholly owned subsidiary of D-M Holdings. Also in December 2019, we and an unrelated organization each became a holder of 50 % of the membership interests in D-M Holdings in exchange for a cash capital contribution of approximately $16.2 million. These capital contributions were made in connection with the acquisition of a property in Texas. Other than incurring $0.4 million and $0.1 million of expenditures, which we have recognized as additional capital contributions during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively, there was no activity associated with D-M Holdings during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020. We account for our investment in D-M Holdings using the equity method. The capital contributions we have made in connection with our 50 % membership interest in D-M Holdings are reported in Acquisitions, net of cash acquired within the investing section in our consolidated cash flow statements.
Debt Discounts and Issuance Costs
Fair Value Measurements
The accounting guidance establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expanded disclosures about fair value measurements. The guidance applies to all assets and liabilities that are measured and reported on a fair value basis. This enables the reader of the financial statements to assess the inputs used to develop those measurements by establishing a hierarchy for ranking the quality and reliability of the information used to determine fair values. The guidance requires that each asset and liability carried at fair value be classified into one of the following categories:
Level 1: Quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2: Observable market-based inputs or unobservable inputs that are corroborated by market data.
Level 3: Unobservable inputs that are not corroborated by market data.
The carrying amounts related to cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, income tax receivable, accounts payable and accrued liabilities approximate fair value.
Fair Value Measurements on a Recurring Basis. We had no material remeasurements of such assets or liabilities to fair value during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020.
Financial Assets and Liabilities. At December 31, 2021, the fair value of our outstanding Term Loan Facility, Secured Notes and Unsecured Notes was approximately $277.0 million, $957.4 million and $494.0 million, respectively. The carrying amount of our outstanding mortgage notes at December 31, 2021 approximates fair value. At December 31, 2020, the carrying amount
F-17
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Marketing Expenses
Litigation
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the differences between the financial statements and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
We record net deferred tax assets to the extent we believe these assets will more likely than not be realized. In making such determination, we consider all available positive and negative evidence, including scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies and recent financial operations. In the event we were to determine that we would be able to realize our deferred income tax assets in the future in excess of their net recorded amount, we would make an adjustment to the valuation allowance, which would reduce the provision for income taxes.
Our income tax returns are periodically audited by U.S. federal, state and local and Canadian tax authorities. At any given time, multiple tax years may be subject to audit by various tax authorities. In evaluating the exposures associated with our various tax filing positions, we may record a liability for such exposures. We recognize, measure, present and disclose a liability for unrecognized tax benefits related to certain tax positions that we have taken or expect to take in our income tax returns. We recognize a tax position when it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including
F-18
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Share-Based Compensation
(Loss) Earnings per Share
Changes in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss
3.Supplemental Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Information
Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets
Prepaid expenses and other current assets consisted of the following:
| December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||
Property held for sale |
$ | $ | |||||||||
Construction contract receivables |
|||||||||||
Deferred membership origination costs |
|||||||||||
Prepaid expenses |
|||||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
$ | $ | |||||||||
F-19
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Of the $49.7 million balance in Property held for sale at December 31, 2020, $43.7 million represents the carrying value of a property that was associated with a sale-leaseback agreement that we entered into with an unrelated third party on December 16, 2020, and the remaining $6.0 million represents excess land purchased as part of our original center site acquisitions. This sale-leaseback transaction closed in March 2021. If property held for sale is currently under contract for sale, the cost is reflected as a current asset and is included in Prepaid expenses and other current assets on our consolidated balance sheet. Property held for sale is stated at the lower of cost or fair value less estimated costs to sell. Property is not depreciated during the period in which it is classified as held for sale.
For more information regarding sale-leaseback transactions with unrelated third parties that were consummated during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, see Note 9, Leases.
Accrued Expenses and Other Current Liabilities
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities consisted of the following:
| December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||
Real estate taxes |
$ | $ | |||||||||
Accrued interest |
|||||||||||
Payroll liabilities |
|||||||||||
Utilities |
|||||||||||
Self-insurance accruals |
|||||||||||
Corporate accruals |
|||||||||||
Current maturities of finance lease liabilities |
|||||||||||
Other |
|||||||||||
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities |
$ | $ | |||||||||
Supplemental Cash Flow Information
Decreases (increases) in operating assets and increases (decreases) in operating liabilities are as follows:
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable | $ | ( |
$ | $ | ( |
||||||||||||
| Center operating supplies and inventories | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | ( |
||||||||||||||||
| Income tax receivable | |||||||||||||||||
| Other assets | |||||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable | ( |
||||||||||||||||
| Accrued expenses | ( |
||||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue | ( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
| Other liabilities | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
F-20
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Additional supplemental cash flow information is as follows:
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Net cash received from income tax refunds, net of taxes paid |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
|||||||||||
Cash payments for interest, net of capitalized interest |
|||||||||||||||||
Capitalized interest |
|||||||||||||||||
Issuance of Series A Preferred Stock in connection with the extinguishment of secured loan—related parties
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Conversion of Series A Preferred Stock to common stock | |||||||||||||||||
See Note 9, Leases for supplemental cash flow information associated with our lease arrangements for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019.
4.Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, net consisted of the following:
| Depreciable | December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| Lives | 2021 | 2020 | |||||||||||||||
Land |
$ | $ | |||||||||||||||
Buildings and related fixtures |
|||||||||||||||||
Leasehold improvements |
|||||||||||||||||
Construction in progress |
|||||||||||||||||
Equipment and other |
|||||||||||||||||
Property and equipment, gross |
|||||||||||||||||
Less accumulated depreciation |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Property and equipment, net |
$ | $ | |||||||||||||||
Included in the construction in progress balances are site development costs which consist of legal, engineering, architectural, environmental, feasibility and other direct expenditures incurred for certain new projects.
Equipment and other includes exercise equipment, capitalized software, computers, audio visual equipment, furniture and fixtures, decor and signage, as well as café, spa, playground and laundry equipment.
Depreciation expense, which is included in Depreciation and amortization in our consolidated statements of operations, for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 was $232.4 million, $241.6 million, and $210.3 million, respectively.
F-21
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
5.Goodwill and Intangibles
Goodwill
The goodwill balance was $1,233.2
Intangible assets consisted of the following:
| December 31, 2021 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gross | Accumulated Amortization |
Net | |||||||||||||||
Intangible Assets: |
|||||||||||||||||
Trade name |
$ | $ | — | $ | |||||||||||||
Member relationships |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Other |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Total intangible assets |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | |||||||||||||
| December 31, 2020 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gross | Accumulated Amortization |
Net | |||||||||||||||
Intangible Assets: |
|||||||||||||||||
Trade name |
$ | $ | — | $ | |||||||||||||
Member relationships |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Other |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Total intangible assets |
$ | $ | ( |
$ | |||||||||||||
Other intangible assets at December 31, 2021 includes a facility license as well as trade names and customer relationships associated with our race registration and timing businesses. Other intangible assets at December 31, 2020 consists solely of the trade names and customer relationships associated with our race registration and timing businesses.
During the year ended December 31, 2021, we acquired a facility license associated with an outdoor enthusiast and bicycling event for approximately $10.2 million, of which approximately $1.1 million had yet to be paid as of December 31, 2021 and is included in Other liabilities on our consolidated balance sheets. This license expires in April 2031. The transaction was accounted for as an asset acquisition. The facility license costs are being amortized on a straight-line basis over its estimated useful life of 9.8 years.
Amortization expense associated with intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 was $1.3 million, $3.8 million and $7.9 million, respectively. Amortization of intangible assets is included in Depreciation and amortization in our consolidated statements of operations.
As of December 31, 2021, the expected remaining amortization associated with intangible assets for the next five years was as follows:
| 2022 | $ | ||||
| 2023 | |||||
| 2024 | |||||
| 2025 | |||||
| 2026 | |||||
F-22
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
6.Revenue
Revenue associated with our membership dues, enrollment fees, and certain services from our in-center businesses is recognized over time as earned. Revenue associated with products and services offered in our cafes and spas, as well as through e-commerce, is recognized at a point in time. The following is a summary of revenue, by major revenue stream, that we recognized during the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019:
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Membership dues and enrollment fees |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
In-center revenue |
|||||||||||||||||
Total center revenue |
|||||||||||||||||
Other revenue |
|||||||||||||||||
Total revenue |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
The timing associated with the revenue we recognized during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 is as follows:
For the Year Ended December 31, 2021 |
For the Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Center Revenue |
Other Revenue |
Total Revenue |
Center Revenue |
Other Revenue |
Total Revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Goods and services transferred over time |
$ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Goods and services transferred at a point in time |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total revenue |
$ | $ | $ | $ | $ | $ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Contract liabilities represent payments or consideration received in advance for goods or services that the Company has not yet transferred to the customer. Contract liabilities consist primarily of deferred revenue for fees collected in advance for membership dues, enrollment fees, personal training and other center services offerings, as well as our media and athletic events. Contract liabilities at December 31, 2021 and 2020 were $35.9 million and $46.1 million, respectively.
Contract liabilities that will be recognized within one year are classified as deferred revenue in our consolidated balance sheets. Deferred revenue at December 31, 2021 and 2020 was $33.9 million and $42.3 million, respectively, and consists primarily of prepaid membership dues, personal training and other in-center services, and enrollment fees. The $8.4 million decrease was primarily driven by the usage of membership dues credits that we gave to members during 2020 as a result of center closures. Also, deferred revenue associated with enrollment fees and center services offerings decreased as a result of our center closures in 2020.
Contract liabilities that will be recognized in a future period greater than one year are classified as a component of Other liabilities in our consolidated balance sheets. Long-term contract liabilities at December 31, 2021 and 2020 were $2.0 million and $3.8 million, respectively, and consist primarily of deferred enrollment fees. The $1.8 million decrease was primarily related to fewer enrollment fees due to center closures during 2020.
F-23
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
7.Income Taxes
The (benefit from) provision for income taxes is comprised of:
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Current tax (benefit) expense |
|||||||||||||||||
Federal |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
State and local |
|||||||||||||||||
Foreign |
|||||||||||||||||
Total current tax (benefit) expense |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Deferred tax (benefit) expense |
|||||||||||||||||
Federal |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
State and local |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
Foreign |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Total deferred tax (benefit) expense |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Non-current benefit |
( |
( |
( |
||||||||||||||
(Benefit from) provision for income taxes |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
The amount of deferred tax (benefit) expense differs from the change in the year-end deferred tax balances due to the tax effect of other comprehensive income, additional paid-in capital items or change in state effective tax rates and foreign currency exchange rates.
On March 27, 2020, Congress enacted the CARES Act to provide certain relief as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. The CARES Act, among other things, includes provisions relating to refundable payroll tax credits for employee retention, deferment of the employer’s portion of social security tax payments, net operating loss carrybacks, alternative minimum tax credit refunds, modifications to the net interest deduction limitations and technical corrections to tax depreciation methods for qualified improvement property. An income tax benefit of $13.4 million was recognized as a result of the favorable federal tax rate differential from the net operating loss carrybacks under the CARES Act. The favorable federal tax rate differential is due to net operating losses generated in tax years with a federal tax rate of 21% whereas the losses were carried back to tax years with a federal tax rate of 35%.
The reconciliation between our effective tax rate on income before income taxes and the statutory tax rate is as follows:
For the Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Income tax (benefit) provision at federal statutory rate |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
State and local income taxes, net of federal tax benefit |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Goodwill impairment |
|||||||||||||||||
CARES Act |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Loss on debt extinguishment |
|||||||||||||||||
Change in valuation allowance |
|||||||||||||||||
Other, net |
|||||||||||||||||
(Benefit from) provision for income taxes |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
F-24
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Deferred income taxes are the result of provisions of the tax laws that either require or permit certain items of income or expense to be reported for tax purposes in different periods than they are reported for financial reporting. The tax effect of temporary differences that gives rise to the net deferred tax liability are as follows:
| December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||
Deferred tax assets: |
|||||||||||
Lease-related liabilities |
$ | $ | |||||||||
Accrued equity compensation |
|||||||||||
Accrued expenses |
|||||||||||
Deferred revenue |
|||||||||||
Net operating loss |
|||||||||||
Business interest |
|||||||||||
Other |
|||||||||||
Valuation allowance |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Total deferred tax assets |
|||||||||||
Deferred tax liabilities: |
|||||||||||
Property and equipment |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Intangibles |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Operating and finance lease right-of-use assets |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Partnership interest |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Debt issuance costs |
( |
||||||||||
Prepaid expenses |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Costs related to deferred revenue |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Other |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Total deferred tax liabilities |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Net deferred tax liability |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
|||||||
We recognize a tax position when it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including resolutions of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits. We adjust our liability for unrecognized tax benefits in the period in which an uncertain tax position is effectively settled, that statute of limitations expires for the relevant taxing authority to examine the tax position or when more information becomes available. Unrecognized tax benefits were not significant in any of the periods presented.
We are subject to taxation in the U.S., Canada and various states. Our tax years 2020, 2019, and 2018 are subject to examination by the tax authorities. With few exceptions, we are no longer subject to U.S. federal, state or local examinations by tax authorities for years before 2018.
As of December 31, 2021, we had a federal income tax net operating loss carryforward related to our U.S. operations of approximately $554.4 million ($116.4 million tax effected), of which approximately $75.8 million ($15.9 million tax effected) expires in 2038 and approximately $478.6 million ($100.5 million tax effected) can be carried forward indefinitely. As of December 31, 2021, we also had state net operating loss carryforwards totaling approximately $436.1 million ($25.4 million tax effected), of which approximately $356.4 million ($19.8 million tax effected) expires between 2026 and 2042 and approximately $79.7 million ($5.6 million tax effected) can be carried forward indefinitely. As it relates to our Canada operations, we had an income tax net operating loss carryforward of approximately $21.4 million ($5.7 million tax effected) as of December 31, 2021, which is subject to expiration between tax years 2032 and 2042.
As of December 31, 2020, we had a federal income tax net operating loss carryforward related to our U.S. operations of approximately $481.7 million ($101.1 million tax effected), of which approximately $75.8 million ($15.9 million tax effected) expires in 2038 and approximately $405.9 million ($85.2 million tax effected) can be carried forward indefinitely. As of December 31, 2020, we also had state net operating loss carryforwards totaling approximately $311.1 million ($18.1 million tax effected), of which approximately $242.0 million ($15.1 million tax effected) expires between 2026 and 2041 and
F-25
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
approximately $69.1 million ($3.0 million tax effected) can be carried forward indefinitely. As it relates to our Canada operations, we had an income tax net operating loss carryforward of approximately $23.0 million ($6.1 million tax effected) as of December 31, 2020, which was subject to expiration between tax years 2032 and 2041.
As of December 31, 2021, we had a business interest carryforward of approximately $133.5 million ($34.2 million tax effected) that can be carried forward indefinitely. As of December 31, 2021, we also had a general business credit carryforward of approximately $2.0 million that can be used to offset future U.S. federal tax liabilities and expires between tax years 2036 and 2041.
As of December 31, 2020, we had a business interest carryforward of approximately $3.1 million ($0.8 million tax effected) that can be carried forward indefinitely. As of December 31, 2020, we also had a general business credit carryforward of approximately $1.6 million that can be used to offset future U.S. federal tax liabilities and expires between tax years 2036 and 2040.
We considered all available positive and negative evidence, including scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies and recent financial operations to determine the extent to which we believe net deferred tax assets will more likely than not be realized. Based on this assessment, as of December 31, 2021, a valuation allowance of $20.4 million has been recorded to reduce the deferred tax asset associated with the state net operating loss carryforwards and other deferred tax assets. As of December 31, 2021, a valuation allowance of approximately $8.4 million has been recorded to reduce the deferred tax asset associated with the Canadian net operating loss carryforward and other deferred tax assets. As of December 31, 2021, we had a foreign tax credit carryforward of approximately $1.1 million that can be used to offset future U.S. federal tax liabilities on foreign-sourced income. We project that our foreign sourced income will not be sufficient to fully utilize the credit carryforward. As a result, a valuation allowance of $1.1 million has been recorded as of December 31, 2021 to reduce the deferred tax asset associated with the foreign tax credit carryforward.
As of December 31, 2020, a valuation allowance of $7.2 million was recorded to reduce the deferred tax asset associated with the state net operating loss carryforwards and other deferred tax assets. As of December 31, 2020, a valuation allowance of approximately $4.1 million was recorded to reduce the deferred tax asset associated with the Canadian net operating loss carryforward and other deferred tax assets. As of December 31, 2020, we had a foreign tax credit carryforward of approximately $1.7 million that can be used to offset future U.S. federal tax liabilities on foreign-sourced income. We project that our foreign sourced income will not be sufficient to fully utilize the credit carryforward. As a result, a valuation allowance of $1.7 million has been recorded as of December 31, 2020, in order to reduce the deferred tax asset associated with the foreign tax credit carryforward.
We consider the earnings of certain non-U.S. subsidiaries to be indefinitely invested outside the United States on the basis of estimates that future domestic cash generation will be sufficient to meet future domestic cash needs and our specific plans for reinvestment of those subsidiary earnings. We have not recorded a deferred tax liability related to the U.S. federal and state income taxes and foreign withholding taxes on undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries indefinitely invested outside the United States.
F-26
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
8.Debt
Debt consisted of the following:
| December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||
| Term Loan Facility, maturing December 2024 | $ | $ | |||||||||
| Prior Term Loan Facility, retired January 2021 | |||||||||||
| Prior Revolving Credit Facility, retired January 2021 | |||||||||||
| Secured Notes, maturing January 2026 | |||||||||||
| Unsecured Notes, maturing April 2026 | |||||||||||
| 2023 Notes, retired February 2021 | |||||||||||
| Secured loan—related parties, retired January 2021 | |||||||||||
| Mortgage notes, various maturities | |||||||||||
| Other debt | |||||||||||
| Fair value adjustment | |||||||||||
Total debt |
|||||||||||
Less unamortized debt discounts and issuance costs |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Total debt less unamortized debt discounts and issuance costs |
|||||||||||
Less current maturities |
( |
( |
|||||||||
Long-term debt, less current maturities |
$ | $ | |||||||||
Refinancing Transactions
During the year ended December 31, 2021, Life Time, Inc., an indirect, wholly-owned subsidiary of Life Time Group Holdings, Inc., as the borrower and issuer, as applicable, together with certain other wholly-owned subsidiaries: (i) refinanced in full the then outstanding balances associated with our previous term loan facility (the “Prior Term Loan Facility”) and our prior revolving credit facility (the “Prior Revolving Credit Facility”) through net cash proceeds Life Time, Inc. received from a new term loan facility (the “Term Loan Facility”) that matures in December 2024 as well as the issuance of senior secured notes (the “Secured Notes”) that mature in January 2026; (ii) refinanced in full our previous senior unsecured notes (the “2023 Notes”) through proceeds Life Time, Inc. received from the issuance of new senior unsecured notes (the “Unsecured Notes”) that mature in April 2026; (iii) converted our then existing related party secured loan into Series A Preferred Stock; and (iv) increased the commitments under the revolving portion of our senior secured credit facility (the “Revolving Credit Facility” and together with the Term Loan Facility, the “Credit Facilities”) and extended their maturity.
Senior Secured Credit Facility
In June 2015, Life Time, Inc. and certain of our other wholly-owned subsidiaries entered into a senior secured credit facility with a group of lenders led by Deutsche Bank AG as the administrative agent. On January 22, 2021, Life Time, Inc. and certain of our other wholly-owned subsidiaries entered into an eighth amendment to the credit agreement governing our senior secured credit agreement (the “Credit Agreement”). Pursuant to such eighth amendment to the Credit Agreement, Life Time, Inc. and such other subsidiaries: (i) entered into the Term Loan Facility and incurred new term loans in an aggregate principal amount of $850.0 million; (ii) paid off the then outstanding balances associated with the Prior Term Loan Facility and the Prior Revolving Credit Facility; and (iii) extended the maturity of $325.2 million of the $357.9 million Prior Revolving Credit Facility to September 2024. On December 2, 2021, Life Time, Inc. and certain of our other wholly-owned subsidiaries entered into a ninth amendment to the Credit Agreement. Pursuant to such ninth amendment, Life Time, Inc. and such other subsidiaries increased the commitments under the Revolving Credit Facility to $475.0 million and extended the maturity of the Revolving Credit Facility to December 2, 2026, except that the maturity will be: (a) September 22, 2024 if we have not refinanced or amended in a manner set forth in such amendment the Term Loan Facility by such date; (b) October 16, 2025 if we have at least $100.0
F-27
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
million remaining outstanding on the Secured Notes on such date; and (c) January 14, 2026 if we have at least $100.0 million remaining outstanding on the Unsecured Notes on such date.
Upon the exercise of an accordion feature and subject to certain conditions, borrowings under the Credit Facilities may be increased subject, in certain cases, to meeting a first lien net leverage ratio. The Credit Facilities are secured by a first priority lien (on a pari-passu basis with the Secured Notes described below) on substantially all of our assets.
The net cash proceeds Life Time, Inc. received under the Term Loan Facility, as well as from the Secured Notes, were used to: (i) refinance in full the then outstanding balances associated with the Prior Term Loan Facility and the Prior Revolving Credit Facility (details of which are described under “—Term Loan Facility” and “—Revolving Credit Facility,” respectively); (ii) pay debt issuance and original issue discount costs associated with each of these financing transactions (details of which are described in “—Debt Discounts and Issuance Costs” below); and (iii) strengthen our balance sheet by adding to our cash position.
Term Loan Facility
At both December 31, 2020 and January 22, 2021 (the effective date of the refinancing), the Prior Term Loan Facility balance was $1,471.6 850.0 million, of which $507.6 million represents cash proceeds received and $342.4 million represents the cashless portion of the Prior Term Loan Facility that was rolled over into the Term Loan Facility. On January 22, 2021, we used the net cash proceeds received from the Term Loan Facility, as well as a portion of the net proceeds received from the Secured Notes, to pay off the remaining $1,129.2 million Prior Term Loan Facility balance.
The $850.0 million Term Loan Facility, which matures in December 2024, initially amortized at 0.25 % quarterly, which required us to make three mandatory quarterly principal repayments of approximately $2.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2021. On October 13, 2021, we used a portion of net proceeds we received in connection with the IPO to pay down $575.7 million (including a $5.7 million prepayment penalty) of our Term Loan Facility. As a result of the pay down, we are no longer required to make quarterly principal payments on the Term Loan Facility prior to its maturity. At December 31, 2021, the Term Loan Facility loan balance was $273.6 million, with interest due at intervals ranging from 30 to 180 days at interest rates ranging from LIBOR plus 4.75 % or base rate plus 3.75 %, in either case subject to a 1.00 % rate floor.
Revolving Credit Facility
The Prior Revolving Credit Facility provided for a $357.9 million revolver. At December 31, 2020 and January 22, 2021 (the effective date of the refinancing), the Prior Revolving Credit Facility balance was $94.0 million and $109.0 million, respectively. Under the Revolving Credit Facility, we extended the maturity of $325.2 million of the $357.9 million revolver to September 2024. The remaining $32.7 million non-extended portion of our Revolving Credit Facility was set to mature in August 2022. On January 22, 2021, we used a portion of the net proceeds we received from the Secured Notes to pay off the then outstanding $109.0 million balance under the Prior Revolving Credit Facility.
On December 2, 2021, we increased the commitments under the Revolving Credit Facility to $475.0 million and extended the maturity to December 2026, as detailed above under “—Senior Secured Credit Facility.”
At December 31, 2021, there were no outstanding borrowings on the Revolving Credit Facility and there were $33.5 million of outstanding letters of credit, resulting in total revolver availability, subject to a $100.0 million minimum liquidity requirement that ended on December 31, 2021 (see “—Debt Covenants” below), of $341.5 million, which was available at intervals ranging from 30 to 180 days at interest rates ranging from LIBOR plus 4.25 % or base rate plus 3.25 %.
The weighted average interest rate and debt outstanding under the Revolving Credit Facility for the year ended December 31, 2021 was 3.85 % and $9.3 million, respectively. The highest month-end balance during the year was $40.0 million.
Secured Notes
On January 22, 2021, Life Time, Inc. issued Secured Notes in an aggregate principal amount of $925.0 million. These notes mature in January 2026 and interest only payments are due semi-annually in arrears at 5.75 %. Life Time, Inc. has the option to call the Secured Notes, in whole or in part, on one or more occasions, beginning on January 15, 2023, subject to the payment of a redemption price that includes a call premium that varies depending on the year of redemption. In addition, at any time prior to January 15, 2023, Life Time, Inc. may redeem up to 40.00 % of the aggregate principal amount of the Secured Notes
F-28
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
outstanding with the net proceeds of certain equity offerings by us at a redemption price equal to 105.75 % of the principal amount of the Secured Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the redemption date. The Secured Notes and the related guarantees are our senior secured obligations and are secured on a first-priority basis by security interests in substantially all of our assets.
Unsecured Notes
In June 2015, Life Time, Inc. issued the 2023 Notes in the original principal amount of $450.0 million, which were scheduled to mature in June 2023. At both December 31, 2020 and February 5, 2021, $450.0 475.0 million. The Unsecured Notes mature in April 2026 and interest only payments are due semi-annually in arrears at 8.00 %. The proceeds from the Unsecured Notes were used to: (i) redeem in full the then outstanding 2023 Notes balance of $450.0 million and satisfy and discharge our obligations thereunder; (ii) pay debt issuance costs associated with the issuance of the Unsecured Notes (details of which are described in “—Debt Discounts and Issuance Costs” below); and (iii) strengthen our balance sheet by adding to our cash position.
Life Time, Inc. has the option to redeem the Unsecured Notes, in whole or in part, on one or more occasions, beginning on February 1, 2023, subject to the payment of a redemption price that includes a call premium that varies depending on the year of redemption. In addition, at any time prior to February 1, 2023, Life Time, Inc. may redeem up to 40.00 % of the aggregate principal amount of the Unsecured Notes outstanding with the net proceeds of certain equity offerings by us at a redemption price equal to 108.00 % of the principal amount of the Unsecured Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but not including, the redemption date. The Unsecured Notes and the related guarantees are our general senior unsecured obligations and will rank equally in right of payment with all of our existing and future senior indebtedness without giving effect to collateral arrangements.
Secured Loan - Related Parties
On June 24, 2020, we closed on an approximate $101.5 million secured loan (the “Related Party Secured Loan”) from an investor group that was comprised solely of our stockholders or their affiliates. The Related Party Secured Loan was scheduled to mature in June 2021. During the year ended December 31, 2021, interest expense of approximately $0.7 million was recognized on this secured loan.
On January 11, 2021, Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries and the investor group associated with the Related Party Secured Loan (or their assignees) entered into a contribution agreement (the “Contribution Agreement”) pursuant to which we converted the total amount of outstanding principal and accrued interest (up though and including January 22, 2021) under the Related Party Secured Loan into Series A Preferred Stock. Effective January 22, 2021, the total outstanding principal and accrued interest balance of approximately $108.6 million was conveyed by the investor group to us and we issued, on a dollar-for-dollar basis, to the investor group approximately 5.4 million shares of Series A Preferred Stock with an estimated fair value of $149.6 million. Because the fair value of the Series A Preferred Stock that was issued exceeded the carrying value of the outstanding principal and accrued interest balance associated with the Related Party Secured Loan that was extinguished, we recognized a $41.0 million debt extinguishment loss, which is included in Interest expense, net of interest income in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2021. Upon the consummation of the IPO on October 12, 2021, the 5.4 million then outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock automatically converted into 6.7 million shares of the Company’s common stock. For more information regarding the Series A Preferred Stock that was issued in connection with this transaction, as well as the subsequent conversion to the Company’s common stock, see Note 10, Stockholders’ Equity.
Mortgage Notes
Certain of our subsidiaries have entered into mortgage facilities with various financial institutions (collectively, the “Mortgage Notes”), which are collateralized by certain of our related real estate and buildings, including one of our corporate headquarters properties. The Mortgage Notes have varying maturity dates from March 2023 through August 2027 and carried a weighted average interest rate of 4.70 % and 4.68 % at December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively. Payments of principal and interest on each of the Mortgage Notes are payable monthly on the first business day of each month. The Mortgage Notes contain customary affirmative covenants, including but not limited to, payment of property taxes, granting of lender access to inspect the properties, maintenance of the properties, providing financial statements, providing estoppel certificates and lender consent to leases. The Mortgage Notes also contain various customary negative covenants, including, but not limited to, restrictions on
F-29
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
transferring the property, change in control of the borrower and changing the borrower’s business or principal place of business. As of December 31, 2021, we were either in compliance in all material respects with the covenants associated with the Mortgage Notes or the covenants were not applicable.
Debt Discounts and Issuance Costs
In connection with the Term Loan Facility, Secured Notes and Unsecured Notes, we incurred debt discounts and issuance costs totaling approximately $44.4 million during the year ended December 31, 2021. Unamortized debt discounts and issuance costs of $25.9 million and $19.1 million are included in Long-term debt, net of current portion on our consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2021 and 2020.
During the year ended December 31, 2021, in connection with the pay down of our Term Loan Facility, as well as the extinguishment of the Prior Term Loan Facility, the 2023 Notes and the Related Party Secured Loan, we recognized $28.6 million of debt discount and issuance cost write-offs, which are included in Interest expense, net of interest income in our consolidated statement of operations.
In connection with both the Revolving Credit Facility and the Prior Revolving Credit Facility, we have incurred total debt issuance costs of $9.8 million, of which $3.2 million were incurred during the year ended December 31, 2021. As of the January 22, 2021 effective date associated with the Credit Facilities, the borrowing capacity (i.e., the product of the remaining term and the maximum available credit) associated with the Revolving Credit Facility was greater than the borrowing capacity associated with the Prior Revolving Credit Facility. Also, as of the effective date associated with the ninth amendment to the Credit Agreement (as described above under “—Senior Secured Credit Facility”), the borrowing capacity associated with the Revolving Credit Facility was greater than that in effect prior to the amendment. Accordingly, the debt issuance costs incurred in connection with the Revolving Credit Facility, as well as the unamortized portion of the debt issuance costs associated with the Prior Revolving Credit Facility, will be amortized over the remaining term of the Revolving Credit Facility. Unamortized revolver-related debt issuance costs of $4.0 million and $1.3 million, respectively, are included in Other assets on our consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
Debt Covenants
We are required to comply with certain affirmative and restrictive covenants under our Credit Facilities, Secured Notes and Unsecured Notes. We are also required to comply with a first lien net leverage ratio covenant under the Revolving Credit Facility. However, the Credit Agreement includes a covenant modification period (the “Covenant Modification Period”) that ended on January 1, 2022. During the Covenant Modification Period, we were not obligated to comply with the first lien net leverage ratio covenant, however, we were required to maintain a minimum liquidity balance of $100.0 million.
Effective as of the end of the first fiscal quarter following the Covenant Modification Period and continuing throughout the remaining term of our Revolving Credit Facility, we will be required to maintain a first lien net leverage ratio, if 30.00 % or more of the Revolving Credit Facility commitments are outstanding shortly after the end of any fiscal quarter (excluding all cash collateralized undrawn letters of credit and other undrawn letters of credit up to $20.0 million). During the first three quarterly test periods following the Covenant Modification Period, certain financial measures used in the calculation of the first lien net leverage ratio will be calculated on a pro forma basis by annualizing the respective financial measures recognized during those test periods.
As of December 31, 2021, we were either in compliance in all material respects with the covenants under the Credit Facilities or the covenants were not applicable.
F-30
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Future Maturities of Long-Term Debt
Aggregate annual future maturities of long-term debt, excluding unamortized issuance costs and fair value adjustments, at December 31, 2021 were as follows:
| 2022 | $ | ||||
| 2023 | |||||
| 2024 | |||||
| 2025 | |||||
| 2026 | |||||
| Thereafter | |||||
Total future maturities of long-term debt |
$ | ||||
9.Leases
Lease Cost
Lease cost included in our consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 consisted of the following:
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 |
Classification in Consolidated
Statement of Operations
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Lease cost: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating lease cost |
$ | $ | $ | Rent | |||||||||||||||||||
Short-term lease cost |
Rent | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Variable lease cost |
Rent | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Finance lease cost: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Amortization of right-of-use assets |
Depreciation and amortization | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest on lease liabilities |
Interest expense, net of interest income | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total lease cost |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||
F-31
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Operating and Finance Lease Right-of-Use Assets and Liabilities
Operating and finance lease right-of-use assets and lease liabilities were as follows:
| December 31, |
Classification on Consolidated
Balance Sheet
|
||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||||||||
Lease right-of-use assets: |
|||||||||||||||||
Operating leases |
$ | $ | Operating lease right-of-use assets | ||||||||||||||
Finance leases (1)
|
|||||||||||||||||
Total lease right-of-use assets |
$ | $ | |||||||||||||||
Lease liabilities: |
|||||||||||||||||
Current |
|||||||||||||||||
Operating leases |
$ | $ | Current maturities of operating lease liabilities | ||||||||||||||
Finance leases |
|||||||||||||||||
Noncurrent |
|||||||||||||||||
Operating leases |
Operating lease liabilities, net of current portion | ||||||||||||||||
Finance leases |
|||||||||||||||||
Total lease liabilities |
$ | $ | |||||||||||||||
(1)Finance lease right-of-use assets were reported net of accumulated amortization of $2.4 million and $1.2 million at December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
Operating Lease Right-of-Use Assets and Liabilities Associated with Unrelated Third-Party Leases
New Leases and Modifications of Existing Leases
In connection with leases with unrelated third parties that commenced during the year ended December 31, 2021, we recognized operating lease right-of-use assets and lease liabilities of $220.2 million and $210.5 million, respectively, on our consolidated balance sheet. In connection with modified leases that were remeasured during the year ended December 31, 2021, we recognized a net decrease in both operating lease right-of-use assets and lease liabilities of $6.3
In connection with leases with unrelated third parties that commenced during the year ended December 31, 2020, we recognized operating lease right-of-use assets and lease liabilities of $241.3 million and $196.8 million, respectively, on our consolidated balance sheet. In connection with modified leases that were remeasured during the year ended December 31, 2020, we recognized a net increase in operating lease right-of-use assets and lease liabilities of $32.1 million and $33.0 million, respectively, on our consolidated balance sheet.
Impairment of Right-of-Use Assets
During the year ended December 31, 2020, we determined that the operating lease right-of-use assets associated with some of our leased centers and some of our ancillary businesses were impaired. Accordingly, we recognized $2.0 million of impairment charges associated with these right-of-use assets, which are included in Other operating in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2020. During the year ended December 31, 2019, we determined that the operating lease right-of-use assets associated with the business operations of MR&S were impaired. Accordingly, we recognized $1.3 million of impairment charges associated with these right-of-use assets, which are included in Other operating in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019.
For more information regarding impairment charges associated with our long-lived assets, see Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies.
F-32
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Finance Lease Right-of-Use Assets and Liabilities Associated with Unrelated Third-Party Leases
In connection with leases with unrelated third parties that commenced during the year ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, we recognized finance lease right-of-use assets and lease liabilities, each of which totaled $1.3 2.6
Operating and Finance Lease Right-of-Use Assets and Liabilities Associated with Related Party Leases
For information on related party leases, see Note 13, Related Party Transactions.
Remaining Lease Terms and Discount Rates
The weighted-average remaining lease terms and discount rates associated with our operating and finance lease liabilities at December 31, 2021 were as follows:
| December 31, 2021 | |||||
Weighted-average remaining lease term (1)
|
|||||
Operating leases |
|||||
Finance leases |
|||||
Weighted-average discount rate |
|||||
Operating leases |
% | ||||
Finance leases |
% | ||||
(1) The weighted-average remaining lease term associated with our operating and finance lease liabilities does not include all of the optional renewal periods available to us under our current lease arrangements. Rather, the weighted-average remaining lease term only includes periods covered by an option to extend a lease if we are reasonably certain to exercise that option.
Sale-Leaseback Transactions
Sale-Leaseback Transactions with Unrelated Third Parties
During the year ended December 31, 2021, we closed on two sale-leaseback transactions involving two properties with unrelated third parties, one of which was associated with an agreement we entered into on December 16, 2020. Under these transactions, we sold assets with a combined net book value of $85.8 million for $76.0 million, which was reduced by transaction costs of $2.0 million, for net cash proceeds of $74.0 million. The estimated fair value of the properties sold was $85.5 million. Accordingly, the aggregate sales price associated with these arrangements was increased by a total of $9.5 million, which resulted in the recognition of an aggregate loss of $2.3 million on these transactions, which is included in Other operating in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2021.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, we entered into sale-leaseback transactions involving five properties with unrelated third parties. Under these agreements, we sold assets with a combined net book value of $237.7 million for $199.2 million, which was reduced by transaction costs of $0.5 million, for net cash proceeds of $198.7 million. The estimated fair value of the five properties sold totaled $243.1 million. Accordingly, the aggregate sales price associated with these arrangements was increased by a total of $43.9 million, which resulted in the recognition of a net gain of $4.9 million on these transactions, which is included in Other operating in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2020.
During the year ended December 31, 2019, we entered into sale-leaseback transactions involving four properties with unrelated third parties. Under these agreements, we sold assets with a combined net book value of $178.5 million for $164.0 million, which was reduced by transaction costs of $1.0 million, for net cash proceeds of $163.0 million. The estimated fair value of the four properties sold totaled $185.3 million. The aggregate sales price associated with these arrangements was increased by a total of $21.3 million, which resulted in the recognition of a net gain of $5.8 million on these transactions, which is included in Other operating in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019.
F-33
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Related Party Sale-Leaseback Transactions
For information on sale-leaseback transactions with related parties, see Note 13, Related Party Transactions.
Supplemental Cash Flow Information
Supplemental cash flow information associated with our operating and finance leases is as follows:
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities |
|||||||||||||||||
Operating cash flows from operating leases |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
Operating cash flows from finance leases |
|||||||||||||||||
Financing cash flows from finance leases |
|||||||||||||||||
Non-cash information: |
|||||||||||||||||
Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for initial lease liabilities |
|||||||||||||||||
Operating leases |
|||||||||||||||||
Finance leases |
|||||||||||||||||
Right-of-use asset adjustments recognized as a result of the remeasurement of existing lease liabilities |
|||||||||||||||||
Operating leases |
( |
||||||||||||||||
Non-cash increase in operating lease right-of-use assets associated with below-market sale-leaseback transactions |
|||||||||||||||||
Impairment charges associated with operating lease right-of-use assets |
( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
Maturities of Operating and Finance Lease Liabilities
The maturities associated with our operating and finance lease liabilities at December 31, 2021 are as follows:
| Operating Leases |
Finance Leases |
Total | |||||||||||||||
| 2022 | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
| 2023 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2024 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2025 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2026 | |||||||||||||||||
Thereafter |
|||||||||||||||||
Total lease payments |
|||||||||||||||||
Less: Imputed interest |
|||||||||||||||||
Present value of lease liabilities |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
F-34
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
10.Stockholders’ Equity
Authorization and Designation
On January 11, 2021, our board of directors adopted and approved an amendment to the Certificate of Incorporation for Life Time Group Holdings, Inc., which (i) increased the amount of authorized shares of common stock, $0.01 par value per share, from 170.0 million to 200.0 million; and (ii) authorized 25.0 million shares of preferred stock, $0.01 par value per share. Also on January 11, 2021, our board of directors authorized 12.0 million shares of Series A convertible participating preferred stock (“Series A Preferred Stock”) of Life Time Group Holdings, Inc., $0.01 par value per share. The rights, preferences, privileges, qualifications, restrictions and limitations relating to the Series A Preferred Stock were set forth in the Certificate of Designations (“COD”), which the Company filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware on January 22, 2021.
On October 12, 2021, in connection with the consummation of the IPO, we adopted an amended and restated Certificate of Incorporation for Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. under which the Company’s authorized share total was increased to 500.0 million shares of common stock, par value $0.01 per share, and 10.0 million shares of preferred stock, par value $0.01 per share, and the Series A Preferred Stock became no longer authorized.
Series A Preferred Stock
Series A Preferred Stock Issuance
On January 11, 2021, Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries and the investor group associated with our then existing related party secured loan (or their assignees) entered into an agreement to convert the total amount of outstanding principal and accrued interest (up though and including January 22, 2021) of approximately $108.6 million under the related party secured loan into 5.4 million shares of Series A Preferred Stock of Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. Accordingly, we recognized a $41.0 million debt extinguishment loss associated with this transaction during the year ended December 31, 2021, which is included in Interest expense, net of interest income in our consolidated statement of operations.
Restricted Series A Preferred Stock Award
During the second quarter of 2021, in lieu of the vast majority of cash compensation for our CEO for 2021, the Company granted an award of 0.5 million shares of restricted Series A Preferred Stock to our CEO. The total grant date fair value of this award was approximately $13.8 million. Effective as of the grant date, our CEO had all of the rights of a stockholder with respect to these shares of restricted Series A Preferred Stock, including the right to receive PIK share or cash dividends. Prior to the granting of this equity award, we had recognized an accrued compensation liability of approximately $1.6 million associated with the portion of our CEO’s 2021 compensation that had been earned as of the grant date. The settlement of this accrued compensation liability through issuance of the restricted Series A Preferred Stock award was recognized as a decrease in Accrued expenses and other current liabilities and an increase in Additional paid-in capital on our consolidated balance sheet.
Fair Value of Series A Preferred Stock and Restricted Series A Preferred Stock
The fair value of the Series A Preferred Stock and the restricted Series A Preferred Stock award was estimated using an as-converted value plus risky put option model. The put option value was estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. Primary assumptions used in determining the estimated issuance date fair value of the Series A Preferred Stock include: the estimated equity value associated with the then outstanding common stock of Life Time Group Holdings, Inc., a strike price of $20.00 per share, PIK dividend yield rate of 15.0 %, expected term of 1.0 year, volatility rate of 65.00 % and a risk-free rate of 0.08 %.
Conversion of Series A Preferred Stock to Common Stock and Conversion of Restricted Series A Preferred Stock to Restricted Common Stock
Upon the consummation of the IPO, the 5.4 million then outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock automatically converted into 6.7 million shares of the Company’s common stock. Upon the consummation of the IPO, the 0.5 million then outstanding shares of restricted Series A Preferred Stock automatically converted into 0.6 million shares of the Company’s restricted common stock.
F-35
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Share-Based Compensation Expense Associated with Restricted Series A Preferred Stock and Restricted Common Stock
Restricted Series A Preferred Stock
Prior to the conversion of the shares of restricted Series A Preferred Stock to shares of the Company’s restricted common stock on October 12, 2021, we recognized $2.9 million of share-based compensation expense associated with the restricted Series A Preferred Stock award, which is included in General, administrative and marketing in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Restricted Common Stock
During the period from October 12, 2021 through December 31, 2021, we recognized $4.3 million of share-based compensation expense associated with the restricted common stock award, which is included in General, administrative and marketing in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2021. Share-based compensation expense associated with the restricted common stock award is being recognized over the remaining vesting period based on the grant date fair value of the original restricted Series A Preferred Stock award, reduced by the $1.6 million of compensation expense associated with the accrued compensation liability that had previously been recognized. As of December 31, 2021, unrecognized share-based compensation expense related to this restricted common stock award was approximately $5.0 million, which is expected to be recognized over a remaining period of 0.3 years.
Common Stock
Common Stock Issued in Connection with the IPO and Over-Allotment Exercise
During the year ended December 31, 2021, in connection with the IPO, including the partial exercise by the underwriters of their over-allotment option, we received total net proceeds of $701.4 million from the issuance of 40.6 million shares of the Company’s common stock. For more information on these sales of the Company’s common stock during the year ended December 31, 2021, see Note 1, Nature of Business and Basis of Presentation.
Common Stock Issued in Connection with Stock Purchase Agreements
During the year ended December 31, 2020, we received proceeds totaling $90.0 million from the sale of 3.6 million shares of the Company’s common stock, which consists of primary equity proceeds (i.e., proceeds associated with the sale of newly issued shares of our common stock) associated with a stock purchase agreement.
During the year ended December 31, 2019, we received net proceeds totaling $105.3 million from the sale of 4.3 million shares of the Company’s common stock, which consist of $108.7 million of primary equity proceeds associated with a stock purchase agreement, reduced by $3.2 million in costs associated with such issuance of primary (i.e., newly-issued) shares of our common stock and $0.2 million in costs associated with an issuance of primary shares of our common stock that was consummated during the year ended December 31, 2020.
Equity Incentive Plans
2015 Equity Plan
On October 6, 2015, our board of directors adopted the LTF Holdings, Inc. 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (as amended, the “2015 Equity Plan”). During the year ended December 31, 2021, our board of directors and stockholders approved an amendment to the 2015 Equity Plan to increase the number of shares of our common stock that are reserved for issuance under the 2015 Equity Plan to approximately 30.6 million shares of our common stock, plus an annual increase on the first day of each calendar year beginning on January 1, 2022 and ending on and including January 1, 2025; provided, that no annual increase shall occur on or after the Company (or its successor) becomes a publicly listed company. Effective with the IPO, no further grants have been or will be made, and no annual increase shall occur, under the 2015 Equity Plan. Approximately 1.0 million shares that were reserved and available for issuance under the 2015 Equity Plan are now available for issuance under the 2021 Equity Plan as detailed below.
F-36
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
2021 Equity Plan
In connection with the IPO and effective October 6, 2021, we adopted the 2021 Incentive Award Plan (the “2021 Equity Plan”), under which we may grant cash and equity-based incentive awards to our employees, consultants and directors. The maximum number of shares of our common stock available for issuance under the 2021 Equity Plan is equal to the sum of (i) approximately 14.5 million shares of our common stock, (ii) an annual increase on the first day of each year beginning in 2022 and ending in and including 2031, equal to the lesser of (A) 4 % of the outstanding shares of our common stock on the last day of the immediately preceding fiscal year and (B) such lesser amount as determined by our board of directors, and (iii) the approximately 1.0 million shares of our common stock that were available for issuance under the 2015 Equity Plan as of October 6, 2021 or that are subject to awards under the 2015 Equity Plan and any other prior equity incentive plans of the Company or its predecessor which are forfeited or lapse unexercised and which following the effective date of the 2021 Equity Plan are not issued under such prior plan; provided, however, no more than 14.5 million shares may be issued upon the exercise of incentive stock options, or ISOs. The share reserve formula under the 2021 Equity Plan is intended to provide us with the continuing ability to grant equity awards to eligible employees, directors and consultants for the ten-year term of the 2021 Equity Plan.
As of December 31, 2021, approximately 13.8 million shares were available for future awards to employees and other eligible participants under the 2021 Equity Plan.
2021 Employee Stock Purchase Plan
In connection with the IPO and effective October 6, 2021, we adopted the 2021 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “ESPP”). The ESPP is designed to allow our eligible employees to purchase shares of our common stock, at periodic intervals, with their accumulated payroll deductions. The ESPP consists of two components: an Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) Code section 423 (“Section 423”) component, which is intended to qualify under Section 423 of the IRS Code and a non-Section 423 component, which need not qualify under Section 423 of the IRS Code. The aggregate number of shares of our common stock that has initially been reserved for issuance under the ESPP is equal to (i) approximately 2.9 million shares of our common stock, and (ii) an annual increase on the first day of each year beginning in 2022 and ending in and including 2031, equal to the lesser of (A) 1 % of the aggregate number of shares of our common stock outstanding on the final day of the immediately preceding calendar year and (B) such smaller number of our shares of common stock as determined by our board of directors; provided that in no event will more than 29.0 million shares of our common stock be available for issuance under the Section 423 component of the ESPP. Our board of directors or the compensation committee will have authority to interpret the terms of the ESPP and determine eligibility of participants.
The ESPP will permit participants to purchase common stock through payroll deductions of up to a percentage of their eligible compensation, which includes a participant’s gross base compensation for services to us. On the first trading day of each offering period, each participant will automatically be granted an option to purchase shares of our common stock. The option will expire at the end of the applicable offering period and will be exercised on each purchase date during such offering period to the extent of the payroll deductions accumulated during the offering period. The purchase price will be the lower of 85 % of the fair market value of a share on the first day of an offering period in which a participant is enrolled or 85 % of the fair market value of a share on the purchase date, which will occur on the last day of each purchase period. Participants may voluntarily end their participation in the ESPP prior to the end of the applicable offering period and will be paid their accrued payroll deductions that have not yet been used to purchase shares of common stock. Upon exercise, the participant will purchase the number of whole shares that his or her accumulated payroll deductions will buy at the option purchase price, subject to the certain participation limitations. Participation will end automatically upon a participant’s termination of employment. No offering periods commenced under the ESPP during the year ended December 31, 2021.
F-37
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Stock Options
Summary of Stock Option Activity
Activity associated with stock options during the year ended December 31, 2021 is as follows:
Stock Options |
Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average
Remaining
Contractual Life
(in years)
|
Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2020 |
$ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Granted |
$ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Forfeited |
( |
$ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2021 |
$ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercisable as of December 31, 2021 |
$ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Options Granted During the Year Ended December 31, 2021
During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company granted approximately 3.8 million stock options, of which approximately 3.2 million were granted under the 2015 Equity Plan and approximately 0.6 million were granted under the 2021 Equity Plan. These options have a 10-year contractual term from the date of grant. The exercise prices and terms of these awards were determined and approved by our board of directors or a committee thereof. The exercise price associated with each of these awards is not less than the fair market value per share of our common stock, as determined by our board of directors or a committee thereof, at the time of grant.
Of the 3.8 million total stock options granted during the year ended December 31, 2021, approximately 3.3 million are time vesting options and approximately 0.5 million are performance vesting options. The time vesting options vest in ratable annual installments on each of the first anniversaries of the grant date, subject to continuous employment or service from the grant date through the applicable vesting date. All or a portion of the performance vesting options shall vest only upon the attainment of certain targets for the twelve-month period commencing on January 1, 2021 and ending on December 31, 2021, as defined in the underlying option agreements, subject to continuous employment from the grant date through the membership dues revenue determination date. Both the time vesting and performance vesting options become exercisable (but not vested) on April 4, 2022, which is the first date following the expiration of the 180-day lock-up period applicable to the optionee related to the IPO, or death or disability, all as defined and subject to the terms and conditions in the underlying option agreements.
Unless otherwise determined by the administrator of the 2015 Equity Plan and the 2021 Equity Plan, with respect to the stock options granted during the year ended December 31, 2021: (i) upon an option holder’s termination of services for any reason, any portion of an option that has not become vested on or prior to the termination date shall be forfeited on such date and shall not thereafter become vested or exercisable, and (ii) upon an involuntary termination by the Company for cause (as defined in the underlying option agreement), any portion of an option that has become vested on or prior to the termination date shall be forfeited on such date and shall not thereafter become exercisable.
At December 31, 2021, as it relates to options granted during 2021, options to purchase approximately 3.7 million shares of our common stock were outstanding and none were exercisable.
Options Granted Prior to 2021
At December 31, 2021, as it relates to options granted prior to 2021, options to purchase approximately 20.9 million shares of our common stock were outstanding, of which approximately 9.4 million were held by our CEO. At December 31, 2021, the 9.4 million outstanding options held by our CEO were fully vested and exercisable. As it relates to the other 11.5 million outstanding options at December 31, 2021, all of the options were fully vested; however, none of the options were exercisable as the 180-day lock-up period applicable to the each optionee related to the IPO had yet to expire.
Prior to July 3, 2019, the vesting and exercisability of outstanding options for our CEO and the exercisability of outstanding options for non-CEO option holders were subject to our principal stockholders’ achievement of certain internal rates of return (“IRR”) on investment or a multiple of invested capital. On May 23, 2019, in connection with transactions that were
F-38
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
consummated pursuant to a stock purchase agreement, our board of directors approved that 100 % of all stock options outstanding as of July 3, 2019 (the date the transactions under the stock agreement were consummated) or granted thereafter would become exercisable on the first measurement date, which is generally defined to include a change in control, an expiration of a lock-up associated with an initial public offering (or the effectiveness of an initial public offering with respect to the options held by our CEO), or the death or disability of our CEO (herein referred to as a “Measurement Date”) without continued measurement of the performance metrics.
In accordance with ASC 718, the approval by our board of directors represented, for accounting purposes, a modification of the original market conditions associated with each of the approximately 21.2 million outstanding options that were held by continuing employees and continuing service providers as of July 3, 2019. Accordingly, we were required to determine the estimated fair value of these options as of July 3, 2019. Since the occurrence of a Measurement Date was deemed at that time, for accounting purposes, improbable of occurring both before and after the modification, no incremental share-based compensation expense was required to be recognized on the modification date. For further information on the weighted average assumptions used to estimate the fair value, see “—Fair Value of Stock Option Awards” within this footnote.
Stock Option Purchase Offer
On June 6, 2019, we launched a voluntary stock option purchase offer (the “Offer”) whereby, subject to certain conditions and limitations, we offered eligible holders (not including our CEO) of qualifying stock options under the 2015 Equity Plan (“Covered Options”) the right to sell up to a certain number of vested Covered Options back to us. In connection with the Offer, approximately 1.6 million Covered Options were purchased for an aggregate price of $23.2 million. Of the aggregate purchase price, $22.4 million was paid to purchase approximately 1.5 million Covered Options from continuing employees and continuing service providers and $0.8 million was paid to purchase approximately 0.1 million Covered Options from former employees and former service providers. Effective with the purchase date associated with each underlying Covered Option, the $23.2 million aggregate stock option purchase payments we made, which are recognized as a decrease in Additional paid-in capital on our consolidated balance sheet, are reported in Purchases of stock options within the financing section in our consolidated statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2019.
As it relates to the approximately 1.5 million Covered Options associated with continuing employees and continuing service providers, no share-based compensation expense had been recognized prior to them being purchased, since the occurrence of a Measurement Date was deemed, for accounting purposes, improbable of occurring. Therefore, effective with the purchase date associated with each of these Covered Options, we recognized $22.4 million of incremental share-based compensation expense, which is included in General, administrative and marketing in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019. The offset to this incremental share-based compensation expense amount was recognized as an increase in Additional paid-in capital on our consolidated balance sheet.
As it relates to the approximately 0.1 million Covered Options associated with former employees and former service providers, $0.1 million of share-based compensation expense had been recognized prior to them being purchased. Therefore, effective with the purchase date associated with each of these Covered Options, we recognized $0.7 million of incremental share-based compensation expense, which is included in General, administrative and marketing in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019. The offset to this incremental share-based compensation expense amount was recognized as an increase in Additional paid-in capital on our consolidated balance sheet.
Fair Value of Stock Option Awards Granted
The fair value of the options granted during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 was calculated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The fair value of the 21.2 million stock options that were deemed, for accounting purposes, to have been modified as of July 3, 2019, as well as the approximately 0.6 million stock option awards that were granted during
F-39
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
the period from July 3, 2019 through December 31, 2019, was also calculated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The following weighted average assumptions were used in determining the fair value of stock options granted:
Year Ended December 31, |
Period from
July 3
through
December 31, 2019
|
||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||||||||
Dividend yield |
% | % | % | ||||||||||||||
Risk-free interest rate (1)
|
% | % | % | ||||||||||||||
Expected volatility (2)
|
% | % | % | ||||||||||||||
Expected term of options (in years) (3)
|
|||||||||||||||||
Fair Value |
$ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
(1)The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. treasury yields, in effect at the time of grant or modification, corresponding with the expected term of the options.
(2)Expected volatility is based on historical volatilities for a time period similar to that of the expected term of the options.
(3)Expected term of the options is based on probability and expected timing of market events leading to option exercise.
For more information on the options that were modified during the year ended December 31, 2019, see “—Options Granted Prior to 2021” within this footnote.
Share-Based Compensation Expense Associated with Stock Options
Share-based compensation expense related to stock options for the year ended December 31, 2021 was $320.5 million, of which $12.7 million, $303.3 million and $4.5 million is included in Center operations, General, administrative and marketing and Other operating, respectively, in our consolidated statement of operations. Share-based compensation expense related to stock options for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $24.2 million, all of which is included in General, administrative and marketing in our consolidated statement of operations. No share-based compensation expense related to stock options was recognized during the year ended December 31, 2020. A significant portion of the share-based compensation expense that we recognized during the year ended December 31, 2021 is associated with stock options that were granted prior to 2021. As of the effective date of the IPO, these stock options became fully vested, and they either became immediately exercisable or they will become exercisable no later than April 4, 2022, subject to continued service through such date. Accordingly, during the period from the effective date of the IPO through December 31, 2021, we have recognized share-based compensation expense associated with these stock options in an amount equal to the proportion of the total service period that has passed from the respective grant date associated with each of these stock option awards through December 31, 2021. Because the vesting and exercisability of these stock options was contingent upon the occurrence of a change of control or an initial public offering, no share-based compensation expense associated with these stock options was recognized prior to the IPO.
As of December 31, 2021, unrecognized share-based compensation expense related to stock options was approximately $31.3 million, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average remaining period of 2.6 years.
F-40
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Restricted Stock Units
Summary of Restricted Stock Unit Activity
Activity associated with restricted stock units during the year ended December 31, 2021 is as follows:
Restricted Stock Units |
Shares | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
||||||||||||
Nonvested at January 1, 2021 |
$ | |||||||||||||
Granted |
$ | |||||||||||||
Forfeited |
( |
$ | ||||||||||||
Nonvested at December 31, 2021 |
$ | |||||||||||||
During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company granted approximately 1.9 million restricted stock unit awards, of which approximately 0.6 million were granted under the 2015 Equity Plan and approximately 1.3 million were granted under the 2021 Equity Plan. Of the 0.6 million restricted stock unit awards granted under the 2015 Equity Plan during the year end December 31, 2021, approximately 0.5 million were granted to our CEO and approximately 0.1 million were granted to non-CEO executives and a director. All of the 1.3 million restricted stock units granted under the 2021 Equity Plan during the year ended December 31, 2021 were granted to non-CEO holders. We did no t grant any restricted stock unit awards during the year ended December 31, 2020.
Restricted Stock Unit Awards Granted under the 2015 Equity Plan
Beginning on March 15, 2020, our CEO decided to forego 100 % of his base salary for the remainder of 2020. During the second quarter of 2021, our compensation committee, in consultation with our CEO and our board of directors, established a new compensation program for our CEO. Under the new program, in light of the foregone salary and bonuses in 2020, the compensation committee determined to grant our CEO an equity award of approximately 0.5 million restricted stock units under the 2015 Equity Plan, 50 % of which vest on each anniversary of the grant date with 100 % full vesting on the date that is 180 days after the effective date associated with an underwritten IPO. Accordingly, this award will be 100 % vested on April 4, 2022. At December 31, 2020, we had recognized an accrued compensation liability of approximately $2.2 million associated with our CEO’s 2020 compensation. For accounting purposes, the settlement of this $2.2 million accrued compensation liability through the issuance of the restricted stock units was recognized as a decrease in Accrued expenses and other current liabilities and an increase in Additional paid-in capital on our consolidated balance sheet.
Also during the second quarter of 2021, our compensation committee granted approximately 0.1 million restricted stock units under the 2015 Equity Plan to certain of our non-CEO executives and a new director, 50 % of which vests on each anniversary of the grant date and, for the grants to our non-CEO executives, 100 % full vesting occurs effective on the date that is 180 days after an initial underwritten public offering. Accordingly, the portion of these awards that were granted to our non-CEO executives will be 100 % vested on April 4, 2022.
Restricted Stock Unit Awards Granted under the 2021 Equity Plan
With respect to the restricted stock units totaling approximately 1.3 million that were granted under the 2021 Equity Plan during the year ended December 31, 2021, nearly all will vest in ratable annual installments on each of the first anniversaries of the grant date, subject to continued service through the applicable vesting dates. Less than 0.1 million of these restricted stock units will vest on April 4, 2022.
Share-Based Compensation Expense Associated with Restricted Stock Units
Share-based compensation expense related to restricted stock units for the year ended December 31, 2021 was $6.6 million. No 6.6 million total share-based compensation expense related to restricted stock units for the year ended December 31, 2021, $0.2 million, $6.3 million and $0.1 million is included in Center operations, General, administrative and marketing and Other operating, respectively, in our consolidated statement of operations. As of December 31, 2021,
F-41
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
unrecognized share-based compensation expense related to restricted stock units was approximately $24.5 million, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average remaining period of 3.2 years.
Stockholder Note Receivable
On August 27, 2018, Life Time, Inc. entered into a loan agreement with our CEO, who is also one of our stockholders, pursuant to which we loaned him $20.0 million. As security for repayment of the loan, our CEO granted to Life Time, Inc. a security interest in 5.0 million shares of our common stock which are held by our CEO. The loan bore interest equal to the highest interest rate associated with the revolving portion of our senior secured credit facility or, if there were no outstanding revolving borrowings, the highest interest rate associated with outstanding borrowings under the term loans portion of our senior secured credit facility. The loan was scheduled to mature at the earlier of August 2023 or upon the occurrence of certain events, including in connection with an initial public offering or a change of control, as well as the period immediately following the officer’s termination of employment.
On July 3, 2019, we amended the loan agreement to reflect our forgiveness of an aggregate principal amount of $5.0 million. All other terms and conditions associated with the initial loan agreement remained unchanged. The principal forgiveness was accounted for as an equity transaction, whereby the Stockholder note receivable and Additional paid-in capital balances recognized on our consolidated balance sheet were each reduced by $5.0 million. The income tax benefit of approximately $1.3 million associated with the principal forgiveness was recognized as an increase in both Income tax receivable and Additional paid-in capital on our consolidated balance sheet. At December 31, 2020 the outstanding stockholder loan balance was $15.0 million, which was recognized as a reduction of stockholders’ equity on our December 31, 2020 consolidated balance sheet.
In August 2021, we entered into an agreement pursuant to which the outstanding balance owed under the stockholder note receivable was cancelled. The cancellation of the $15.0 15.0
11.(Loss) Earnings Per Share
For the year ended December 31, 2021, our potentially dilutive securities include stock options, restricted stock units and restricted stock. Due to the net loss that we recognized during the year ended December 31, 2021, the potentially dilutive shares of common stock associated with our stock options, restricted stock units and restricted stock were determined to be antidilutive and, therefore, are excluded from the computation of diluted loss per share for the year ended December 31, 2021.
For the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, our potentially dilutive securities include stock options, all of which were subject to performance conditions that were not met as of the end of each respective period. Accordingly, the contingently issuable shares associated with our stock options are excluded from the computation of diluted (loss) earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019.
The following table sets forth the calculation of basic and diluted (loss) earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019:
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Net (loss) income attributable to Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding – basic and diluted |
|||||||||||||||||
(Loss) earnings per share – basic and diluted |
$ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
F-42
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
The following is a summary of potential shares of common stock that were excluded from the computation of diluted (loss) earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019:
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| Stock options | |||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock units | |||||||||||||||||
| Restricted stock | |||||||||||||||||
| Potential common shares excluded from diluted (loss) earnings per share | |||||||||||||||||
For more information regarding our stock options, restricted stock units and restricted stock, see Note 10, Stockholders’ Equity.
12.Commitments and Contingencies
Purchase Commitments
We have entered into various unconditional purchase obligations that primarily include software licenses and support, and marketing services. As of December 31, 2021, these purchase obligations totaled approximately $20.5 million, the majority of which are expected to be settled within the next four years . These unconditional purchase obligations are in addition to the current and long-term liabilities recorded on our December 31, 2021 consolidated balance sheet and exclude agreements that are cancellable at any time without penalty.
Legal Matters
Bartell et al. v. LTF Club Operations Company, Inc.
We defended a putative class action asserting that Life Time failed to honor cancellation requests and refund payments made by former members of Life Time’s Ohio health clubs under membership agreements that allegedly violate the Ohio Prepaid Entertainment Contract Act (“PECA”) and the Ohio Consumer Sales Practices Act (“CSPA”). The case is Laurence Bartell, et al. v. LTF Club Operations Company, Inc., Case No. 2:14-cv-401, in the United States District Court, Southern District of Ohio, Eastern Division. LTF Club Operations Company, Inc. is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Life Time, Inc.
The District Court granted final approval to the parties’ settlement of this case on August 7, 2020. Under the terms of the settlement, we agreed to contribute to a settlement fund of $14.0 million from which all costs of settlement would be paid, including awards to the class, settlement administration expenses, and court-awarded service awards and attorneys’ fees. Class members were allowed to claim either (1) a cash award of dues they paid to Life Time after providing notice of cancellation of their membership (“Cash Award”) or (2) a membership award of a dues credit with a face value of three times the Cash Award toward any access membership with Life Time (“Membership Award”). The period for the class members to make this election ended on July 8, 2020. Based on the Cash Awards and Membership Awards claimed by the class members and the amount awarded for plaintiff’s attorneys’ fees and costs and a class representative service award, we paid $13.3 million during the quarter ended September 30, 2020. Because our cost to service a membership is less than the Membership Award, the amount of our loss did not ultimately directly correspond to the total settlement amount of $14.0 million.
Life Time, Inc. et al. v. Zurich American Insurance Company
On August 19, 2020, Life Time, Inc., several of its subsidiaries, and a joint venture entity, Bloomingdale Life Time Fitness LLC (collectively, the “Life Time Parties”) filed a complaint against Zurich American Insurance Company (“Zurich”) in the Fourth Judicial District of the State of Minnesota, County of Hennepin (Case No. 27-CV-20-10599) (the “Action”) seeking declaratory relief and damages with respect to Zurich’s failure under a property/business interruption insurance policy to provide certain coverage to the Life Time Parties related to the closure or suspension by governmental authorities of their business activities due to the spread or threat of spread of COVID-19. On March 15, 2021, certain of the Life Time Parties filed a First Amended Complaint in the Action adding claims against Zurich under a Builders’ Risk policy related to the suspension of multiple construction projects. The parties are currently in discovery. The Action is subject to many uncertainties, and the outcome of the matter is not predictable with any assurance.
F-43
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
Other
We are also engaged in other proceedings incidental to the normal course of business. Due to their nature, such legal proceedings involve inherent uncertainties, including but not limited to court rulings, negotiations between affected parties and governmental intervention. We establish reserves for matters that are probable and estimable in amounts we believe are adequate to cover reasonable adverse judgments. Based upon the information available to us and discussions with legal counsel, it is our opinion that the outcome of the various legal actions and claims that are incidental to our business will not have a material adverse impact on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. Such matters are subject to many uncertainties, and the outcomes of individual matters are not predictable with assurance.
401(k) Savings and Investment Plan
We offer a 401(k) savings and investment plan (the “401(k) Plan”) to substantially all full-time employees who have at least six months of service and are at least 21 years of age. The cost associated with the Company’s discretionary contributions to the 401(k) Plan during the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 were not material.
Letters of Credit and Posted Bonds
As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, we had $33.5 million and $22.6 million, respectively, in irrevocable standby letters of credit outstanding, which were issued primarily to municipalities, for sites under construction, as well as certain insurance carriers to guarantee payments of deductibles for various insurance programs, such as workers’ compensation and commercial liability insurance. Such letters of credit are secured by the collateral under our senior secured credit facility. As of both December 31, 2021 and 2020, no amounts had been drawn on any of these irrevocable standby letters of credit.
As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, we had posted bonds totaling $36.4 million and $37.1 million, respectively, related to construction activities and operational licensing.
13.Related Party Transactions
Related Party Leases
We did not enter into any related party leases, including related party sale-leaseback transactions, during the year ended December 31, 2021.
Sale-Leaseback Transactions
During the year ended December 31, 2020, we consummated a sale-leaseback transaction involving one property with a subsidiary of a limited liability company jointly owned by our CEO, a former executive of the Company, and another member of our board of directors, among other investors (“LTRE”). Under this agreement, we sold assets with a net book value of $35.1 million for $37.0 million, which was reduced by transaction costs totaling approximately $0.1 million, for net proceeds of $36.9 million. Accordingly, we recognized a gain of $1.8 million, which is included in Other operating in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2020. In connection with this lease, we recognized an operating lease right-of-use asset and lease liability of $31.7 million and $31.4 million, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, we paid rent associated with this lease of $2.5 million and $0.3 million, respectively, and rent expense associated with this lease was $3.0 million and $0.5 million, respectively.
During the year ended December 31, 2019, we entered into a sale-leaseback transaction involving one property with a limited liability company jointly owned by our CEO and another member of our board of directors. Under this agreement, we sold assets with a net book value of $37.5 million for $32.0 million, which was reduced by transaction costs totaling approximately $0.2 million, for net cash proceeds of $31.8 million. Upon consummation of this transaction, we recognized a loss of $5.7 million, which is included in Other operating in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2019. During the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, we paid rent associated with this lease of $2.8 million, $1.5 million, and $2.2 million, respectively, and rent expense associated with this lease was $2.6 million, $2.6 million and $2.4 million, respectively.
During the year ended December 31, 2018, we entered into a sale-leaseback transaction involving one property with a limited liability company in which our CEO owns a 33 % interest. During the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, we paid
F-44
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
rent associated with this lease of $1.5 million, $0.8 million, and $1.2 million, respectively, and rent expense associated with this lease was $1.4 million, $1.4 million and $1.4 million, respectively.
During the year ended December 31, 2017, we entered into sale-leaseback transactions involving two properties with a limited liability company that is a related party to one of our existing stockholders. During the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, we paid rent associated with these leases of $6.0 million, $4.5 million, and $6.0 million, respectively, and rent expense associated with these leases was $7.4 million, $7.4 million and $7.4 million, respectively.
Other Property Leases
In September 2015, our CEO, through two limited liability companies in which he had a 100 % interest, acquired the Woodbury, Minnesota facility that we have occupied and operated as a tenant since 1995. The terms of the existing lease were unchanged upon the change in ownership. On September 29, 2020, our CEO contributed his ownership of our center in Woodbury, Minnesota to LTRE. Following this contribution, we terminated our existing lease with the entities owned by our CEO and entered into a new lease for the Woodbury center with subsidiaries of LTRE.
The new Woodbury lease, which we are currently accounting for as an operating lease, has an initial term of 20 years, and includes four renewal options of five years each. In connection with this lease, we recognized an operating lease right-of-use asset and lease liability, each of which totaled $13.6 0.9 million and $1.1 million, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, rent payments associated with the new Woodbury lease were $1.2 million and $0.3 million, respectively, and rent expense associated with the new Woodbury lease was $1.3 million and $0.3 million, respectively. As it relates to the previous Woodbury lease, we paid rent during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 of $0.2 million and $1.0 million, respectively.
In October 2003, we leased a center located within a shopping center that is owned by a general partnership in which our CEO has a 100 % interest. During the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, we paid rent associated with this lease of $1.1 million, $0.5 million, and $0.8 million, respectively, and rent expense associated with this lease was $0.9 million, $0.9 million and $0.9 million, respectively.
Stockholder Note Receivable
For information on the stockholder note receivable, see Note 10, Stockholders’ Equity.
Arrangements with our Investors and Management Stockholders
For information on the sale of our common stock with certain of our stockholders and on the voluntary stock option purchase offer, see Note 10, Stockholders’ Equity.
Related Party Secured Loan
For information on the secured loan from an investor group comprised of our stockholders or their affiliates, see Note 8, Debt.
Unsecured Notes Offering
An affiliate of one of our stockholders was one of the initial purchasers in Life Time, Inc.’s offering of the Unsecured Notes and received customary initial purchaser discounts and commissions.
Other
Life Time, Inc. and an entity owned by our President and Chief Financial Officer, Mr. Bergmann, jointly own an aircraft. In connection with this joint ownership, Life Time, Inc. and Mr. Bergmann’s entity entered into certain co-ownership, maintenance and personnel agreements under which the entity owned by Mr. Bergmann contributes approximately $0.1 million per year to an operations fund for the fixed costs for the aircraft. Life Time, Inc. and the entity owned by Mr. Bergmann have agreed to pay for the costs associated with their respective trips.
F-45
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
14.Executive Nonqualified Plan
During 2006, we implemented the Executive Nonqualified Excess Plan of Life Time Fitness, a non-qualified deferred compensation plan. This plan was established for the benefit of our highly compensated employees, which our plan defines as our employees whose projected compensation for the upcoming plan year would meet or exceed the IRS limit for determining highly compensated employees. This unfunded, non-qualified deferred compensation plan allows participants the ability to defer and grow income for retirement and significant expenses in addition to contributions made to our 401(k) Plan.
All highly compensated employees eligible to participate in the Executive Nonqualified Excess Plan of Life Time Fitness, including but not limited to our executives, may elect to defer up to 50 % of their annual base salary and/or annual bonus earnings to be paid in any coming year. The investment choices available to participants under the non-qualified deferred compensation plan are of the same type and risk categories as those offered under our 401(k) Plan and may be modified or changed by the participant or us at any time. Distributions can be paid out as in-service payments or at retirement. Retirement benefits can be paid out as a lump sum or in annual installments over a term of up to 10 years. We made matching contributions to this plan of less than $0.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2019. We did no 13.2 million and $11.9 million, respectively, had been deferred and is being held on behalf of the employees. These amounts are included in Other liabilities on our consolidated balance sheets.
15.Subsequent Events
In March 2022, the Company entered into definitive agreements for the sale-leaseback of four properties with an aggregate sales price of approximately $175 million. The closing on two of these properties is expected to be completed on or before March 31, 2022 for approximately $80 million in gross proceeds to Life Time. The closing on the remaining two properties is expected to be completed on or before September 30, 2022 for approximately $95 million in gross proceeds to Life Time.
We have evaluated all subsequent events through the date of the consolidated financial statements were issued and determined that there have been no other such events or transactions which would have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements and therefore would require recognition or disclosure.
16.Condensed Financial Information of Registrant (Parent Company Only)
Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. is a holding company with no material operations of its own that conducts substantially all of its activities through its subsidiaries. Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. has no cash and, as a result, all expenditures and obligations of the Company are allocated to and paid by its subsidiaries. Life Time, Inc. is the borrower under our senior secured credit facility and the indentures governing our Secured Notes and our Unsecured Notes, the terms and conditions of which limit Life Time, Inc.’s ability to declare dividends or make any payment on equity to, directly or indirectly, fund a dividend or other distribution to Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. in connection with those borrowings. Dividends, redemptions and other payments on equity (restricted payments) are limited to those permitted under the senior secured credit facility and the indentures governing our Secured Notes and Unsecured Notes. Due to the aforementioned restrictions, substantially all of the net assets of our subsidiaries are restricted. For information regarding our senior secured credit facility, Secured Notes and Unsecured Notes, see Note 8, Debt.
The following condensed financial statements have been presented on a “parent-only” basis. Under a parent-only presentation, our investment in our subsidiaries is presented under the equity method of accounting. During the year ended December 31, 2021, we recognized share-based compensation expense related to stock options, restricted stock and restricted stock units of $334.3 million, of which $12.9 million, $316.8 million and $4.6 million is included in Center operations, General, administrative and marketing and Other operating, respectively, in our parent-only condensed statement of operations. Also during the year ended December 31, 2021, we recognized a $41.0 million debt extinguishment loss related to the conversion of the Related Party Secured Loan to Series A Preferred Stock, which is included in Interest expense, net of interest income in our parent-only condensed statement of operations. This debt extinguishment loss is not recognized for tax purposes. During the
F-46
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
year ended December 31, 2019, we recognized share-based compensation expense related to stock options of $24.2 million, which is included in General, administrative and marketing expenses in our parent-only condensed statement of operations. No share-based compensation expense was recognized during the year ended December 31, 2020.
A condensed statement of cash flows is not presented because Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. has no cash, and, therefore, no material operating, investing, or financing cash flow activities for years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019. The financing cash flow activities associated with the proceeds we received from the issuance of our common stock during the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, as well as the payments we made to purchase stock options during the year ended December 31, 2019, were non-cash transactions for Life Time Group Holdings, Inc., as the cash inflows and outflows associated with those transactions occurred at our subsidiary, Life Time, Inc and were accounted for as our equity contributions to Life Time, Inc. For more information regarding these transactions, see Note 10, Stockholders’ Equity.
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC.
(PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
CONDENSED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except per share data)
| December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | ||||||||||
| ASSETS | |||||||||||
| Current assets | $ | $ | |||||||||
| Noncurrent assets: | |||||||||||
| Investment in subsidiaries | |||||||||||
| Total noncurrent assets | |||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | $ | |||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||||||
| Current liabilities | $ | $ | |||||||||
| Noncurrent liabilities | |||||||||||
| Total liabilities | |||||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity: | |||||||||||
Common stock, $ |
|||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | |||||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | ( |
( |
|||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity | |||||||||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | $ | |||||||||
F-47
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Table amounts in thousands except per share data)
LIFE TIME GROUP HOLDINGS, INC.
(PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In thousands)
| For the Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||
| 2021 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
| Total Revenue | $ | $ | $ | ||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: | |||||||||||||||||
| Center operations | |||||||||||||||||
| General, administrative and marketing | |||||||||||||||||
| Other operating | |||||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses | |||||||||||||||||
| Loss from operations | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
| Other (expense) income: | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense, net of interest income | ( |
||||||||||||||||
| Total other expense | ( |
||||||||||||||||
| Loss before income taxes | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
| Benefit from income taxes | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
| Net loss before equity in net (loss) income of subsidiaries | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
| Net (loss) income of subsidiaries attributable to Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. | ( |
( |
|||||||||||||||
| Net (loss) income attributable to Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. | $ | ( |
$ | ( |
$ | ||||||||||||
F-48
Item 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES
None.
Item 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company’s management, with the participation of the CEO and Chief Financial Officer, has carried out an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”)) as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report. Based upon that evaluation, the CEO and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of such date, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective at a reasonable assurance level.
Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting identified in connection with the evaluation required by Rule 13a-15(d) and 15d-15(d) of the Exchange Act during the fourth quarter of the year ending December 31, 2021 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Management's Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
This Annual Report does not include a report of management's assessment regarding internal control over financial reporting or an attestation report of the Company’s registered public accounting firm due to a transition period established by rules of the SEC for newly public companies.
Item 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
Item 9C. DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS.
None.
PART III
Item 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The information required by this item will be included in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC pursuant to Regulation 14A in connection with our 2022 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information required by this item will be included in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC pursuant to Regulation 14A in connection with our 2022 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The information required by this item will be included in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC pursuant to Regulation 14A in connection with our 2022 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
79
Item 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
The information required by this item will be included in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC pursuant to Regulation 14A in connection with our 2022 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The information required by this item will be included in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC pursuant to Regulation 14A in connection with our 2022 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
Item 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
1.Consolidated Financial Statements (included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K):
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2021 and 2020
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive (Loss) Income for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
2.Exhibits
All exhibits as set forth on the Exhibit Index.
| Exhibit Number |
Description of Exhibit | Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.1 | 8-K | 001-40887 | 3.1 | 10/12/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3.2 | 8-K | 001-40887 | 3.2 | 10/12/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.1 | S-1 | 333-259495 | 4.1 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.2 | S-1 | 333-259495 | 4.2 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4.3 | Filed herewith | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.1 | 8-K | 001-40887 | 10.1 | 12/6/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.2 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.10 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.3 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.11 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
80
| Exhibit Number |
Description of Exhibit | Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.4 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.12 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.5 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.13 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.6 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.14 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.7 †# | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.17 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.8 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.18 | 9/29/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.9 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.19 | 9/29/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.10 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.20 | 9/29/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.11 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.21 | 9/29/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.12 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.22 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.13 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.27 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.14 †# | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.32 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.15 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.28 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.16 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.29 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.17 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.30 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.18 # | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.31 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.19 | S-1 | 333-259495 | 10.33 | 9/13/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10.20 | 8-K | 001-40887 | 10.1 | 10/12/2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21.1 | Filed herewith | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23.1 | Filed herewith | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24.1 | Power of Attorney (included in the signature page to the Annual Report). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31.1 | Filed herewith | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31.2 | Filed herewith | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32.1 | Furnished herewith | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 32.2 | Furnished herewith | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
81
| Exhibit Number |
Description of Exhibit | Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101. INS | Inline XBRL Instance Document –– the Instance Document does not appear in the interactive data file because its XBRL tags are Embedded within the Inline XBRL Document. | Filed herewith | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101.SCH | Inline XBRL Schema Document. | Filed herewith | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101.CAL | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. | Filed herewith | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101.DEF | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. | Filed herewith | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101.LAB | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. | Filed herewith | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 101.PRE | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. | Filed herewith | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 104 | Cover Page Interactive Data File –– the cover page interactive data file does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document. | Filed herewith | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
† Certain of the exhibits and schedules to this Exhibit have been omitted in accordance with Regulation S-K Item 601(a)(5). The Registrant agrees to furnish a copy of all omitted exhibits and schedules to the SEC upon its request.
# Management contract, plan, or arrangement.
Item 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY
None.
82
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. | ||||||||
| Date: March 10, 2022 | By: | /s/ Thomas E. Bergmann | ||||||
| Thomas E. Bergmann | ||||||||
| President & Chief Financial Officer | ||||||||
The undersigned directors and officers of Life Time Group Holdings, Inc. hereby constitute and appoint Bahram Akradi and Thomas E. Bergmann, and each of them, as the individual’s true and lawful attorney in fact and agent, with full power of substitution and resubstitution, for the person and in his name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign this report and any or all amendments, and all other documents in connection therewith to be filed with the SEC, granting unto said attorney in fact and agent full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in and about the premises, as fully to all intents and purposes as he might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorney in fact as agent, or his substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereto.
83
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||||||
| /s/ Bahram Akradi | Founder, Chairman & Chief Executive Officer |
March 10, 2022 | ||||||
| Bahram Akradi | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||||||
| /s/ Thomas E. Bergmann |
President & Chief Financial Officer | March 10, 2022 | ||||||
| Thomas E. Bergmann | (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) | |||||||
| /s/ Jimena Almendares | Director | March 9, 2022 | ||||||
| Jimena Almendares | ||||||||
| /s/ Joel Alsfine | Director | March 9, 2022 | ||||||
| Joel Alsfine | ||||||||
| /s/ Jonathan Coslet | Director | March 9, 2022 | ||||||
| Jonathan Coslet | ||||||||
| /s/ John G. Danhakl | Director | March 9, 2022 | ||||||
| John G. Danhakl | ||||||||
| /s/ J. Kristofer Galashan | Director | March 9, 2022 | ||||||
| J. Kristofer Galashan | ||||||||
| /s/ Paul Hackwell | Director | March 9, 2022 | ||||||
| Paul Hackwell | ||||||||
| /s/ David A. Landau | Director | March 9, 2022 | ||||||
| David A. Landau | ||||||||
| /s/ Stuart Lasher | Director | March 9, 2022 | ||||||
| Stuart Lasher | ||||||||
| /s/ Alejandro Santo Domingo | Director | March 9, 2022 | ||||||
| Alejandro Santo Domingo | ||||||||
| /s/ Andres Small | Director | March 9, 2022 | ||||||
| Andres Small | ||||||||
84